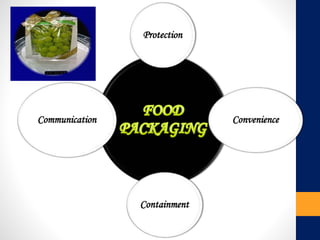
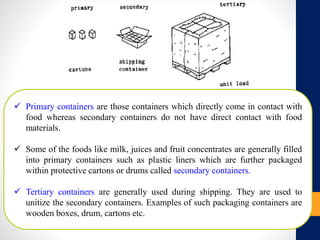
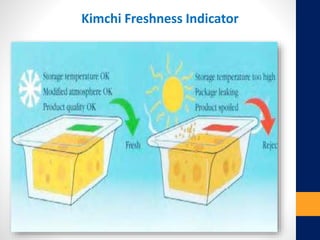
The document discusses various types of packaging materials essential for preserving the quality and marketability of food products. It categorizes packaging into primary, secondary, and tertiary types, highlighting features such as protection from contamination, ease of disposal, and moisture control. Additionally, it touches on the importance of intelligent packaging and biodegradable options for enhancing product safety and sustainability.