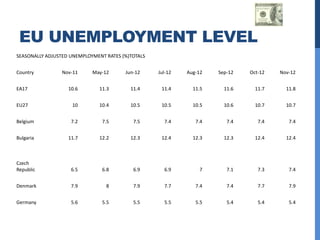
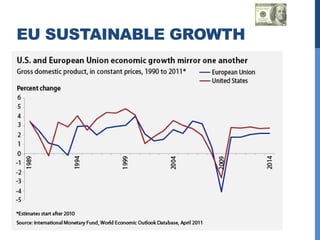
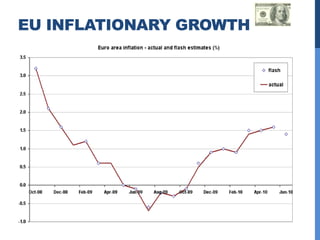
The document summarizes several central banking institutions:
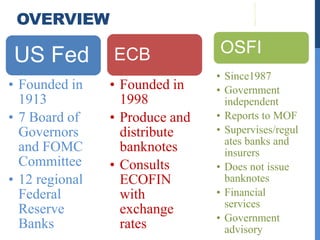
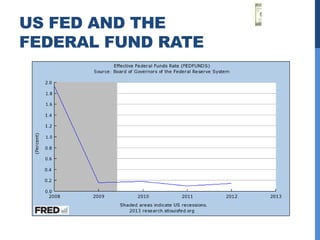
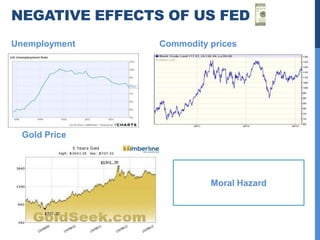
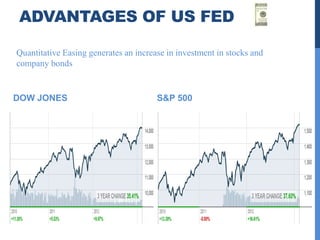
1) The US Federal Reserve (Fed) was founded in 1913 and oversees monetary policy and acts as lender of last resort. It aims to control interest rates and inflation.
2) The European Central Bank (ECB) was founded in 1998 and manages the eurozone's monetary policy, with the primary aim of maintaining price stability.
3) The Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) is Canada's financial services regulator, supervising banks, insurers, private pensions and more since 1987. It ensures safety and soundness through rule-making and oversight.