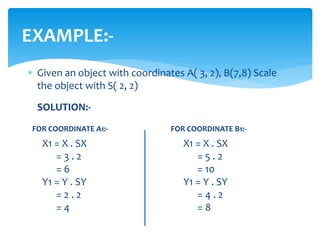
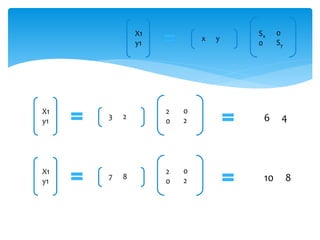
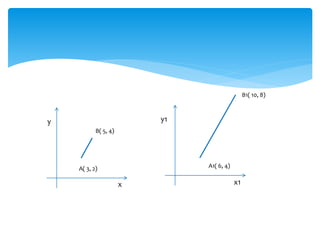
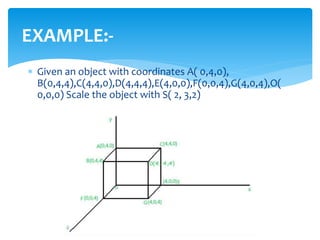
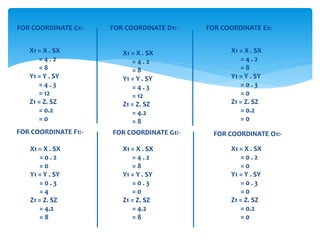
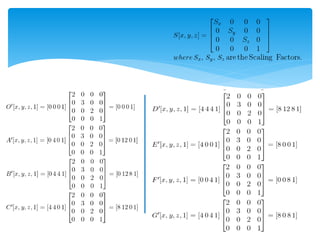
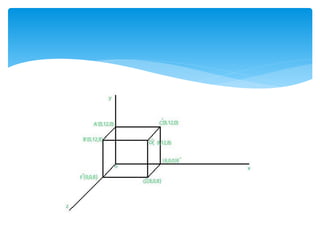
This document discusses two-dimensional and three-dimensional scaling in computer graphics. It defines scaling as modifying the size of objects by applying scaling factors to their coordinate points. Two-dimensional scaling scales objects in the x and y plane, while three-dimensional scaling also scales along the z-axis. Scaling factors above 1 increase size, below 1 decrease size, and 1 keeps the original size. Examples are given of applying scaling factors to 2D and 3D coordinate points.