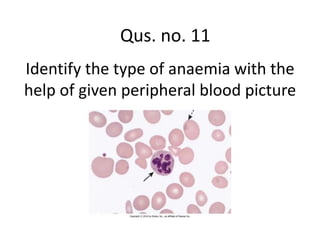
This document contains 19 questions about blood cells and the immune system. The questions cover topics like: factors involved in prothrombin time, changes to red blood cell size in pernicious anemia, differences in red blood cell count between males and females, how hypoxia stimulates erythropoiesis, the contents of Heme's fluid, plasma proteins and their roles, T lymphocytes, identifying types of anemia from blood pictures, instruments and their uses in blood analysis, physiological conditions with high ESR, differences between white blood cell and red blood cell pipettes, macrophage locations in the body, the role of the thymus in the immune system, causes of anisocytosis, and advantages of the bicon