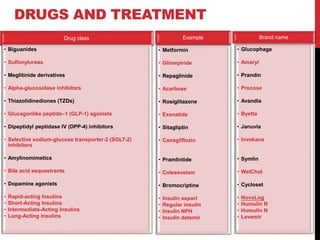
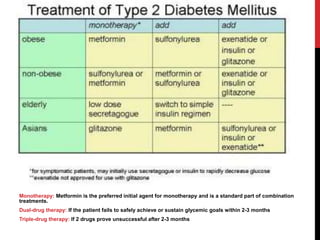
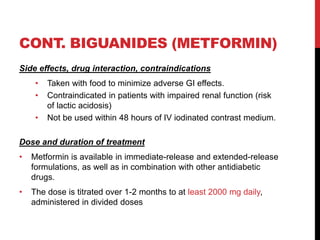
Type 2 diabetes results from insulin resistance and inadequate insulin secretion. It is characterized by hyperglycemia and increases the risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications if poorly controlled. Treatment involves lifestyle modifications and medications to control blood glucose levels and prevent complications. The goals are to eliminate symptoms, prevent complications, and achieve an A1C under 7%. First line treatment is often metformin, while additional drugs may be added if goals are not met.






![COMPLICATIONS
Cardiovascular risk * *2-4 times greater in patients with
diabetes* *
1. Lipid abnormalities:
• small, dense low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol
• high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
• triglyceride-rich remnant lipoproteins
2. Thrombotic abnormalities:
• type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor [PAI-1]
• fibrinogen
3. Hypertension](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/type2dm-161007090230/85/Type2-dm-8-320.jpg)