The document discusses different types of e-commerce:
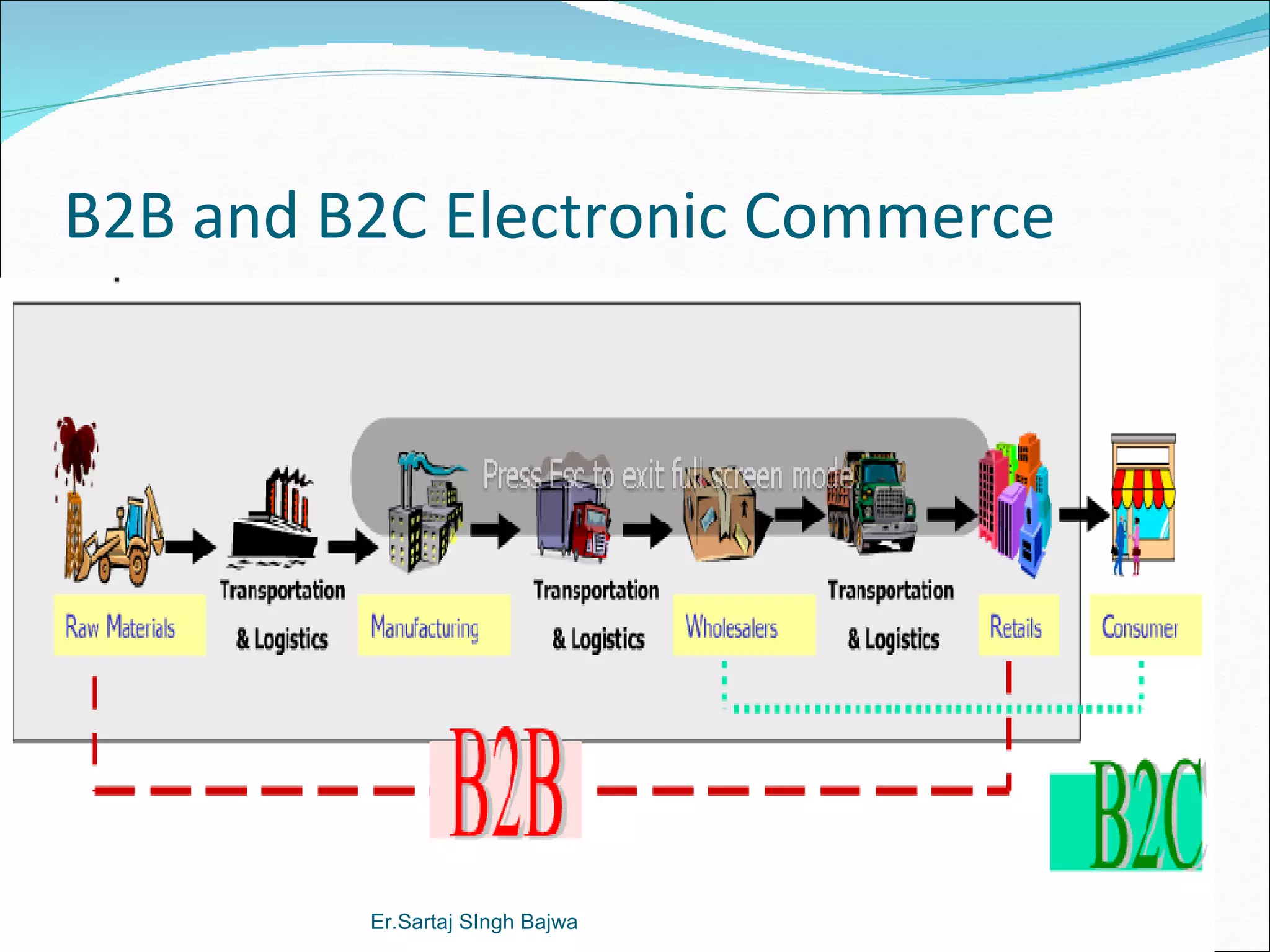
- Business-to-business (B2B) e-commerce involves transactions between companies, accounting for 80% of e-commerce.
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) involves companies selling to individual consumers.
- Business-to-government (B2G) involves companies selling goods/services to government agencies.
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) involves individuals selling directly to other individuals, such as on eBay.
- Mobile commerce (m-commerce) uses wireless devices like phones for commerce.