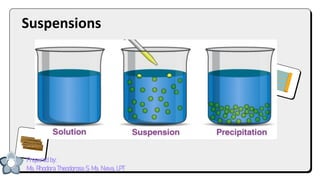
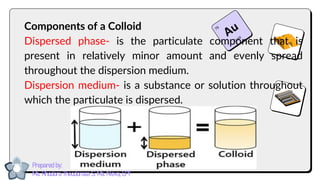
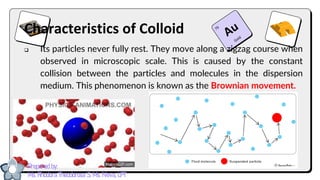
This document discusses different types of mixtures and their characteristics. It defines a mixture as a physical combination of substances that retain their individual properties. Mixtures are categorized as either homogeneous or heterogeneous. Homogeneous mixtures like solutions are uniform mixtures where particles cannot be seen, while heterogeneous mixtures like suspensions and colloids have particles that can be seen and are suspended in another substance. The document provides examples and details on the components, properties, and types of various mixtures.