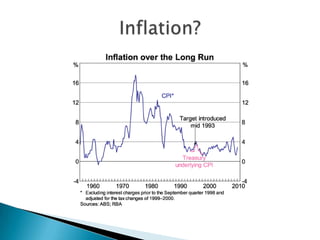
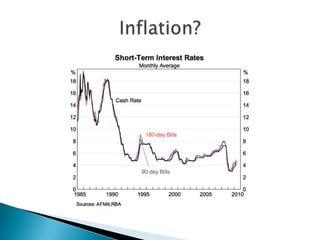
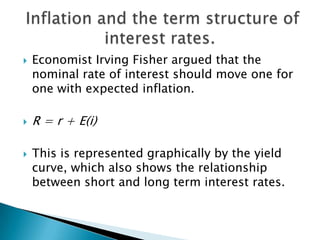
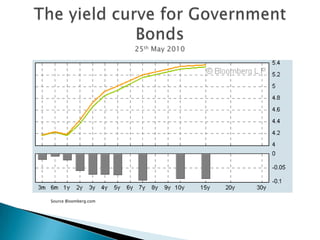
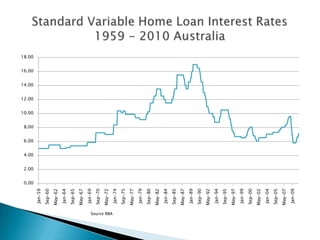
Interest rates refer to the percentage charged or paid for the use of money in a loan or other financial transaction. The Reserve Bank of Australia sets interest rates in Australia to achieve price stability and full employment through monetary policy. It aims to keep inflation between 2-3% annually by adjusting the cash rate, which influences other interest rates set by banks and lenders. Factors like inflation expectations, borrower risk, and global economic conditions also impact interest rate levels.