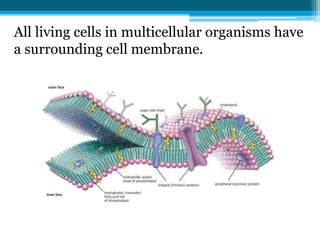
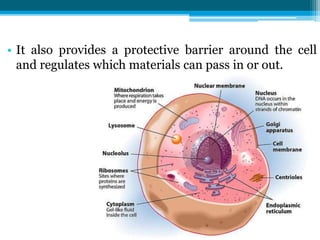
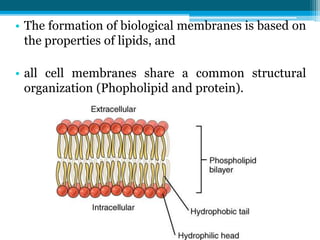
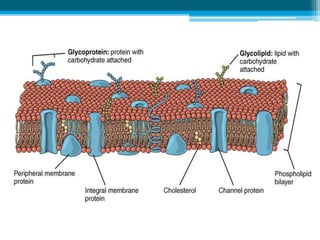
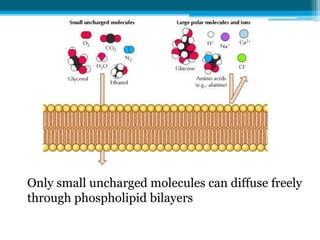
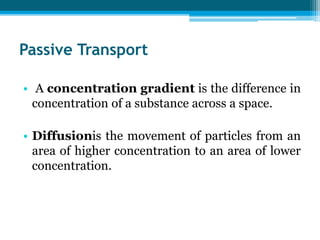
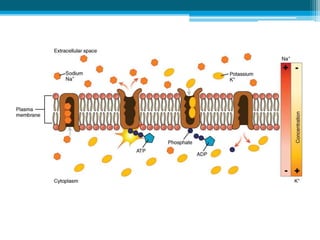
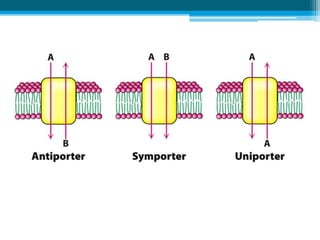
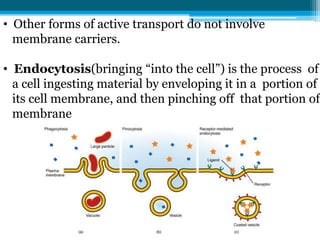
The cell membrane is made up of phospholipids and proteins that create a selectively permeable barrier around the cell. Phospholipids form a bilayer that allows only small, uncharged molecules to diffuse directly through. Integral and peripheral proteins embedded in or attached to the membrane help transport molecules in and out via passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport pumps, symporters, antiporters, and endocytosis. The cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell to maintain homeostasis and carry out its functions.