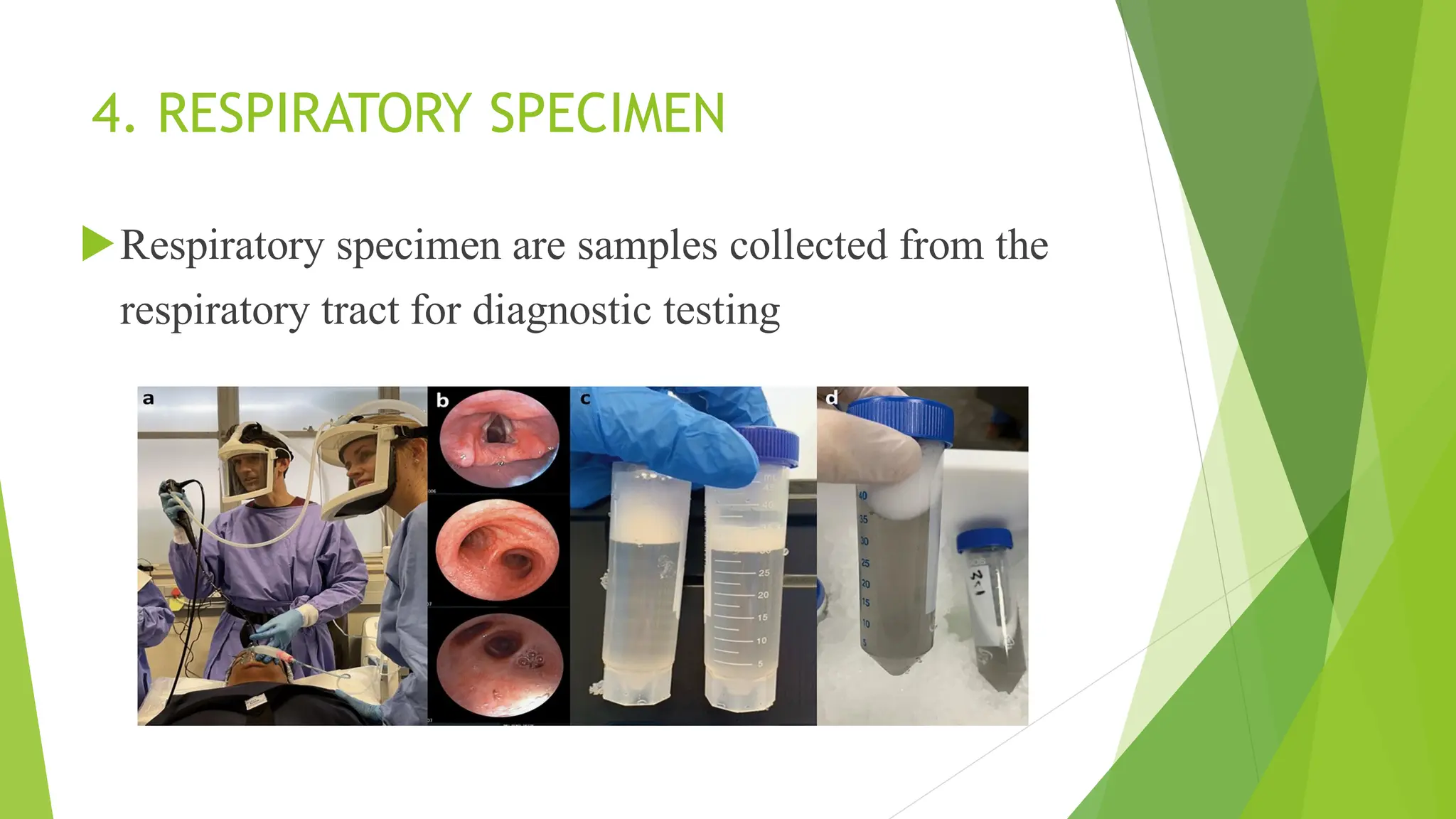
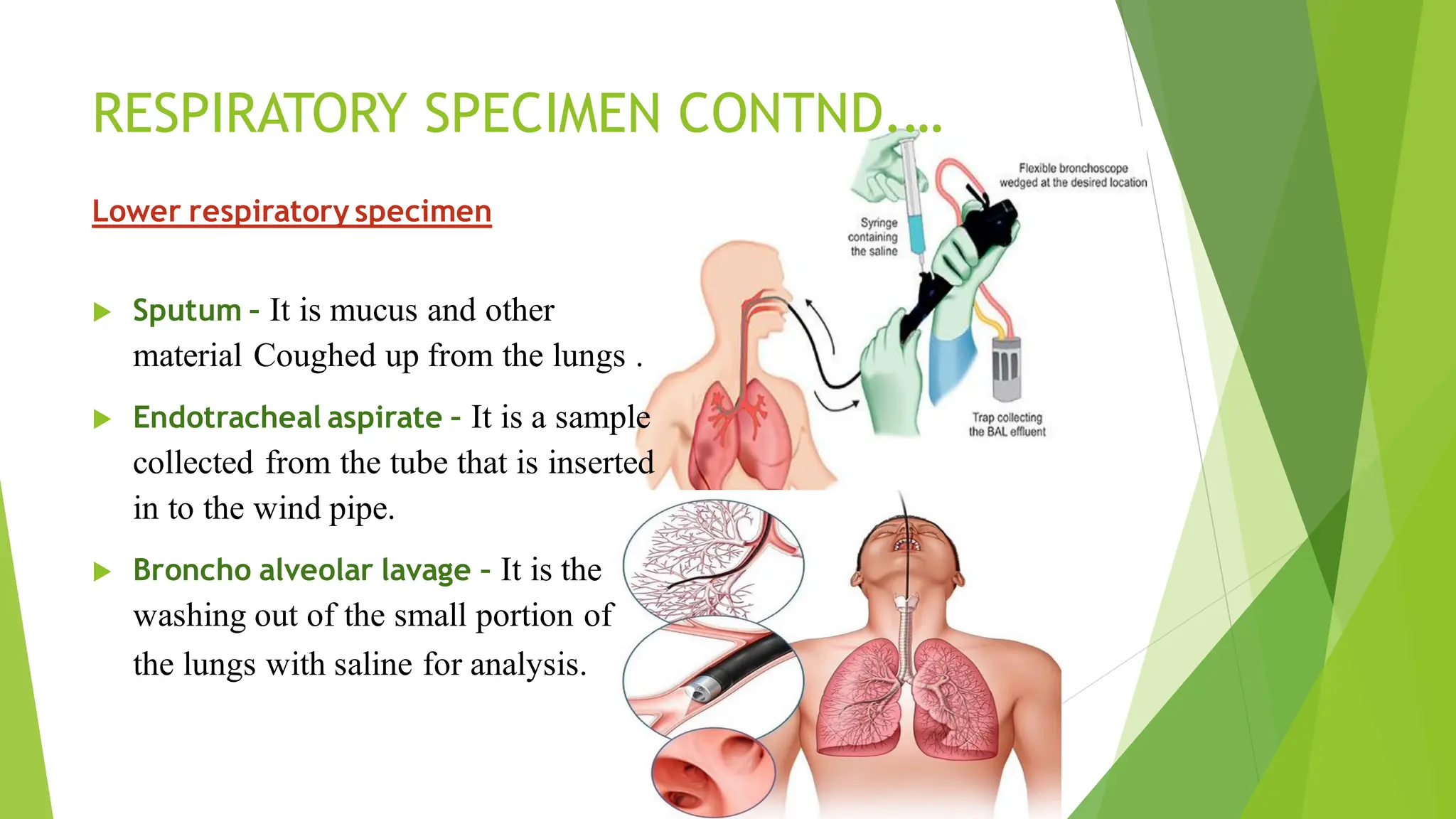
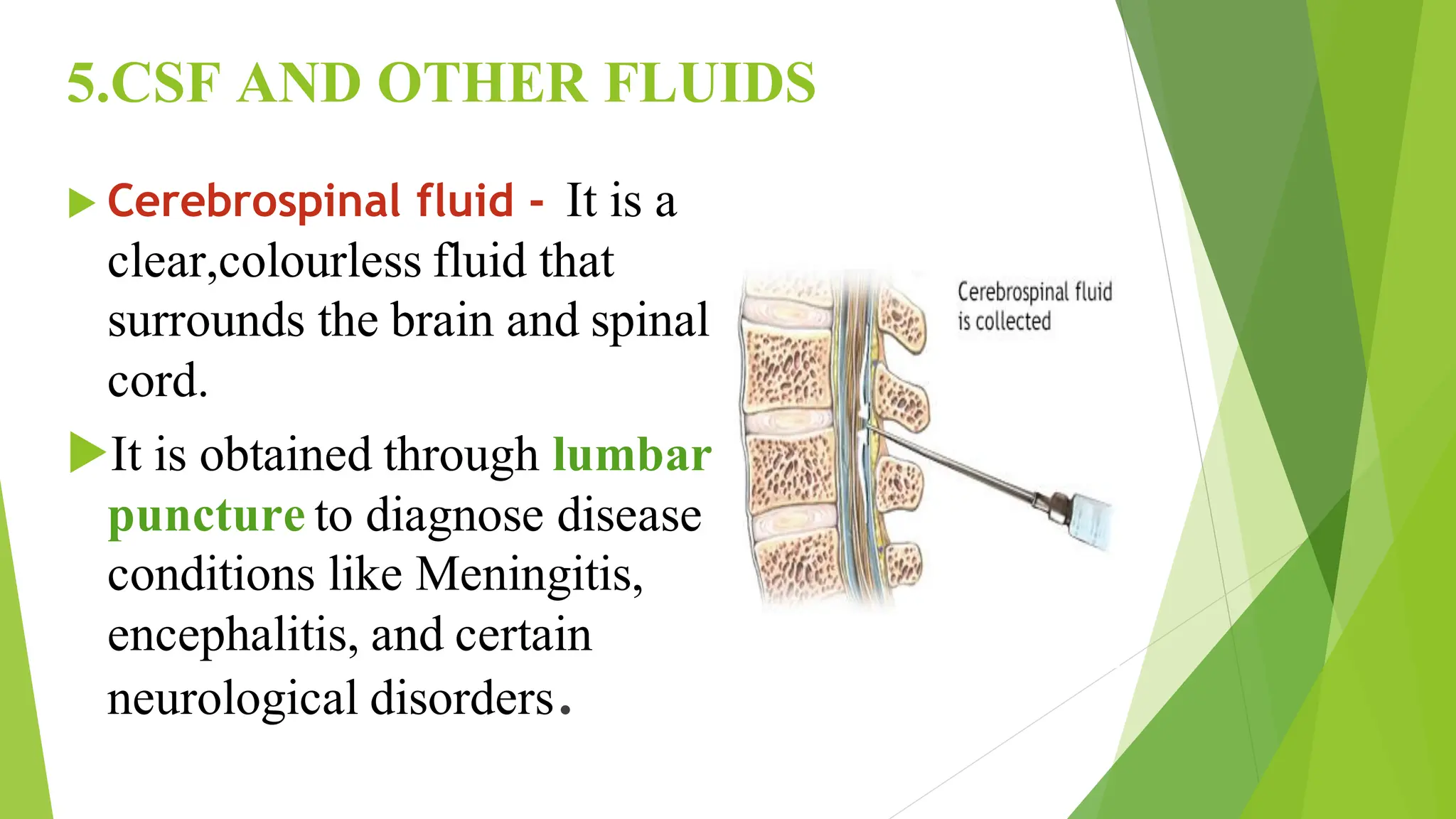
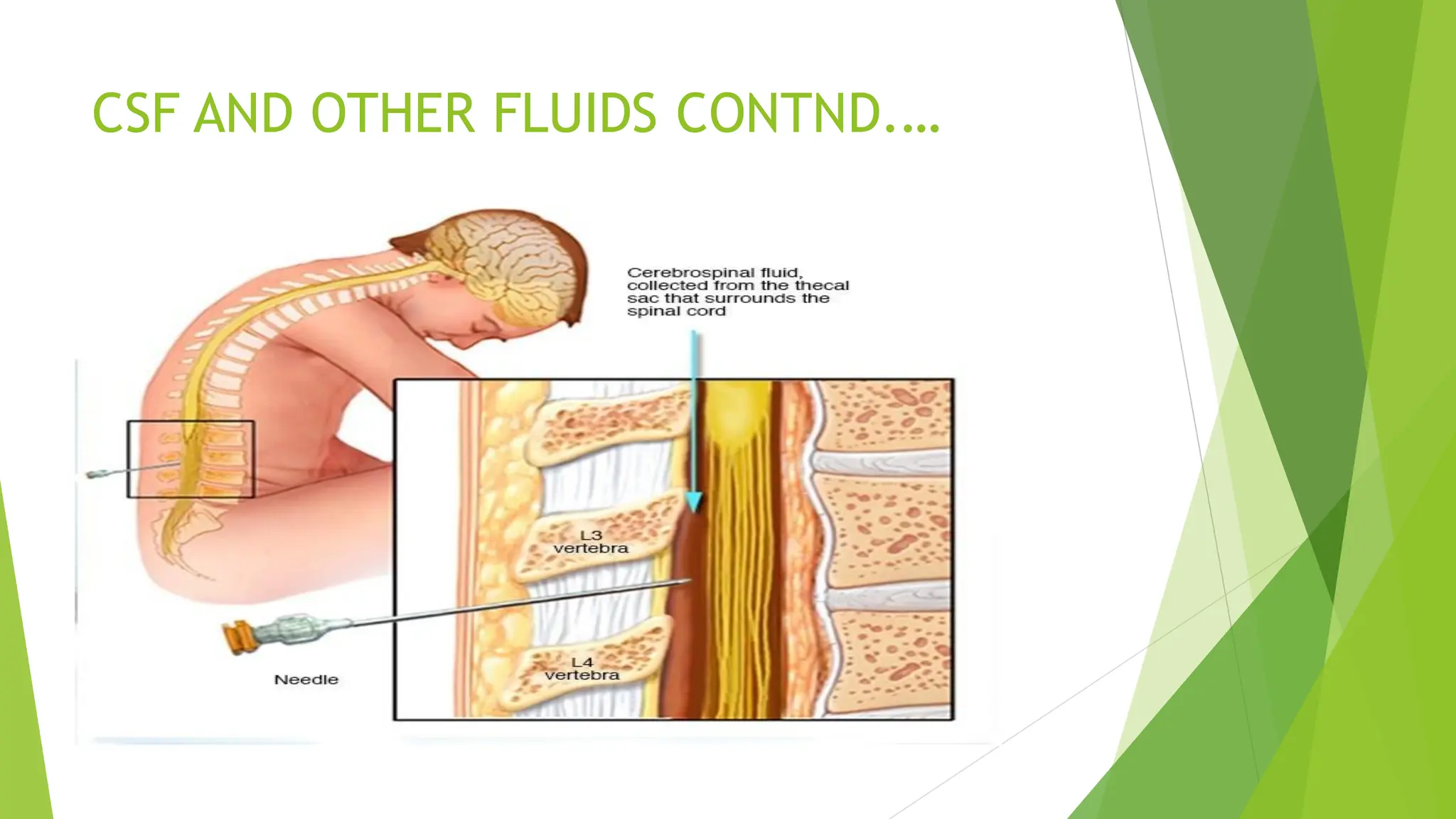
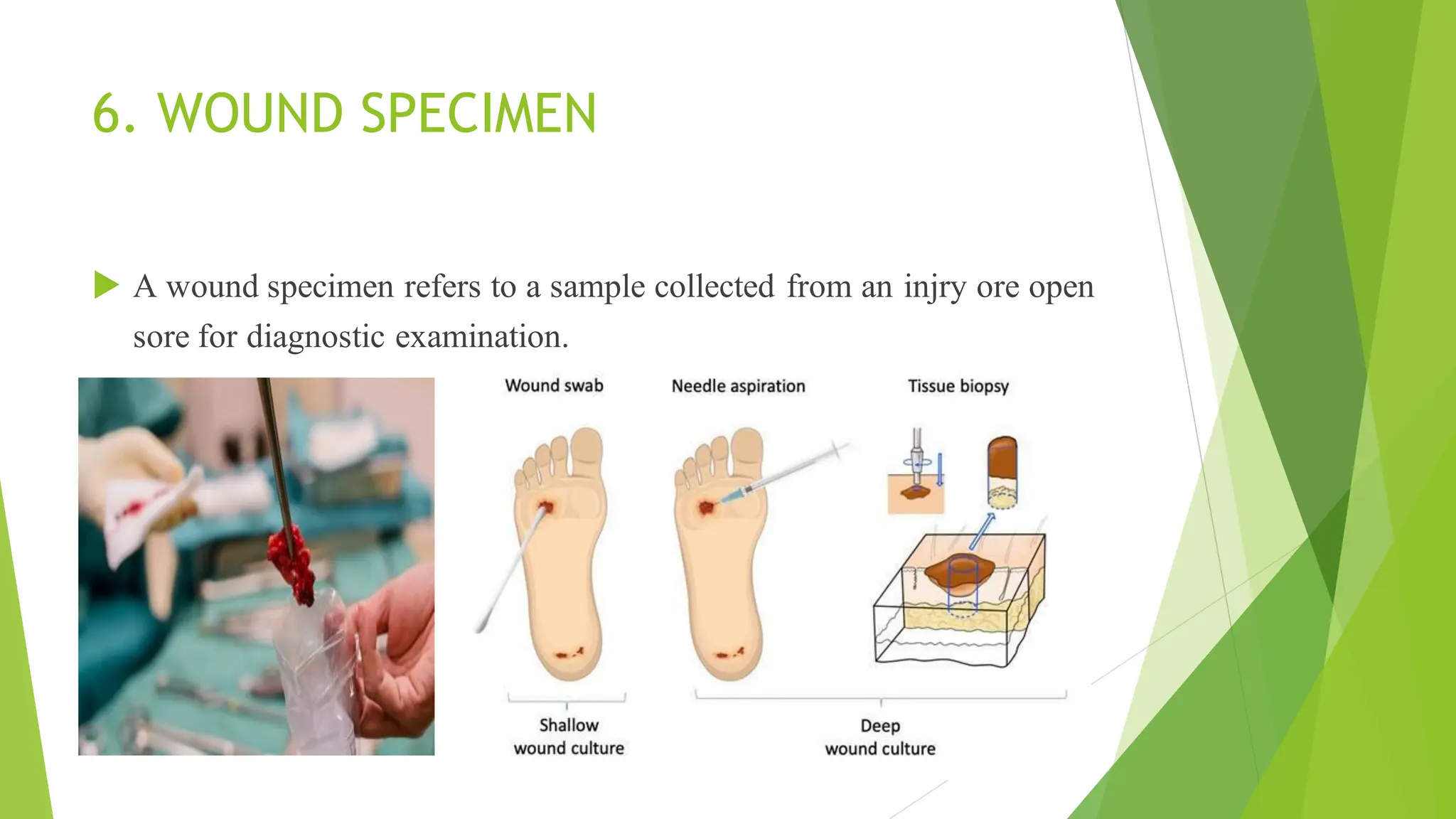
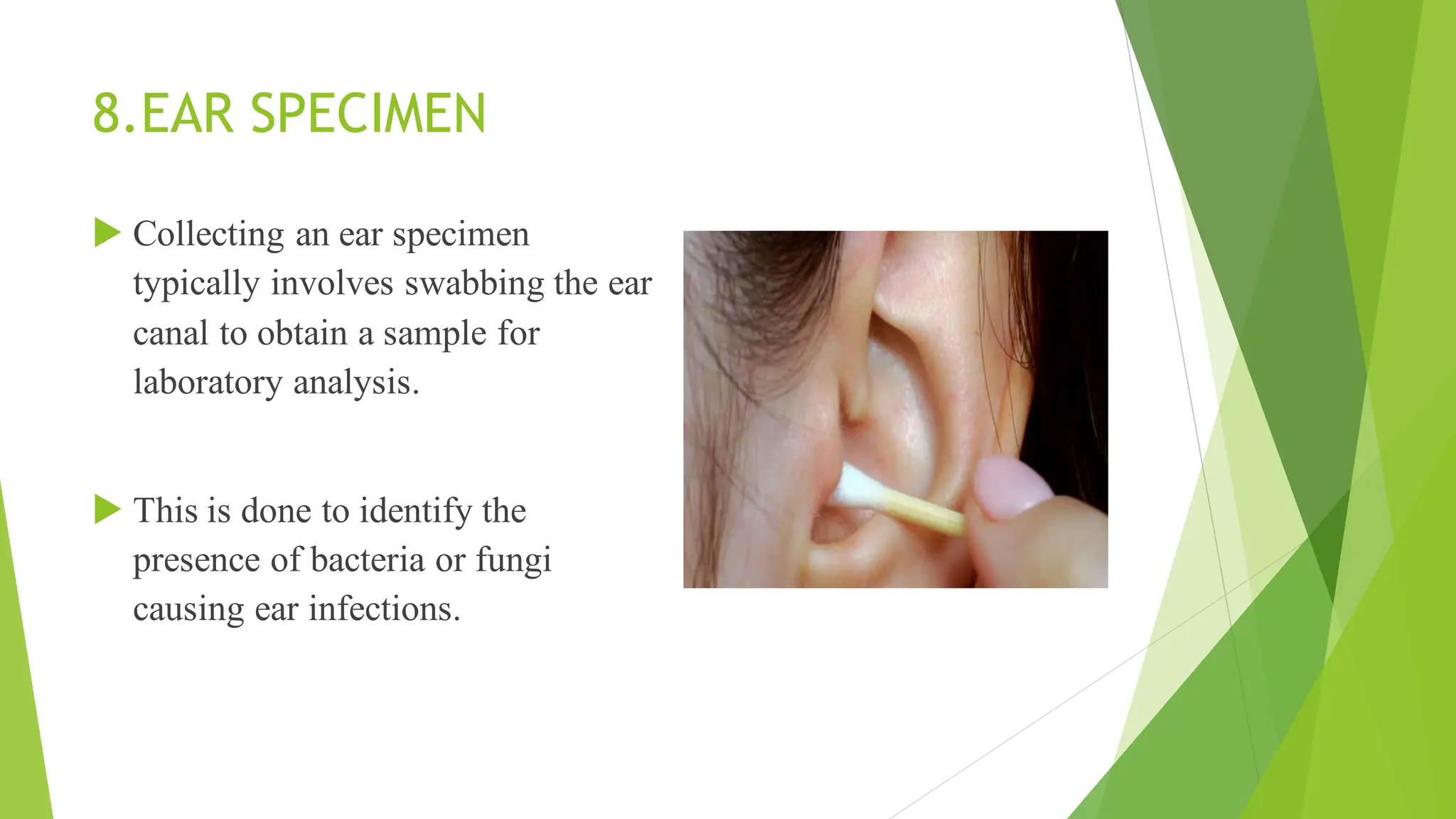
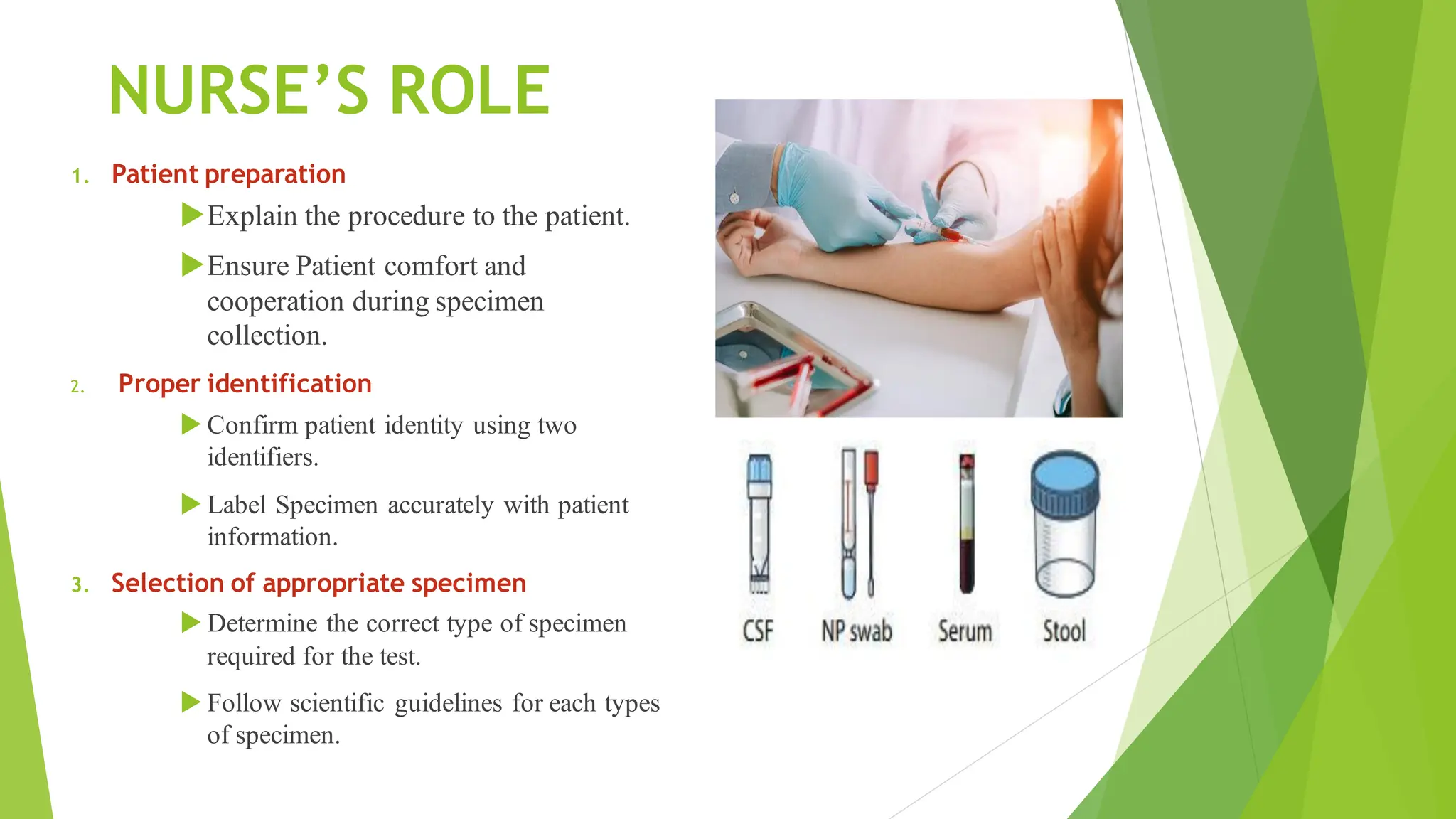
This document discusses types of specimens collected for medical diagnosis and the nurse's role in specimen collection. It describes 9 common types of specimens including blood, urine, stool, respiratory, CSF and other fluids, wounds, genital, ear, and conjunctival specimens. For each type, it provides details on collection methods and uses. The nurse's responsibilities in proper specimen collection include patient preparation, identification, technique, documentation, transportation, and ensuring quality assurance.