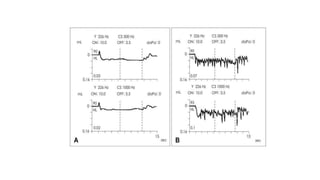
Tympanometry is a technique used to assess middle ear function by measuring the mobility of the tympanic membrane (TM). It provides an objective and fast way to evaluate outer and middle ear pathology. Different types of tympanograms - Type A, As, Ad, B, and C - can be produced based on the middle ear pressure and compliance. Each type has a characteristic interpretation and examples of possible middle ear conditions it may indicate. The acoustic reflex is also measured to further analyze middle ear disorders.