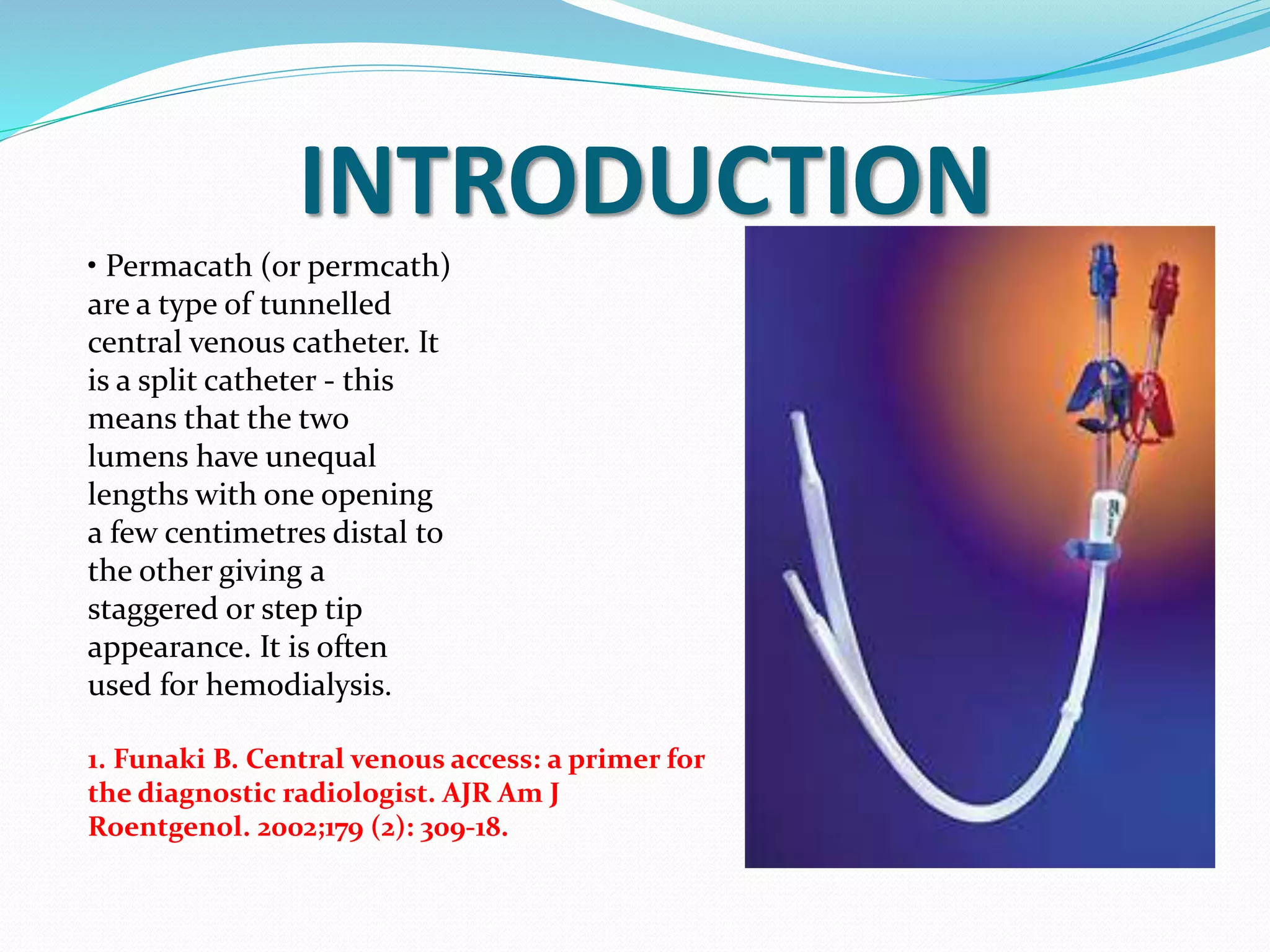
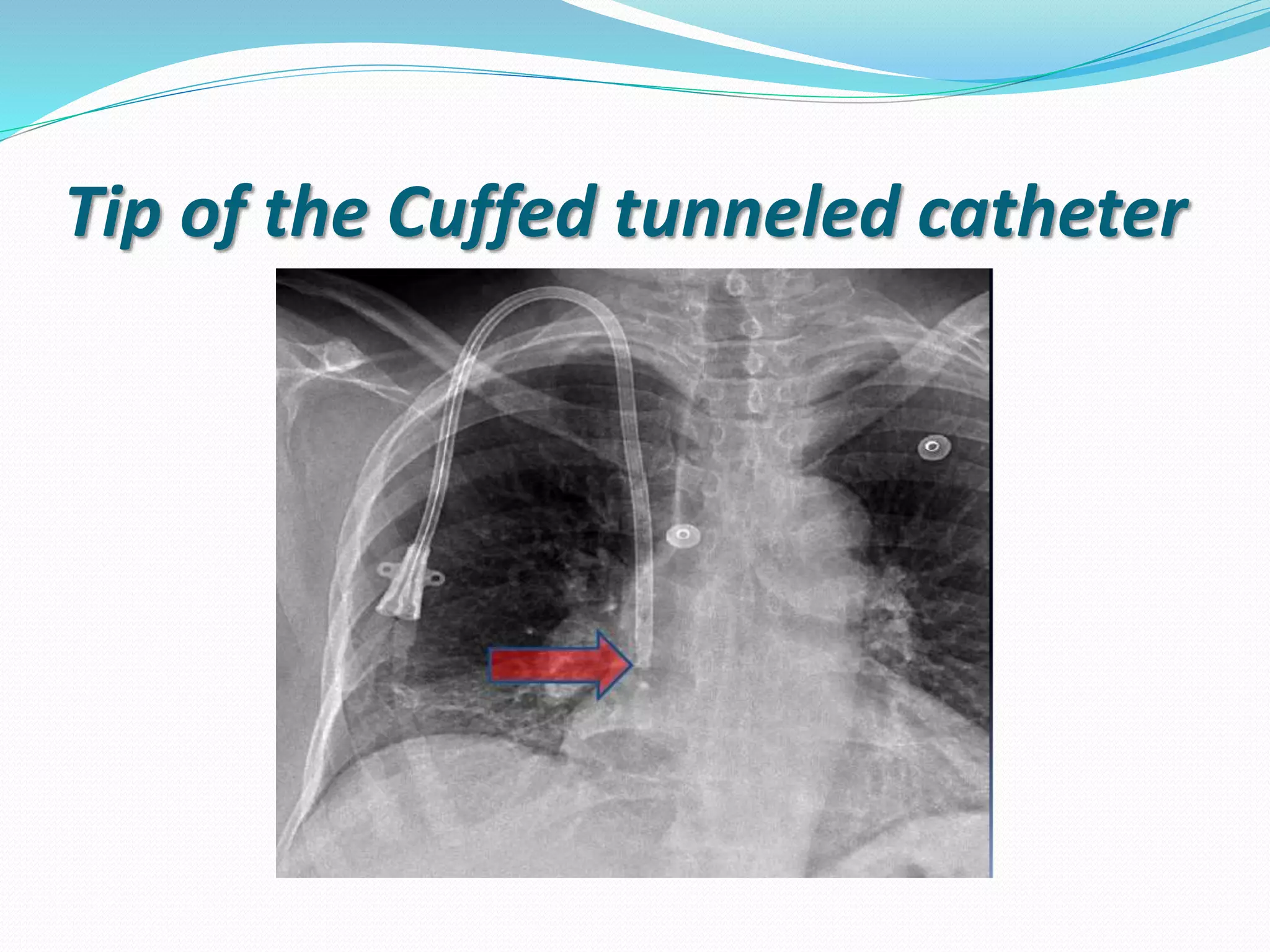
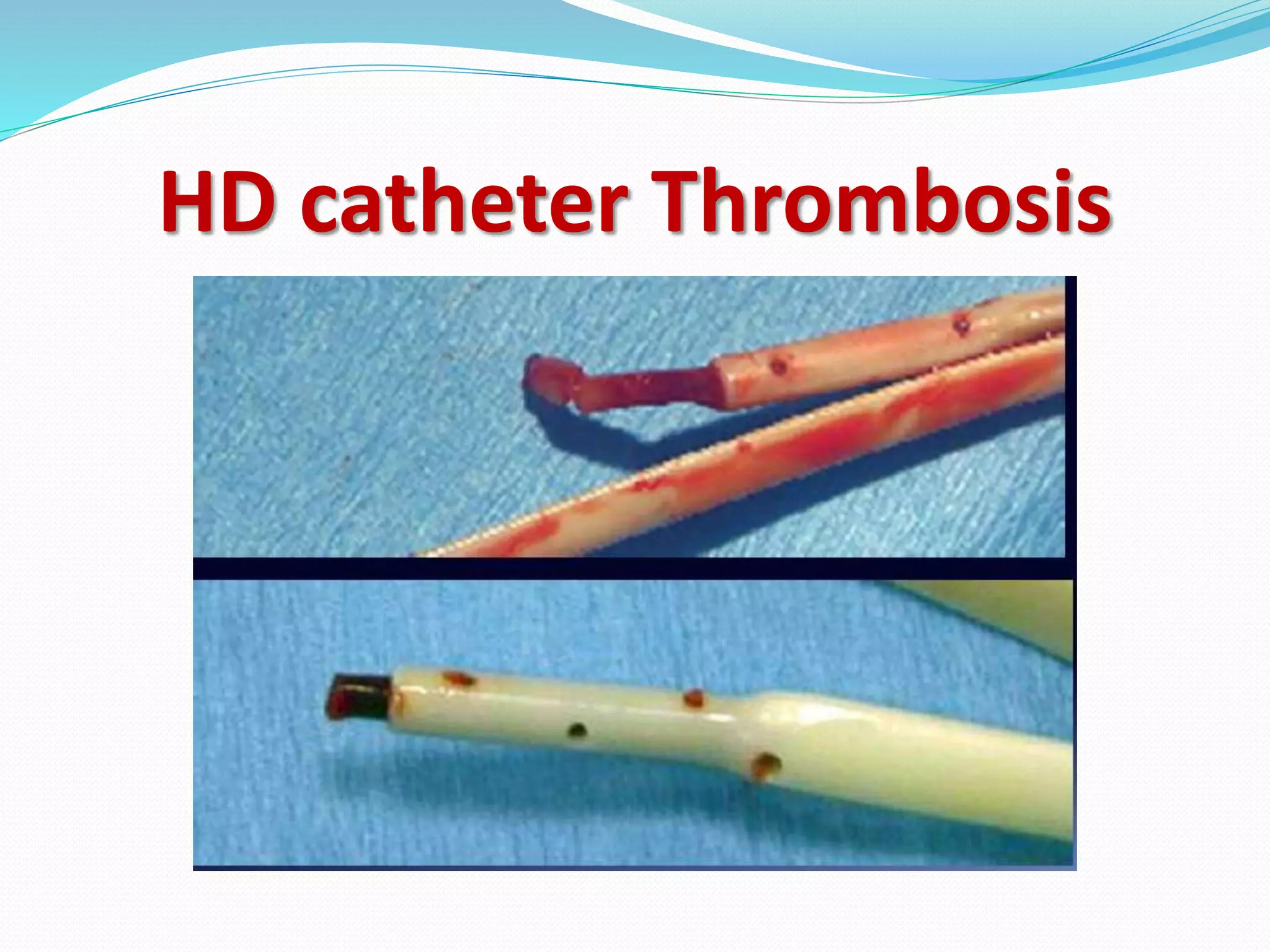
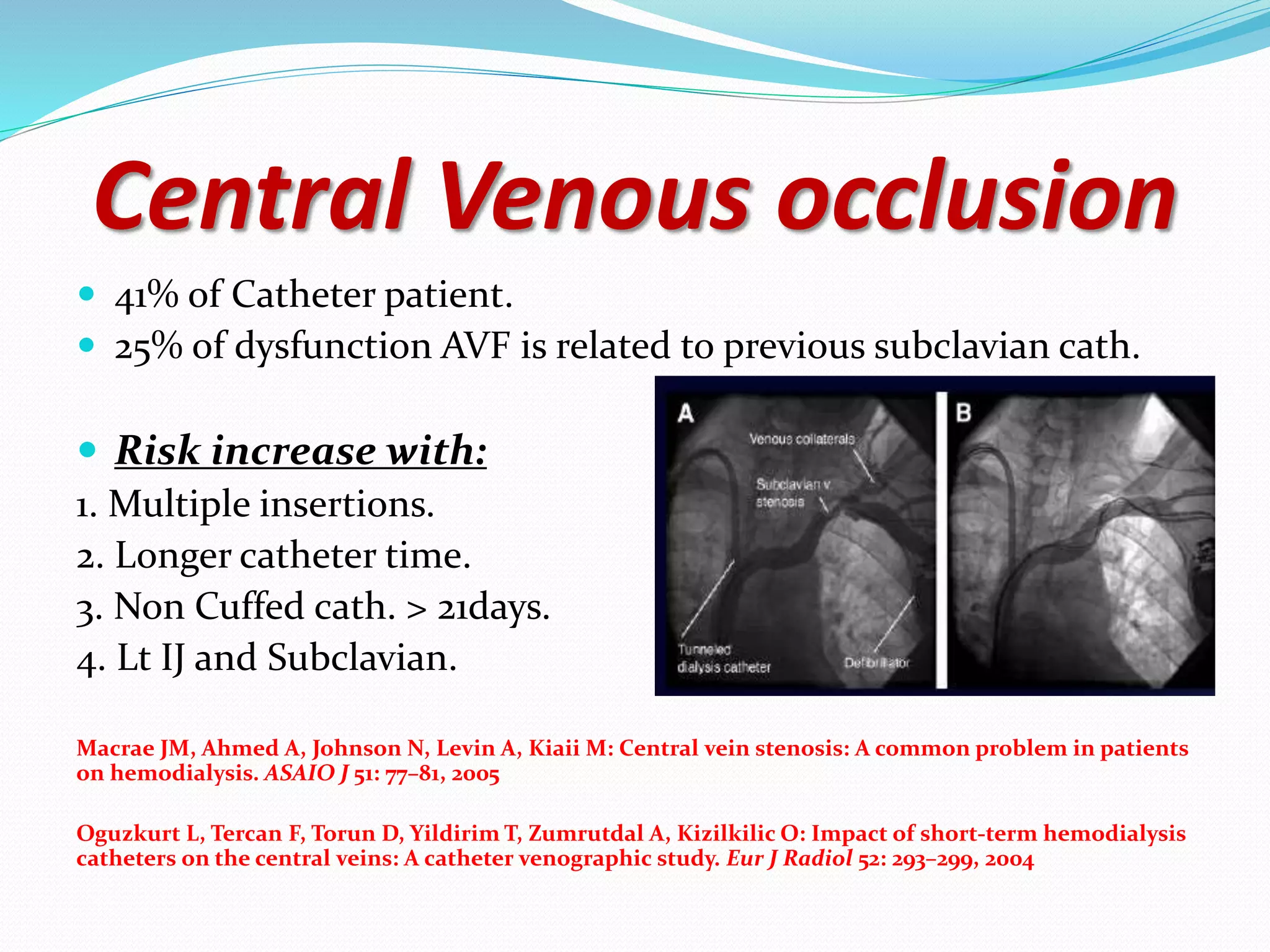
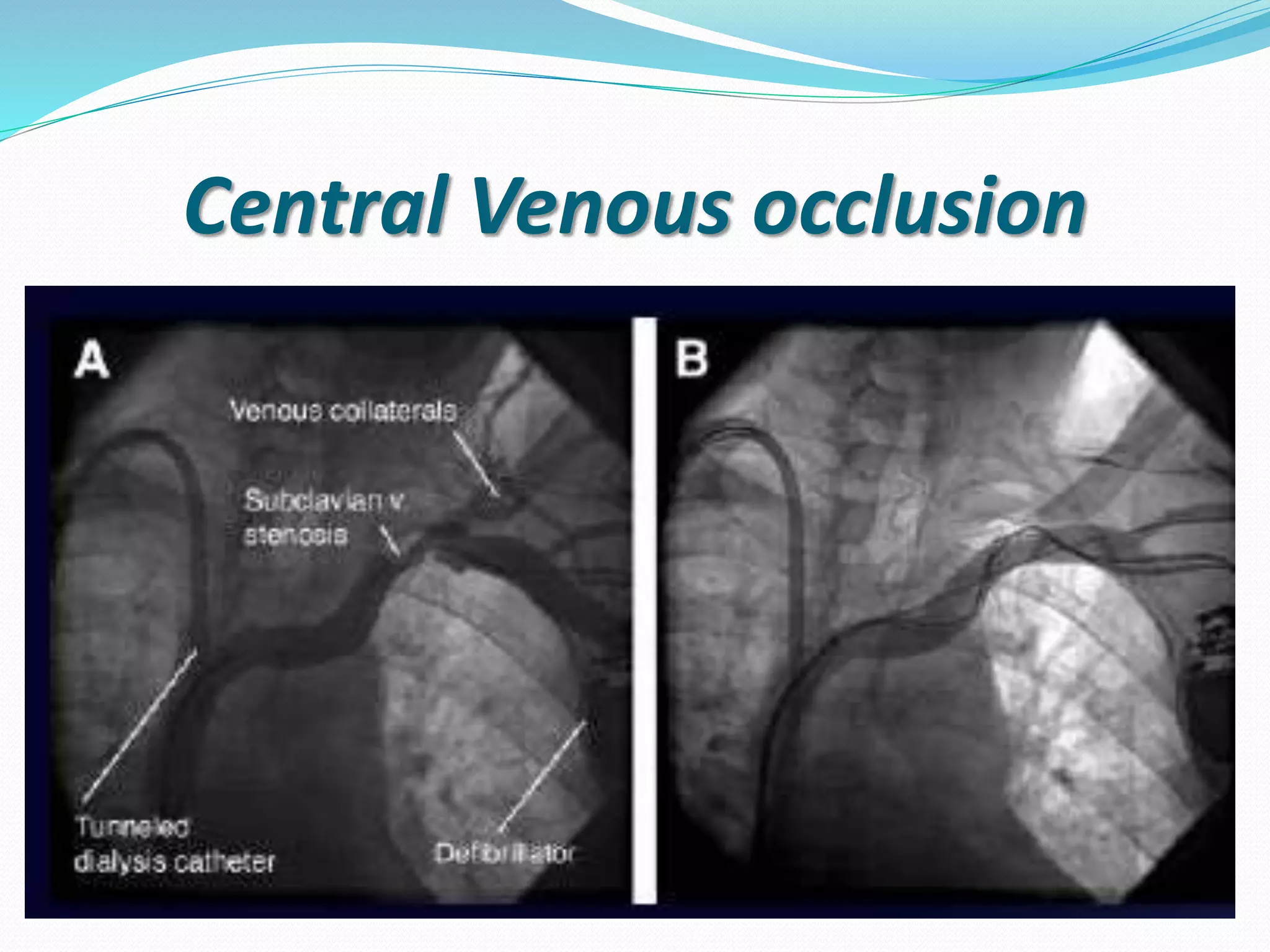
This document provides information on hemodialysis catheters. It begins by describing the characteristics of an ideal catheter and then discusses permacath catheters, which are tunnelled central venous catheters often used for hemodialysis. The document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of catheters compared to arteriovenous fistulas. It also discusses various complications associated with catheters including thrombosis, fibrin sheath formation, infection, and vascular thrombosis. The document provides details on preventing, diagnosing, and treating these complications.