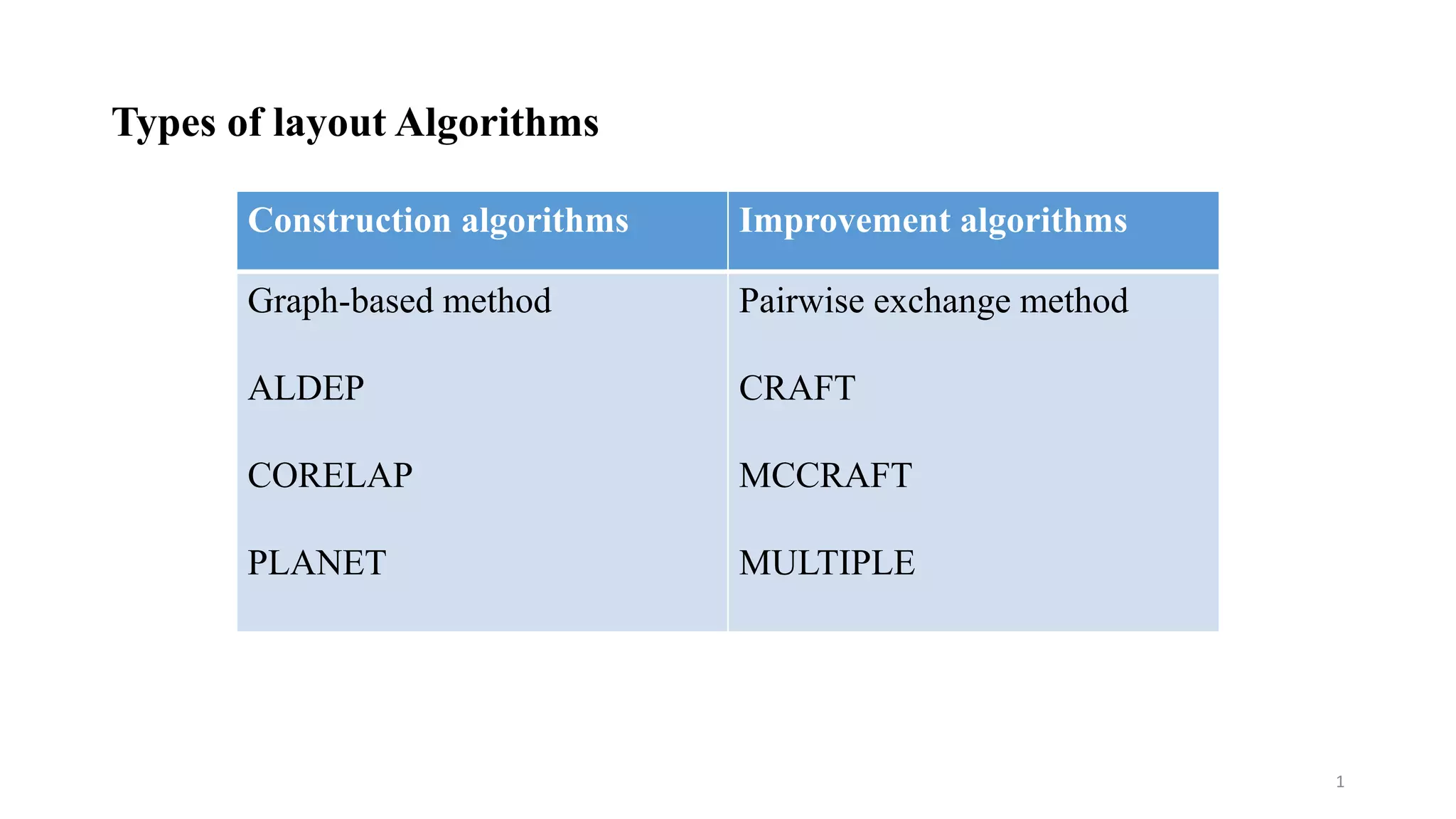
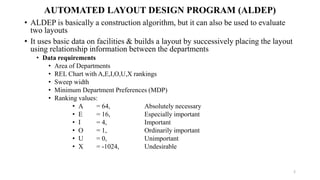
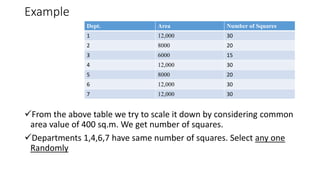
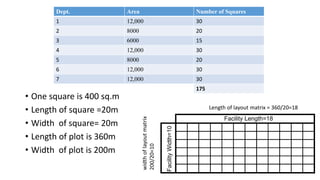
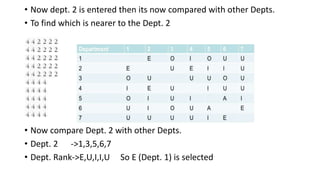
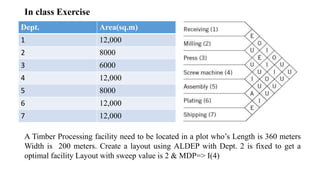
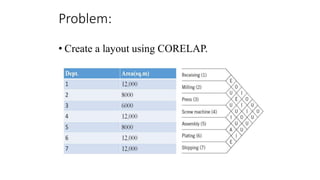
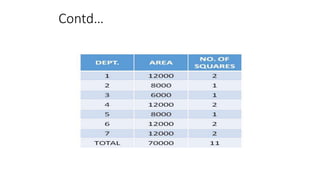
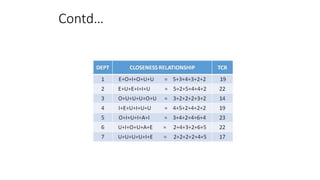
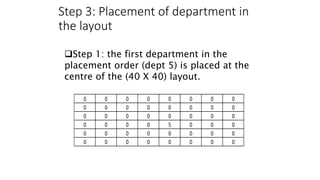
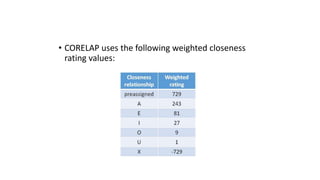
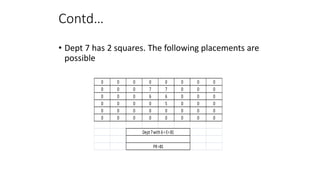
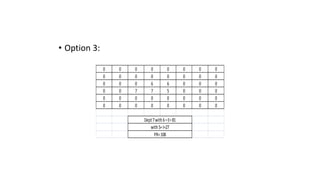
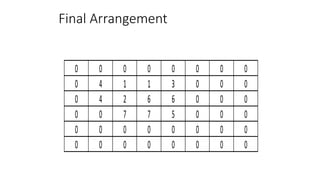
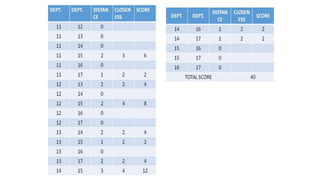
Types of layout algorithms include construction algorithms like ALDEP and CORELAP as well as improvement algorithms like pairwise exchange methods. ALDEP is a construction algorithm that builds a layout by successively placing departments based on their relationship information and minimum department preferences. It requires inputs like department areas, a REL chart, and sweep width. CORELAP is also a construction algorithm that determines department placement order based on total closeness ratings and places departments to maximize placing ratings, resulting in an optimal layout.