The document discusses clinical microbiology and the diagnosis of infectious diseases. It covers the following key points in 3 sentences:
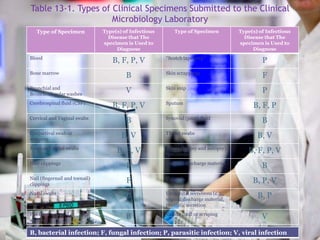
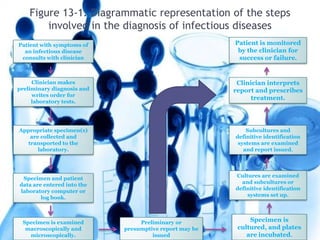
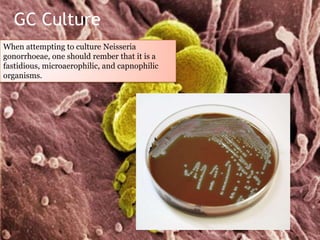
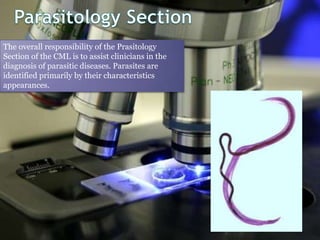
Clinical specimens must be properly collected, transported, and processed to accurately diagnose infectious diseases. A variety of specimen types can be used to identify different types of bacterial, fungal, parasitic and viral infections. The clinical microbiology laboratory works to isolate, identify, and test pathogens from specimens to assist clinicians in diagnosing and treating infectious diseases.