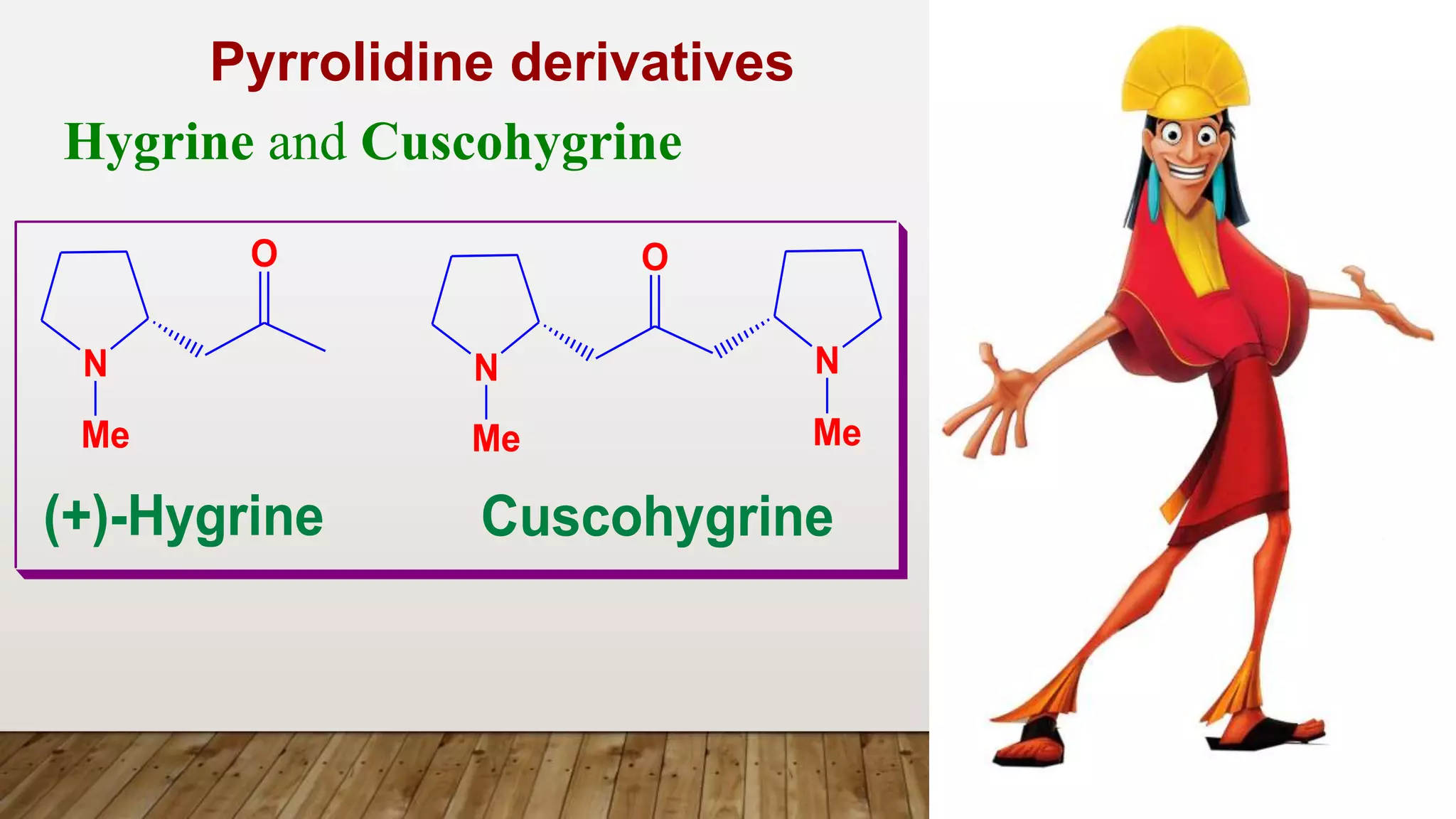
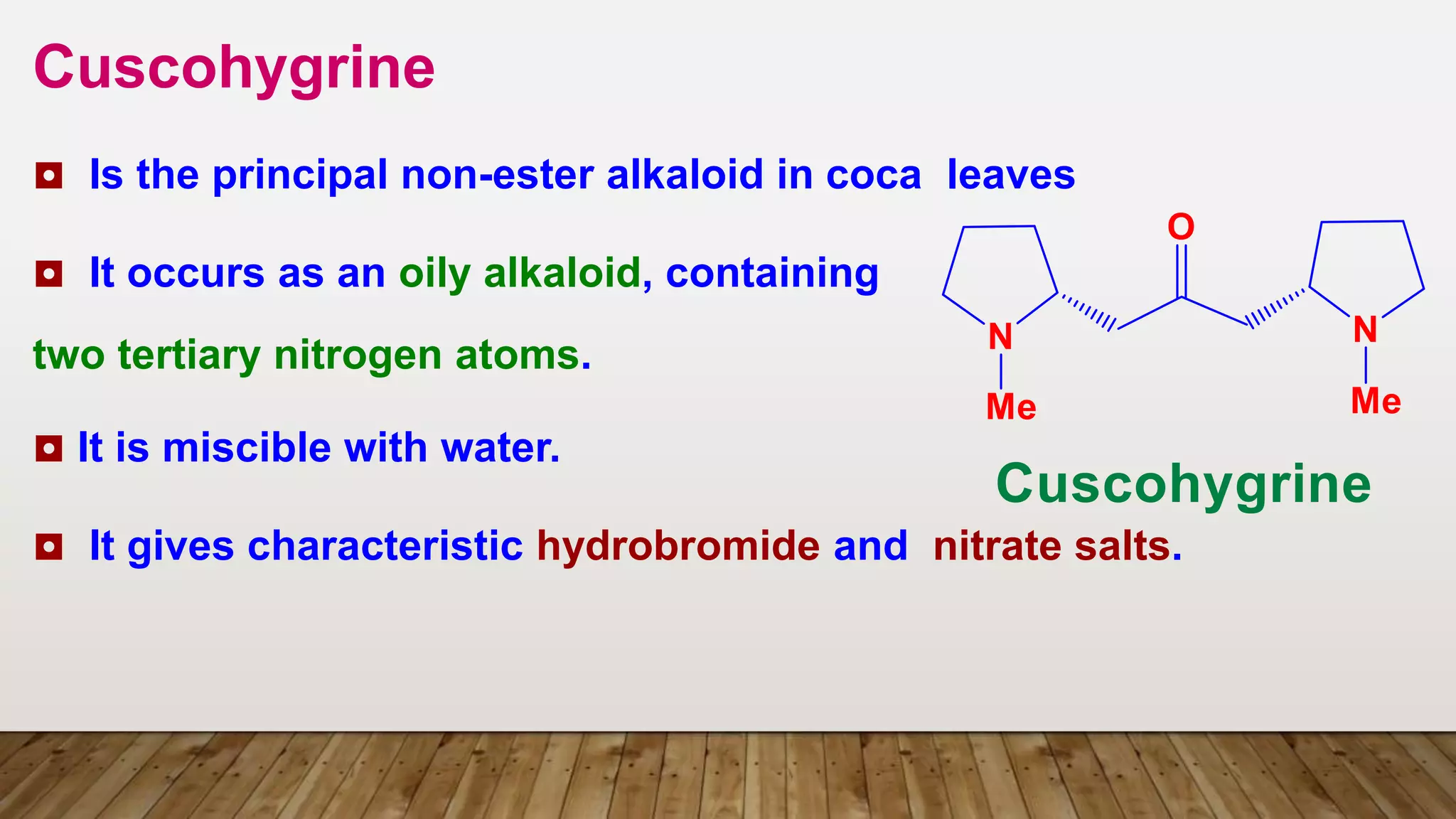
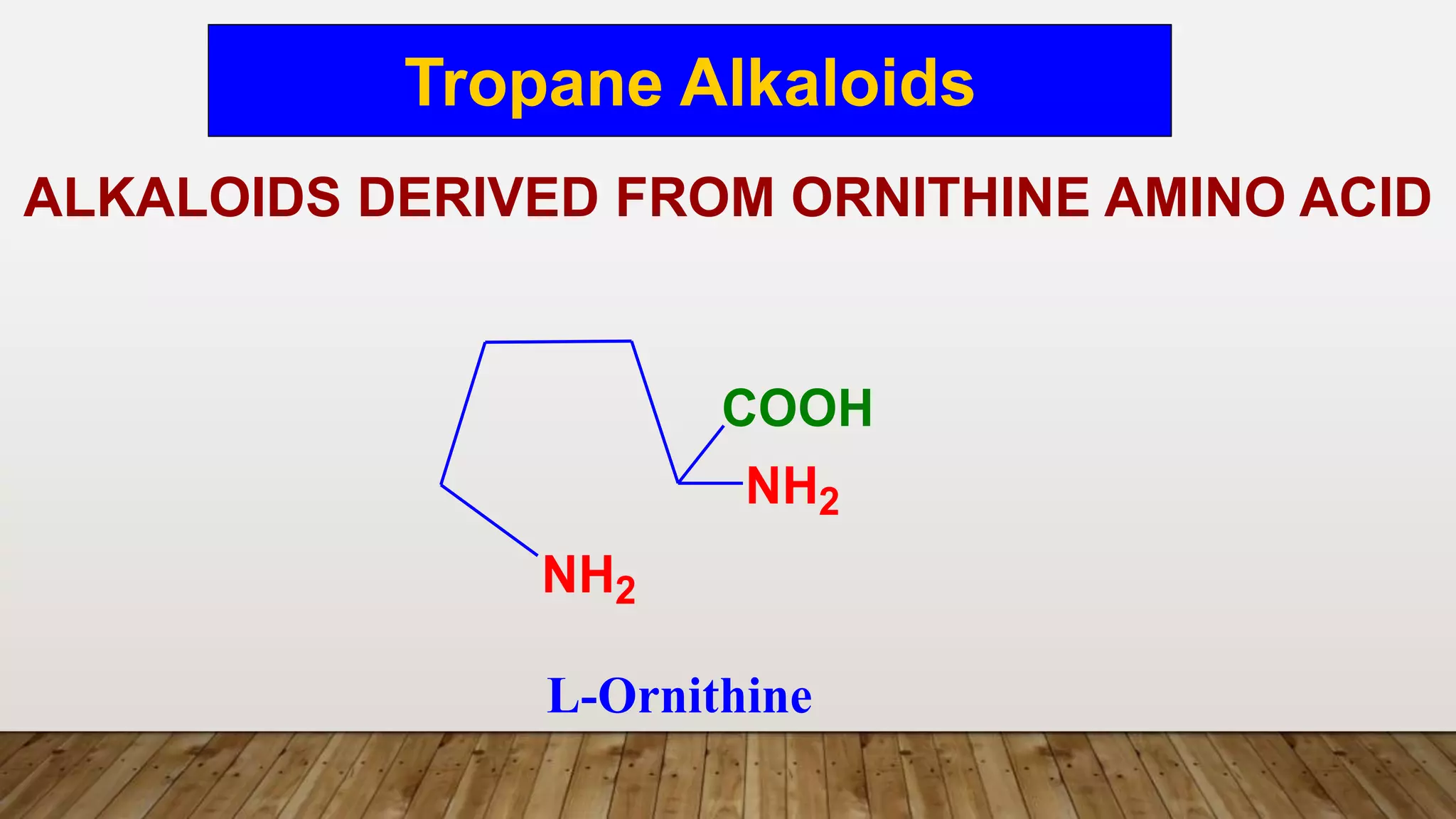
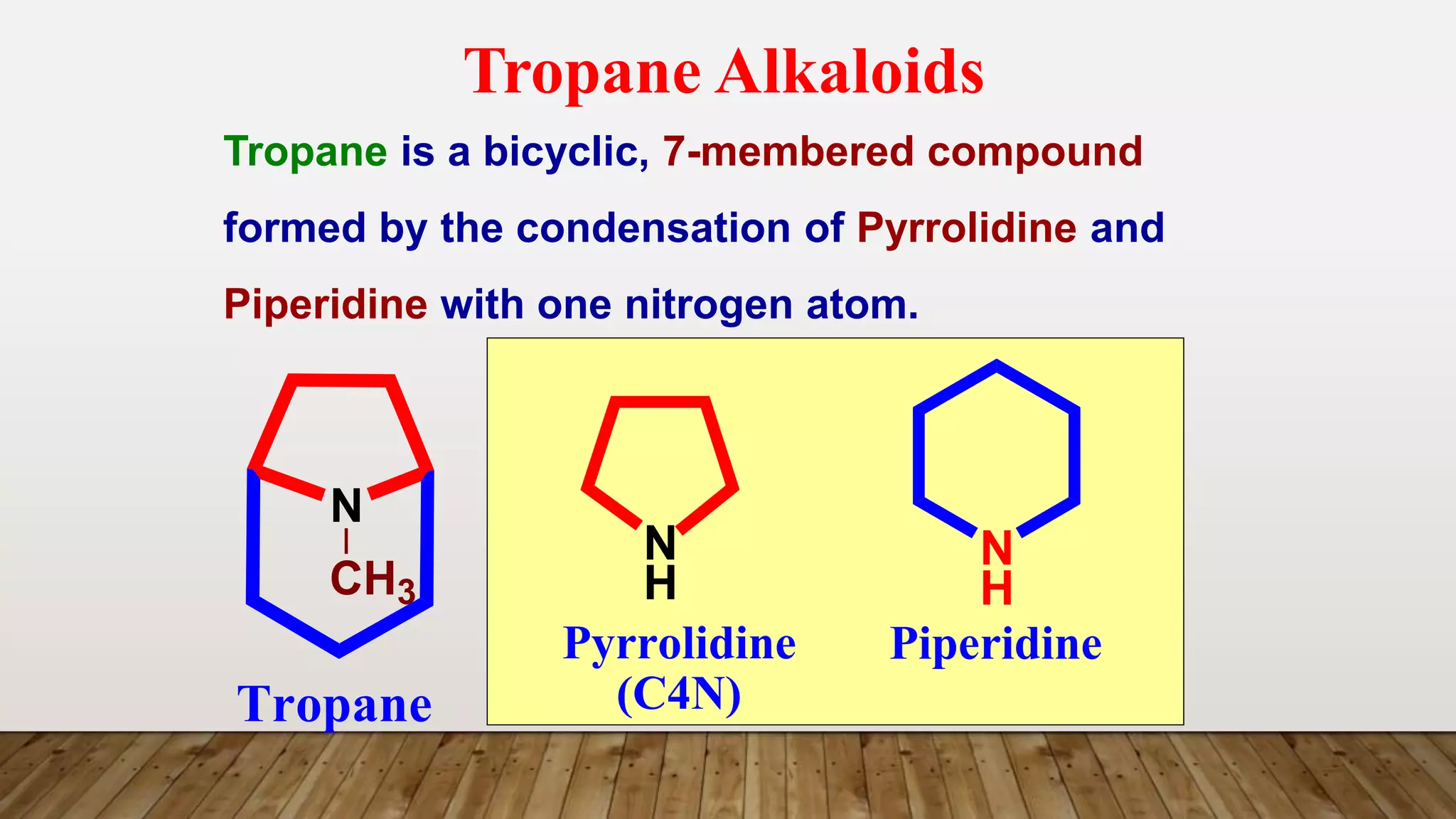
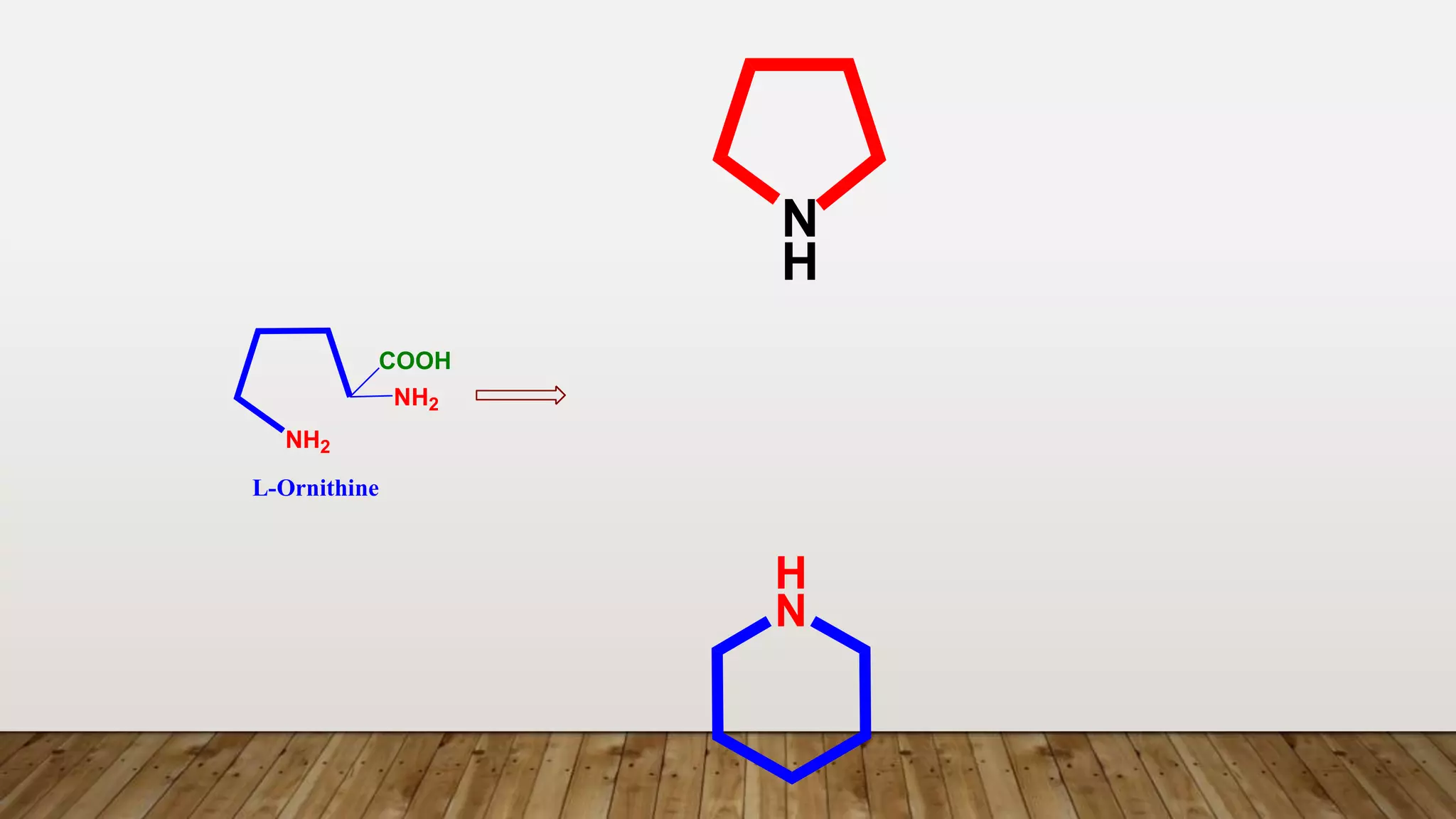
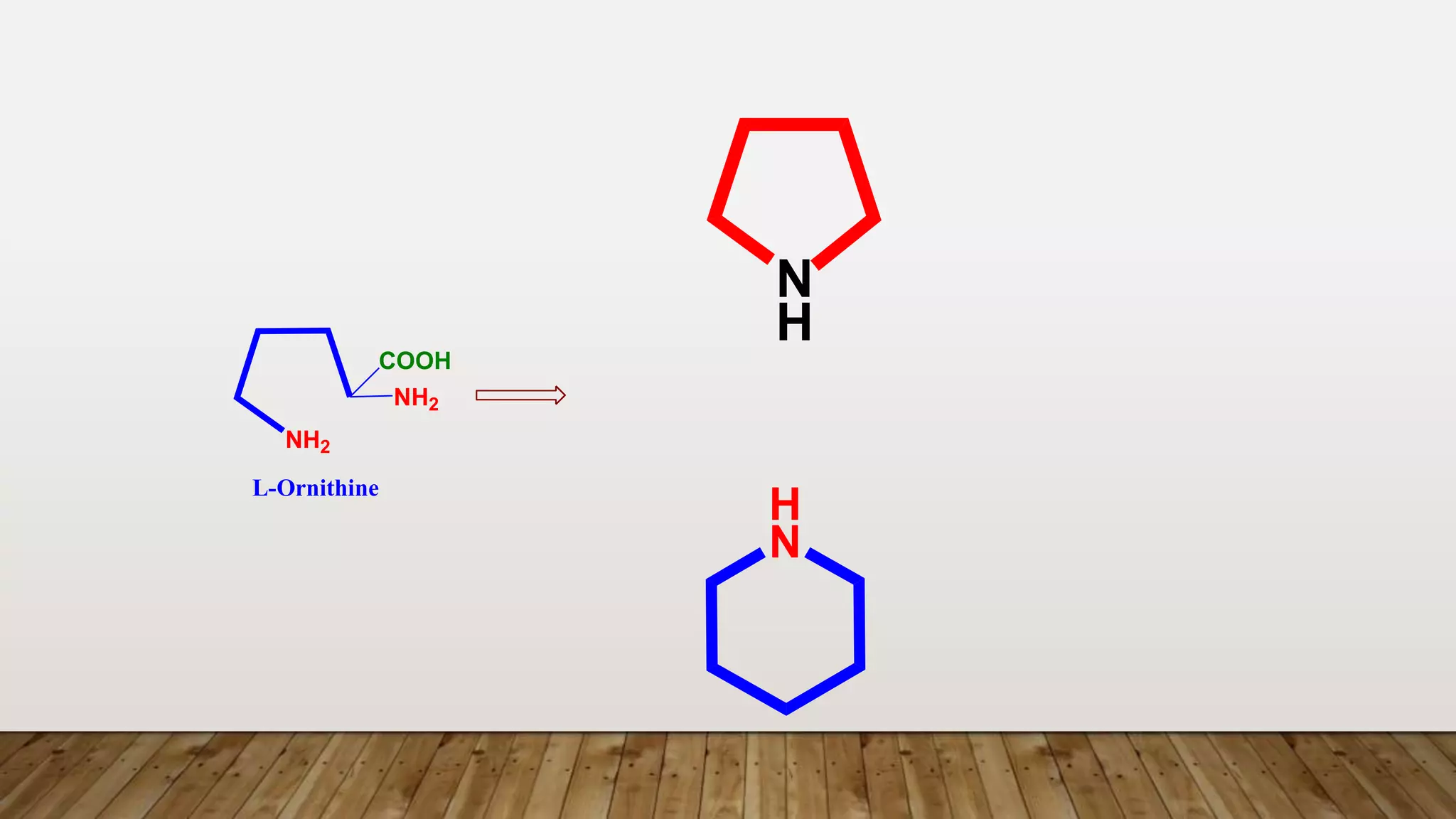
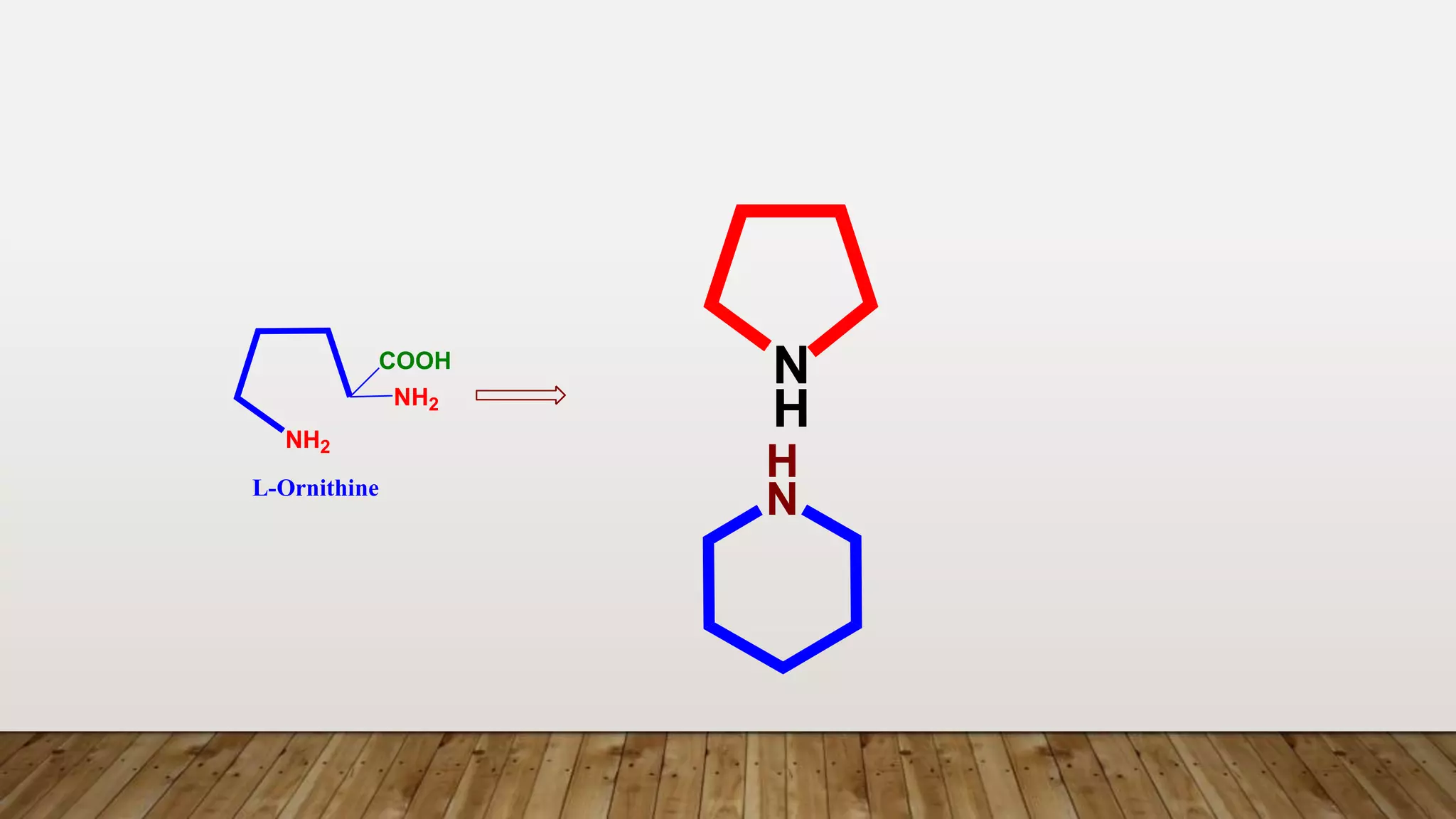
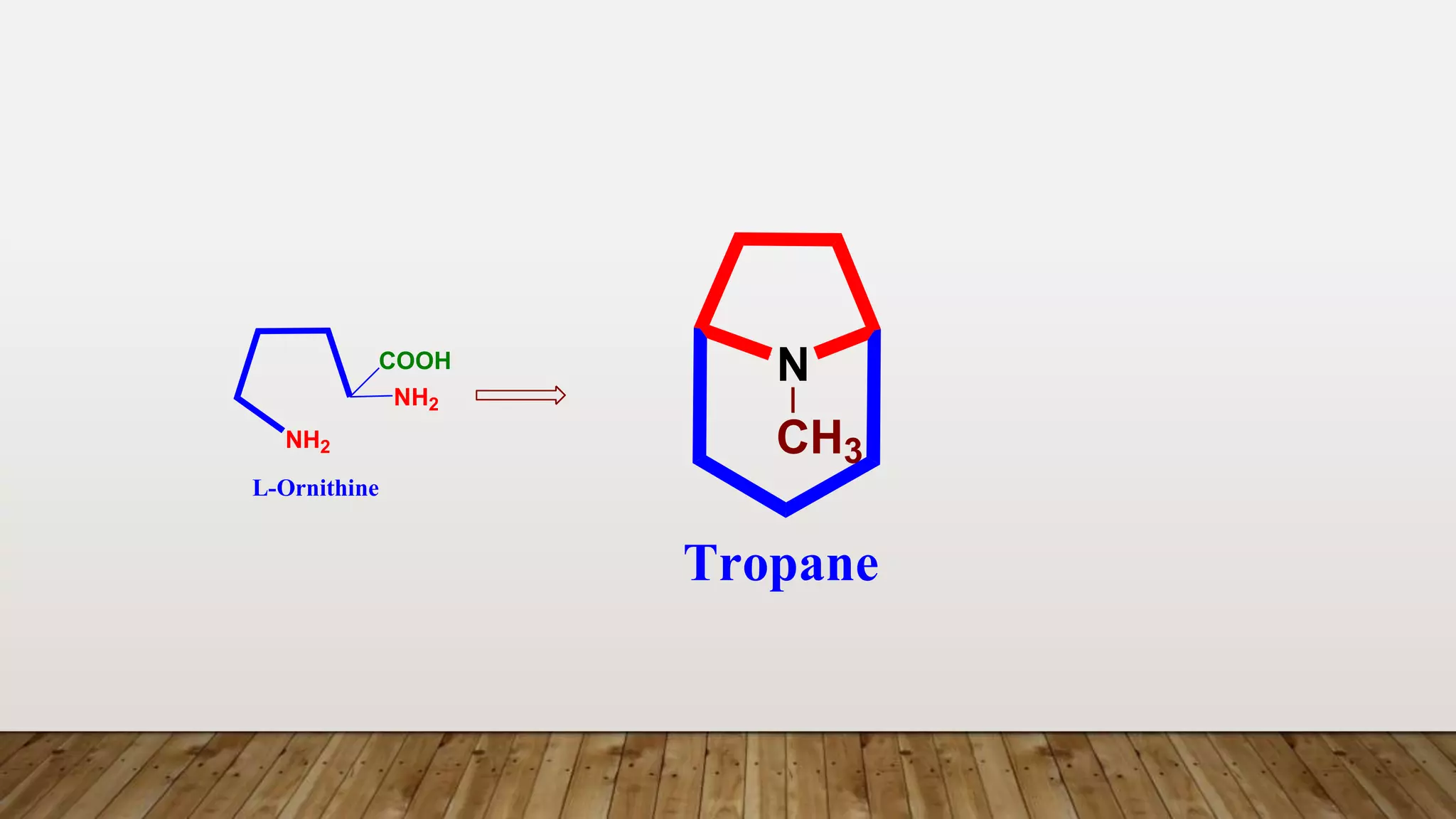
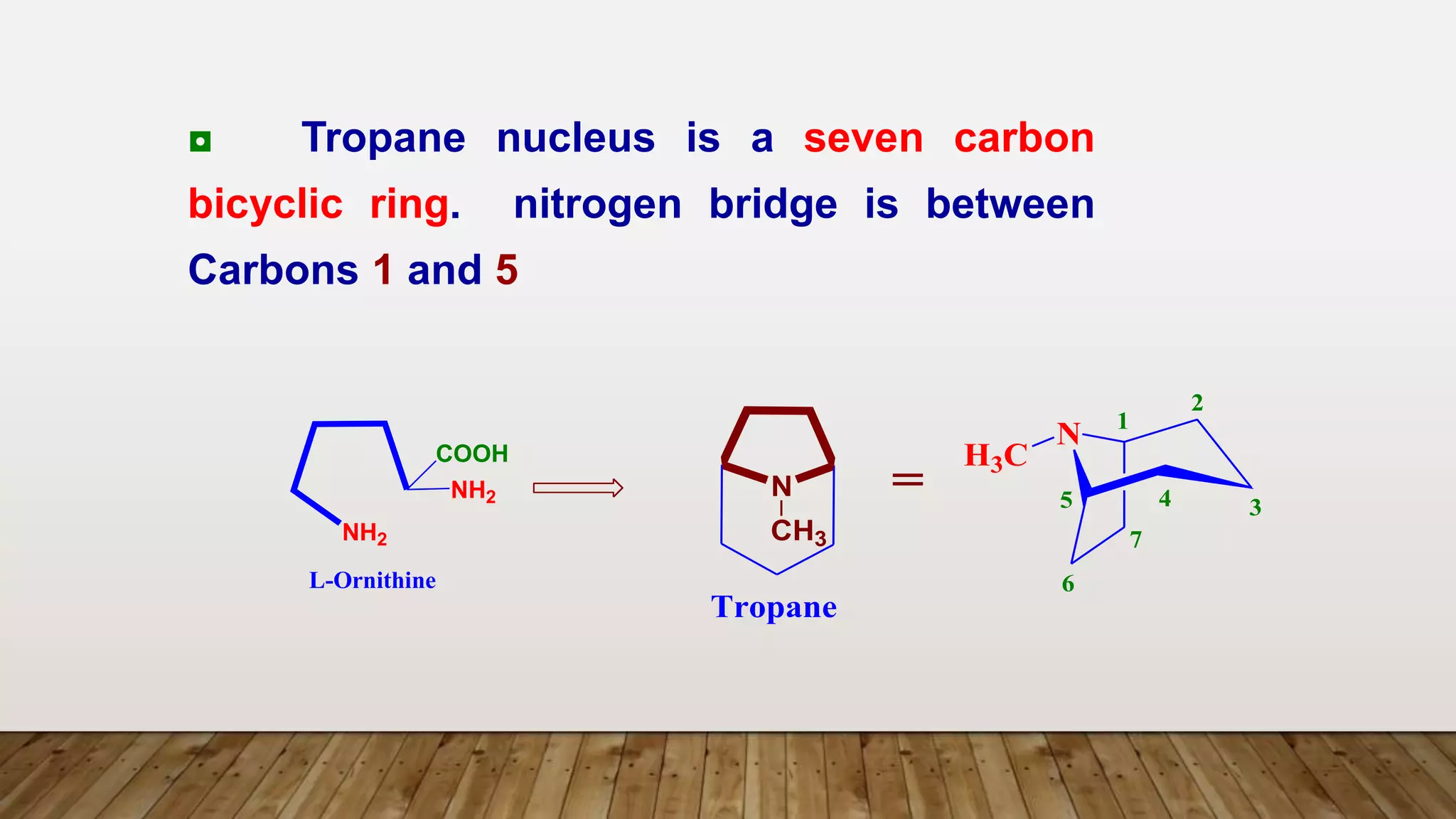
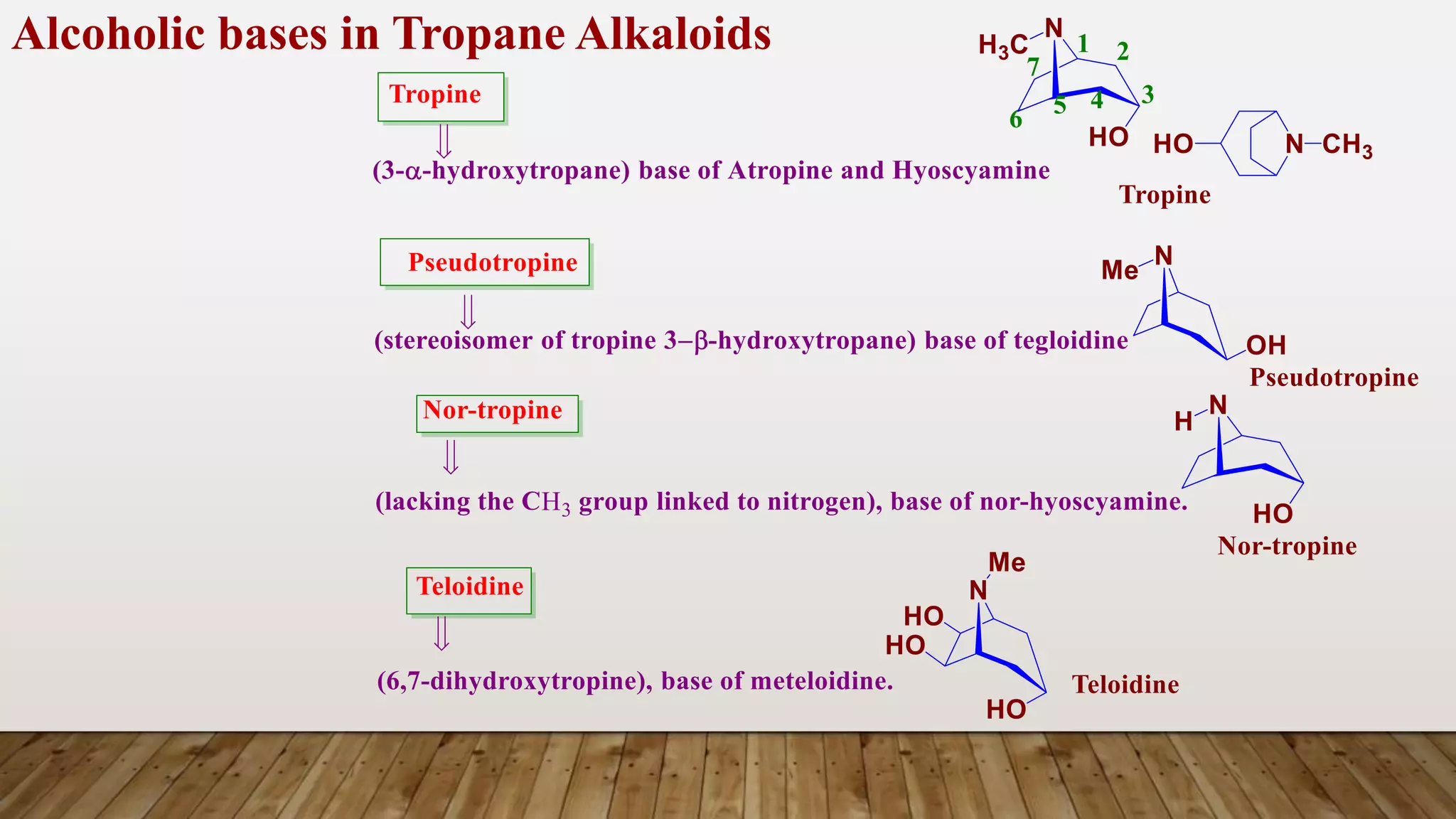
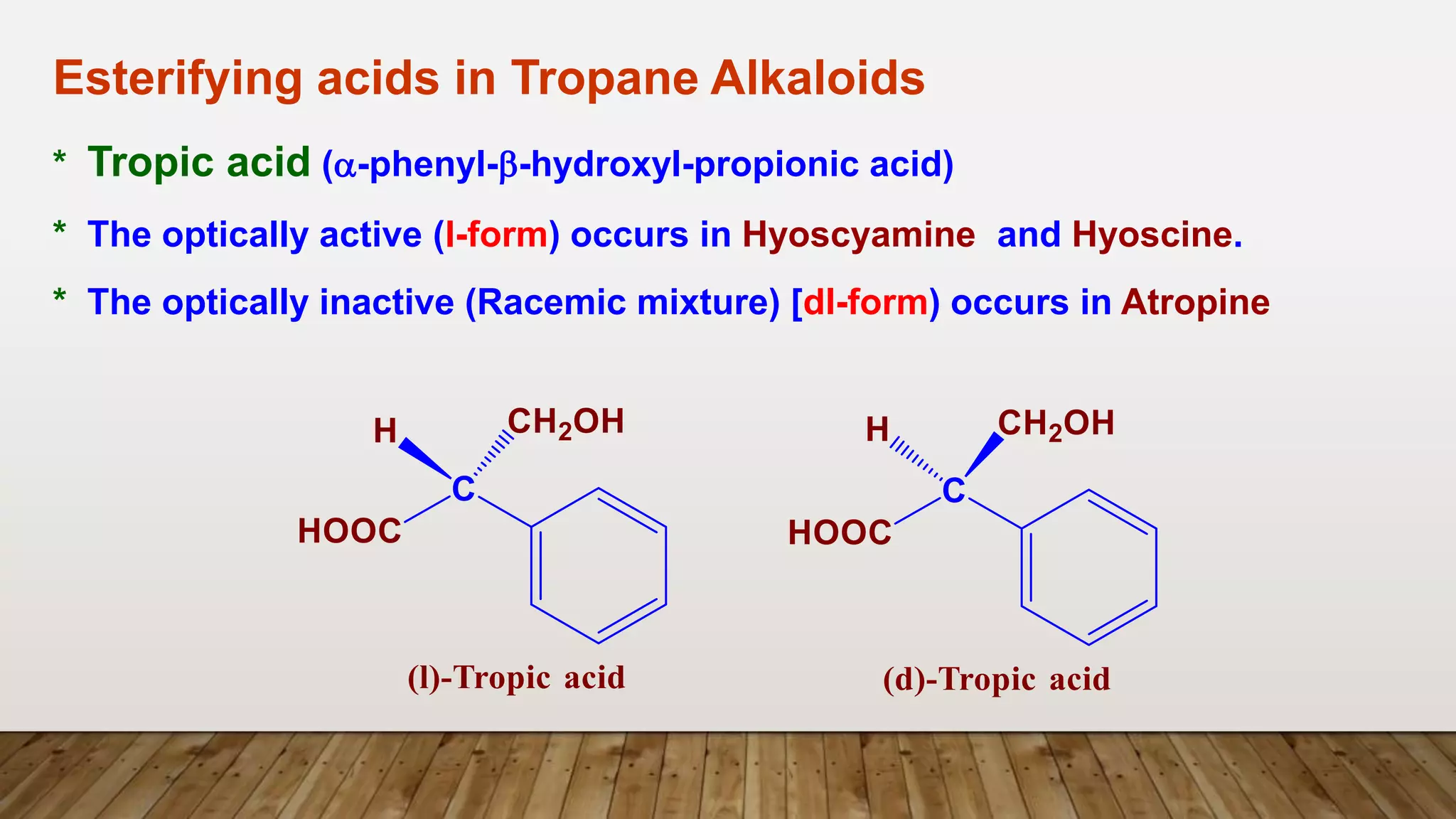
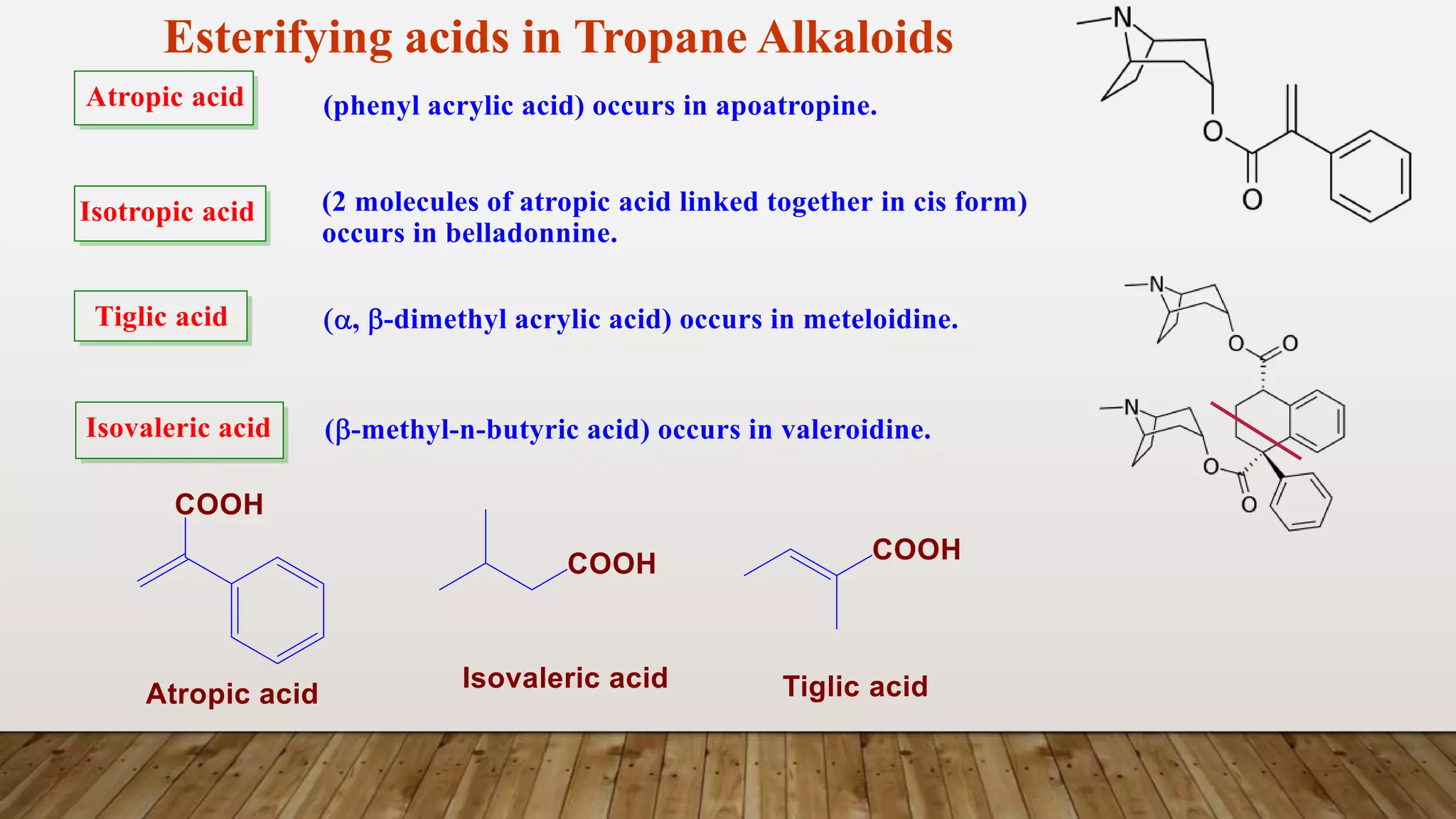
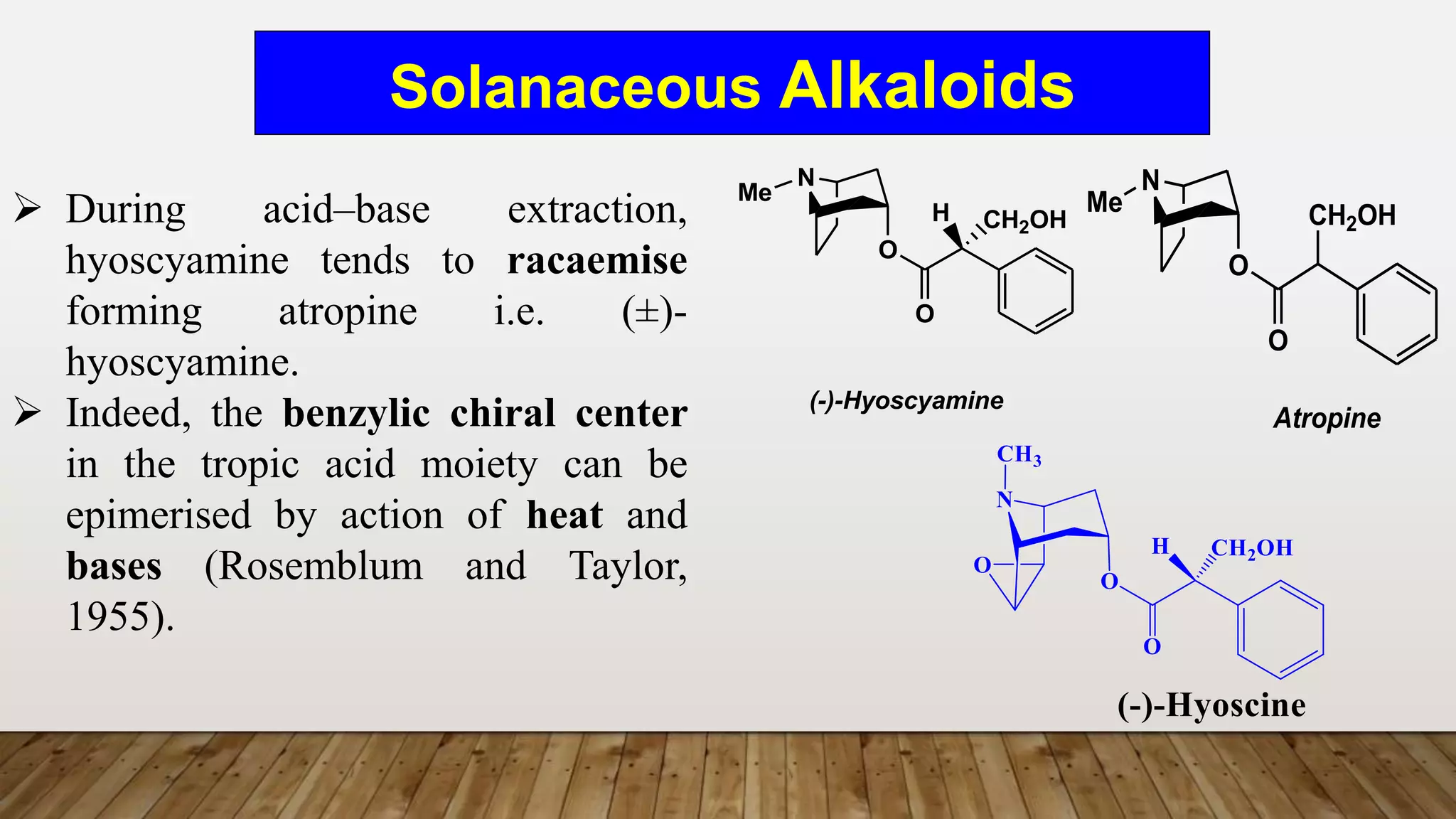
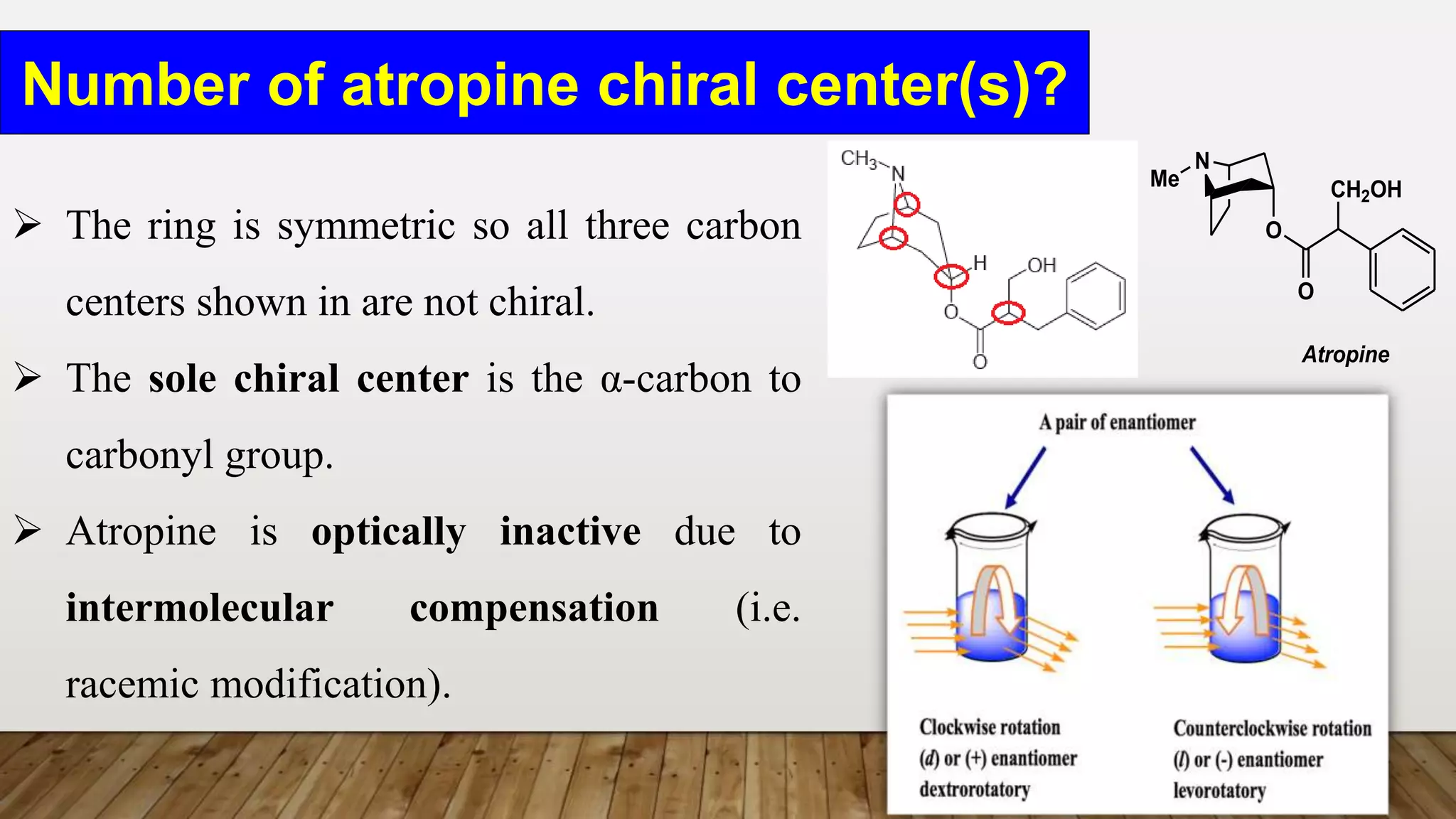
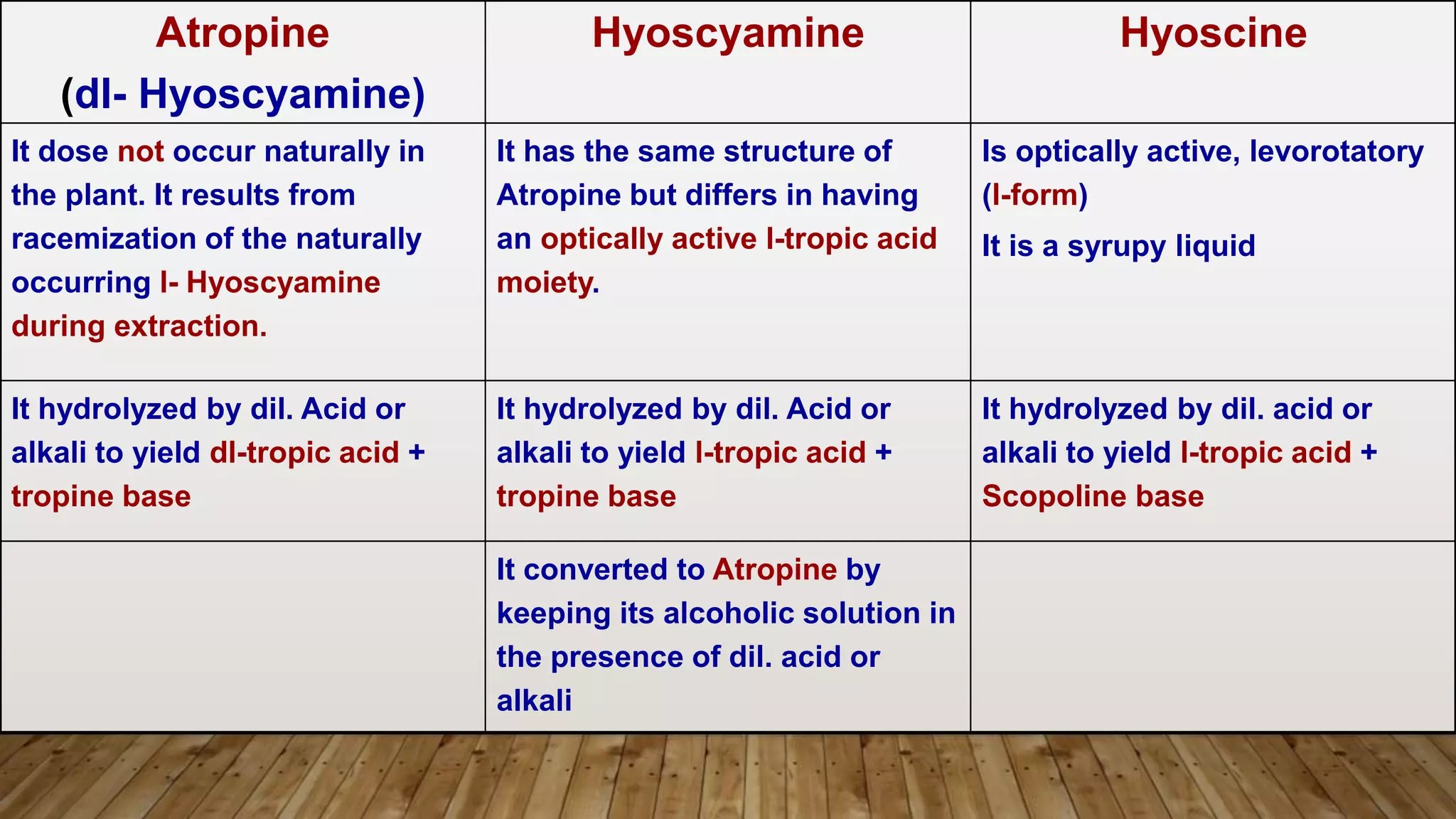
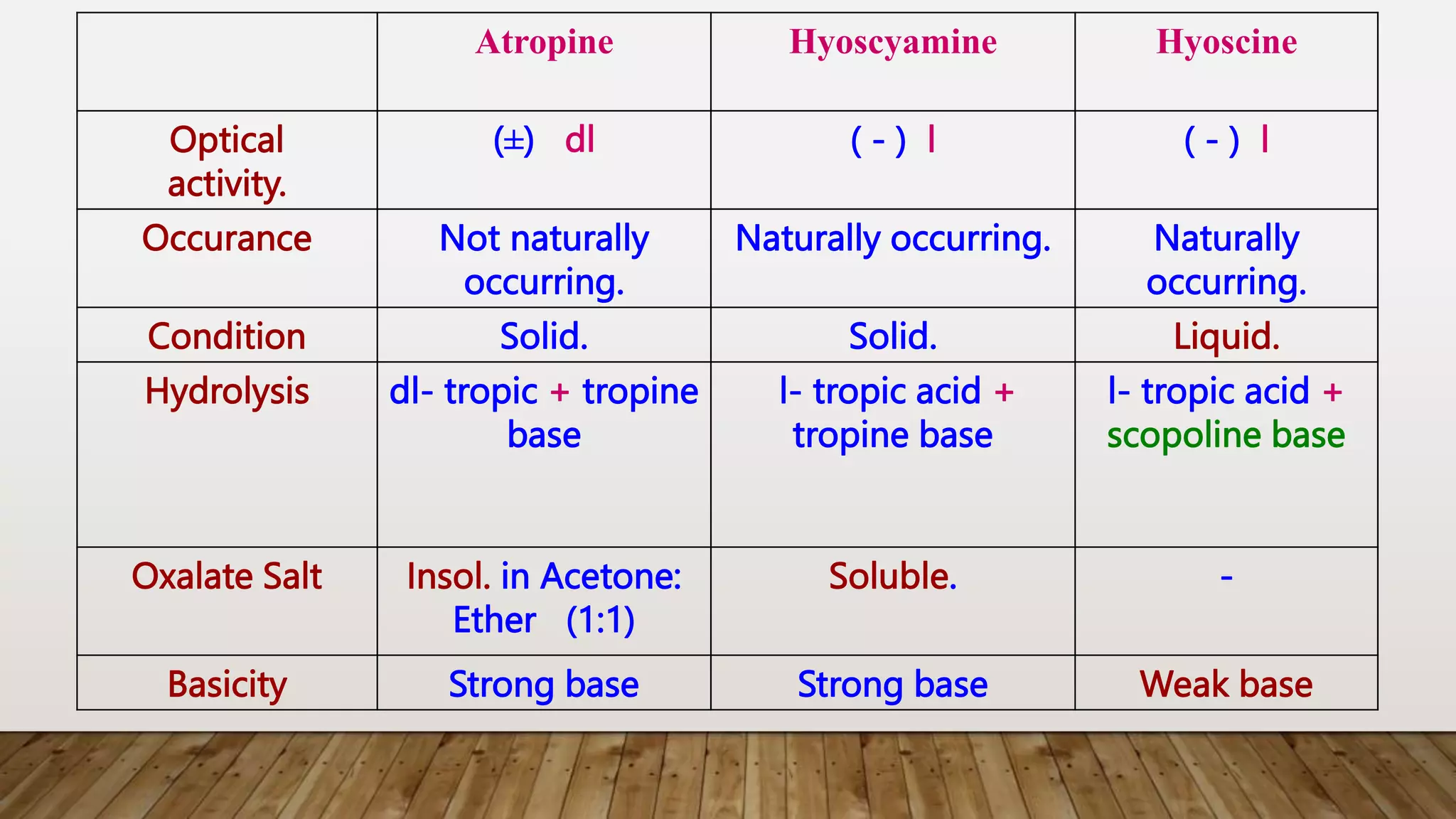
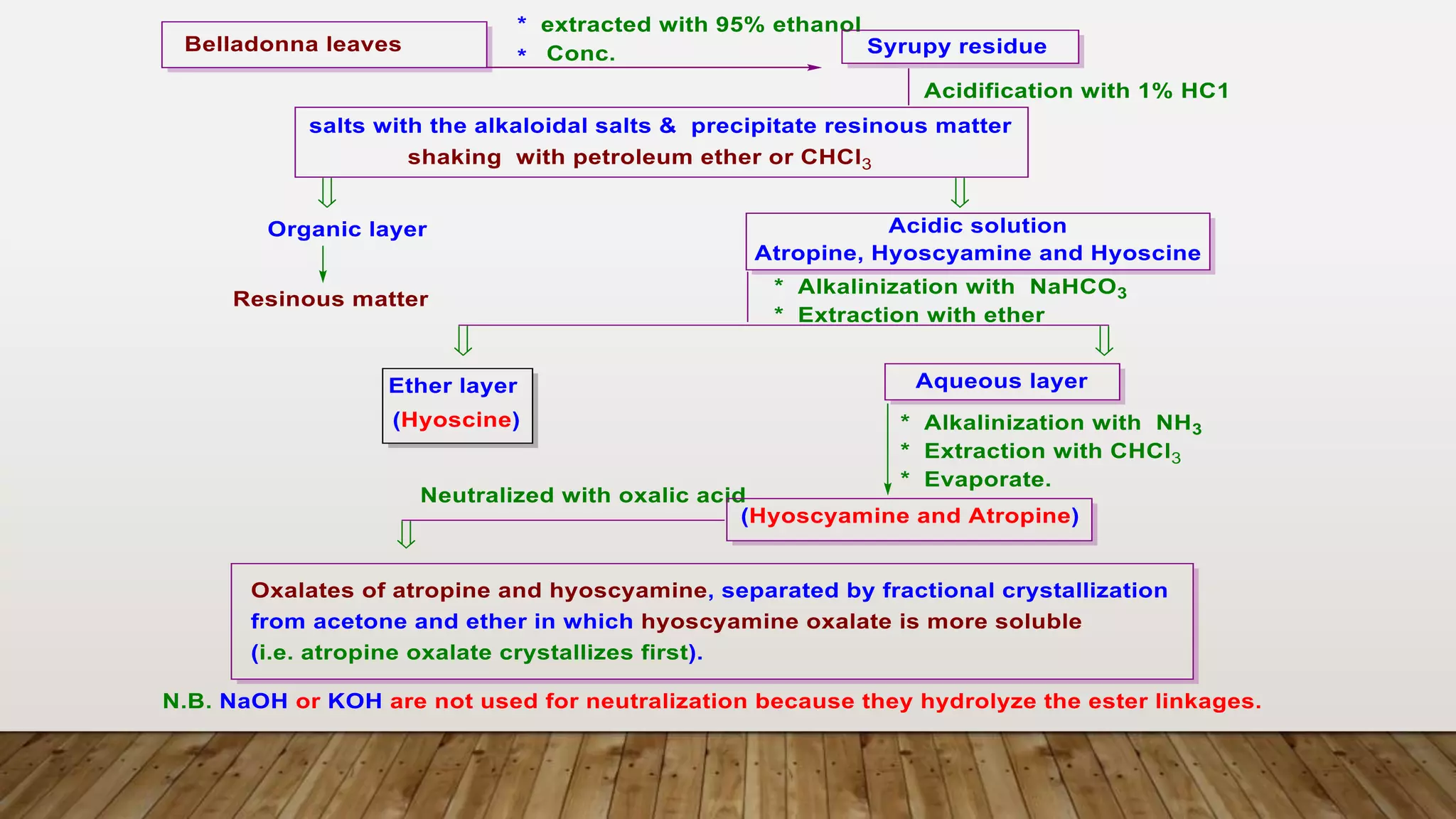
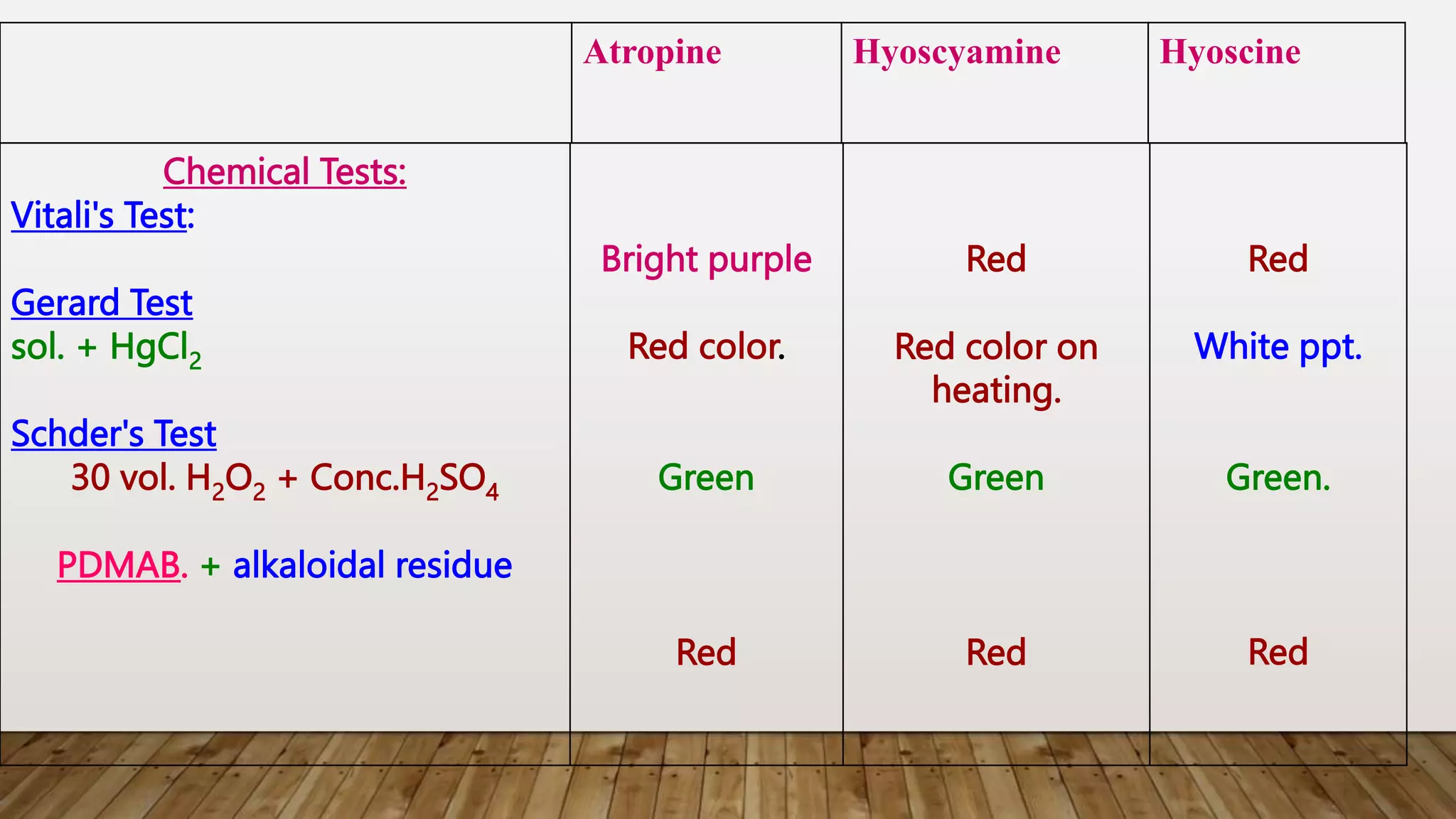
The document provides a detailed overview of tropane alkaloids, including structural information, classifications, and examples such as atropine, hyoscyamine, and cocaine. It discusses their synthesis, extraction processes, and pharmacological effects, highlighting the differences in activity and uses among various alkaloids. Furthermore, it addresses chemical tests used for identification and characterization of these compounds.













![* Coca alkaloids are classified according to the chemical
structures into 3 basic types:
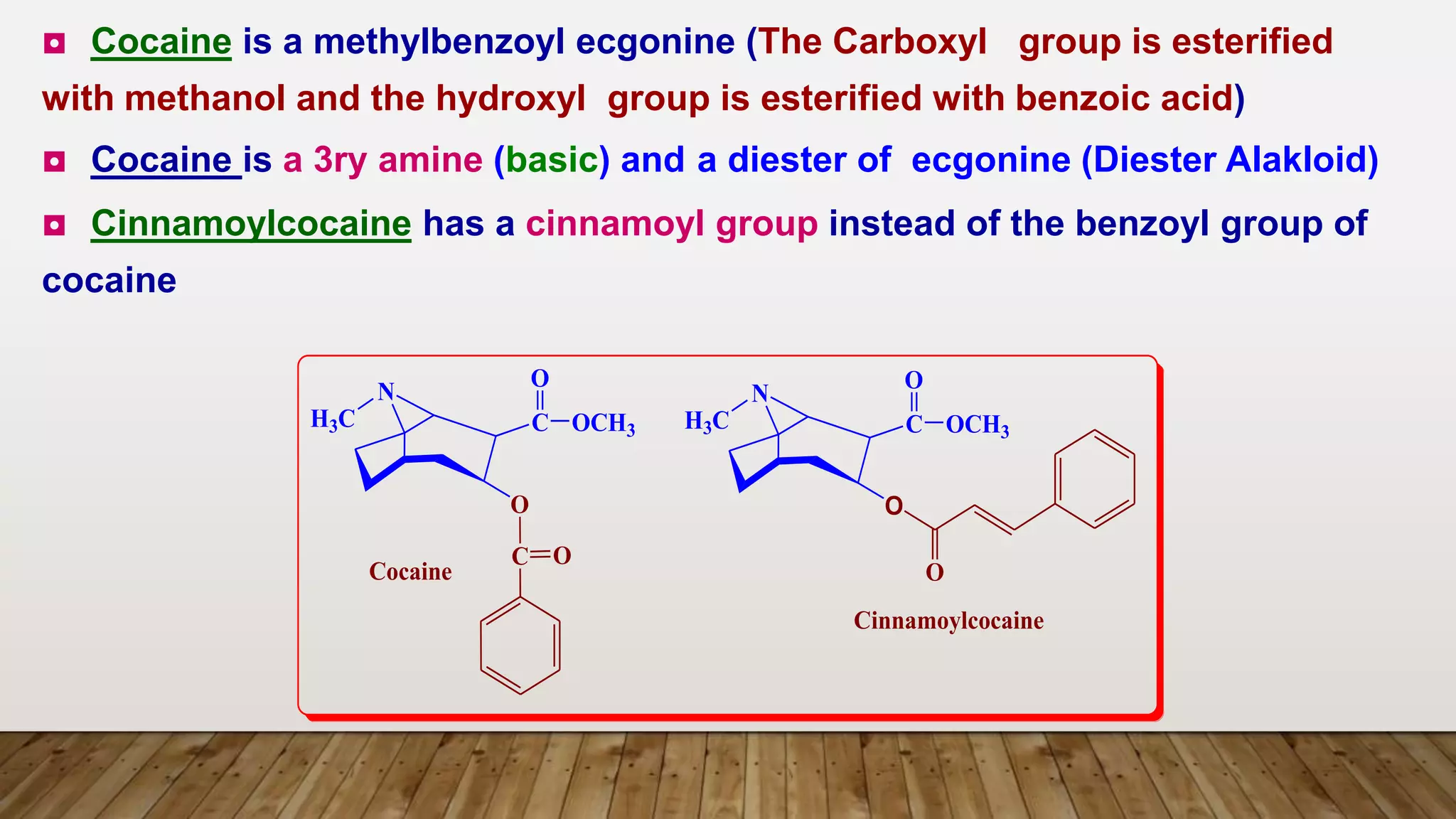
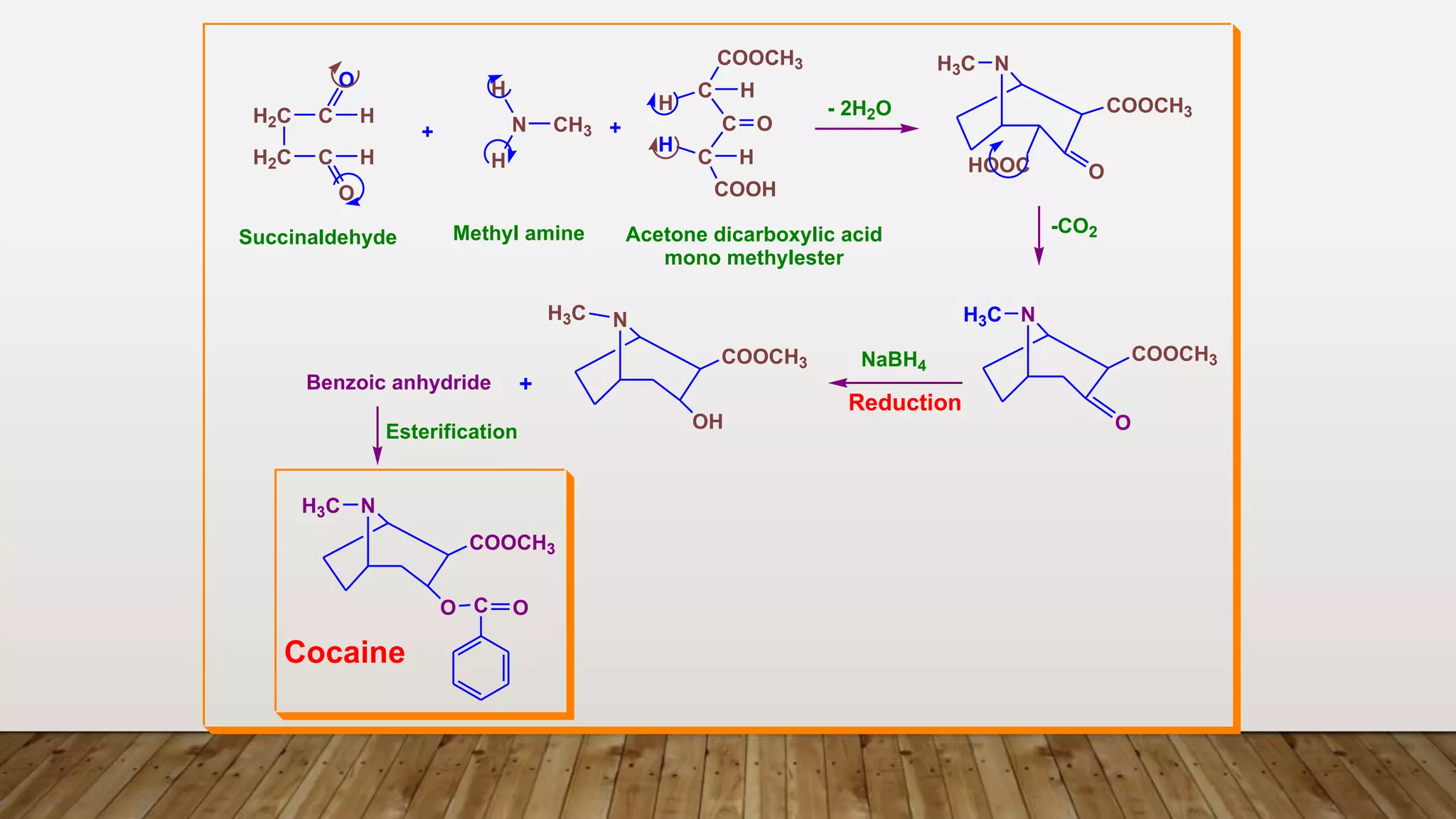
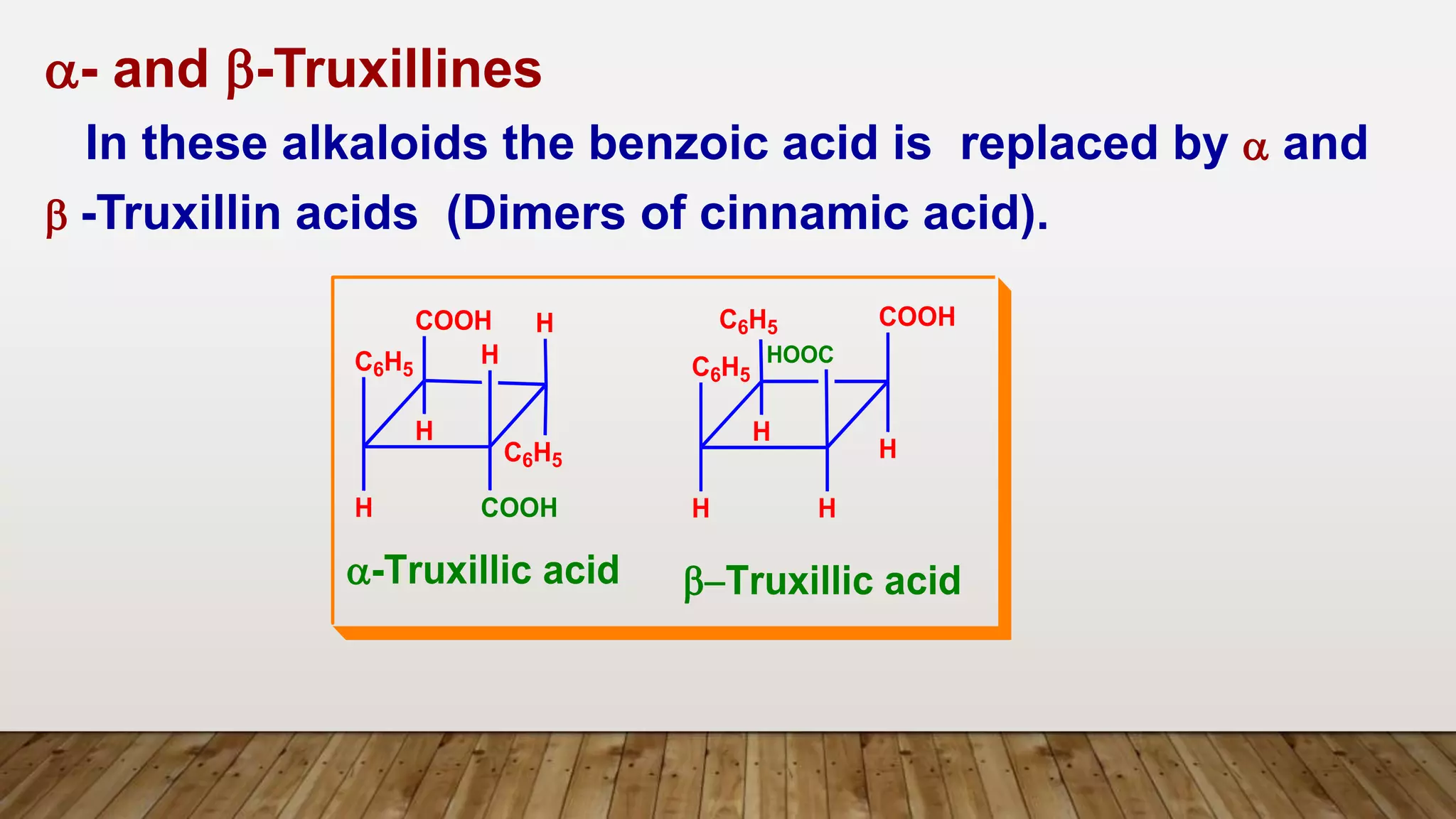
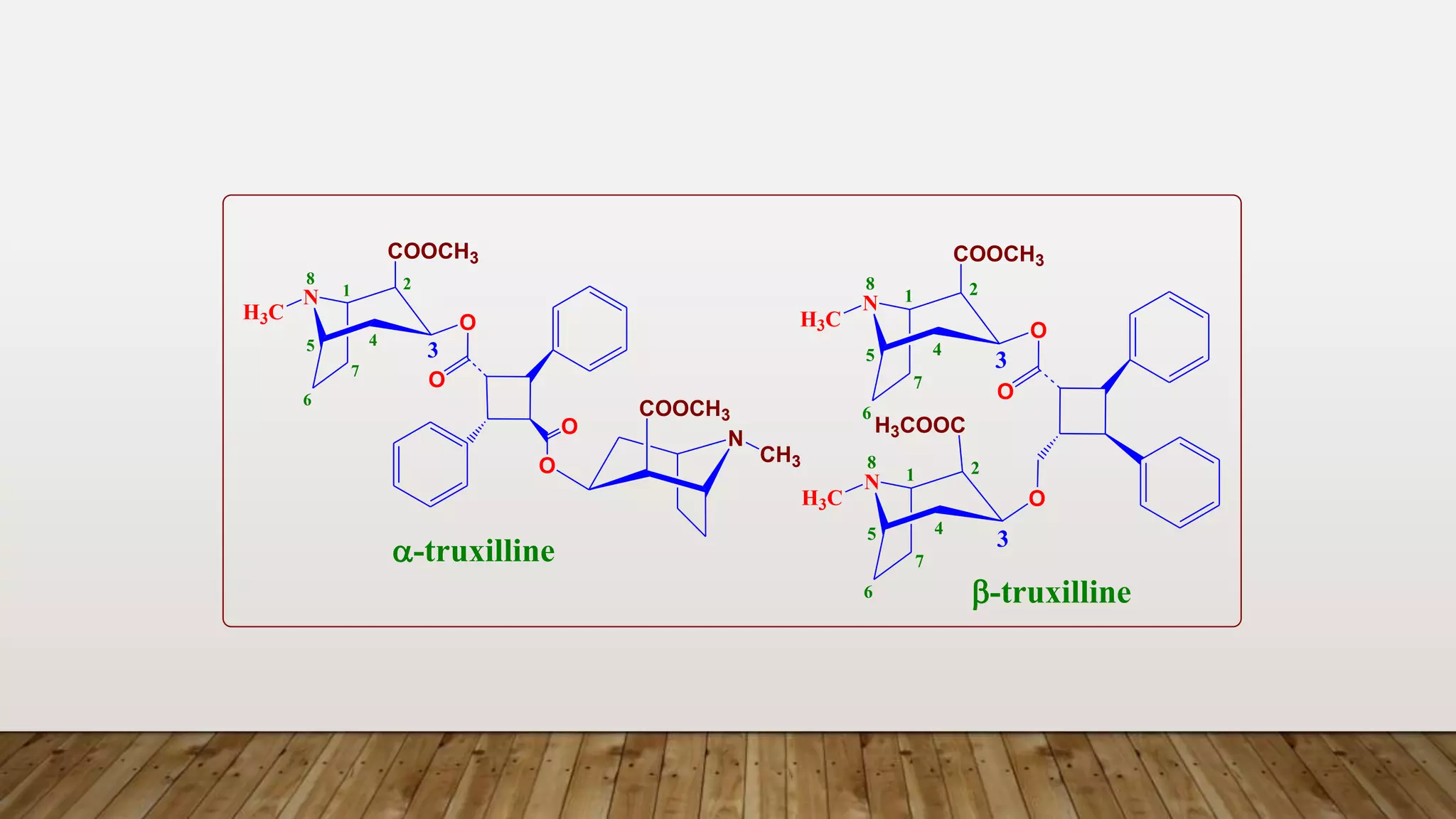
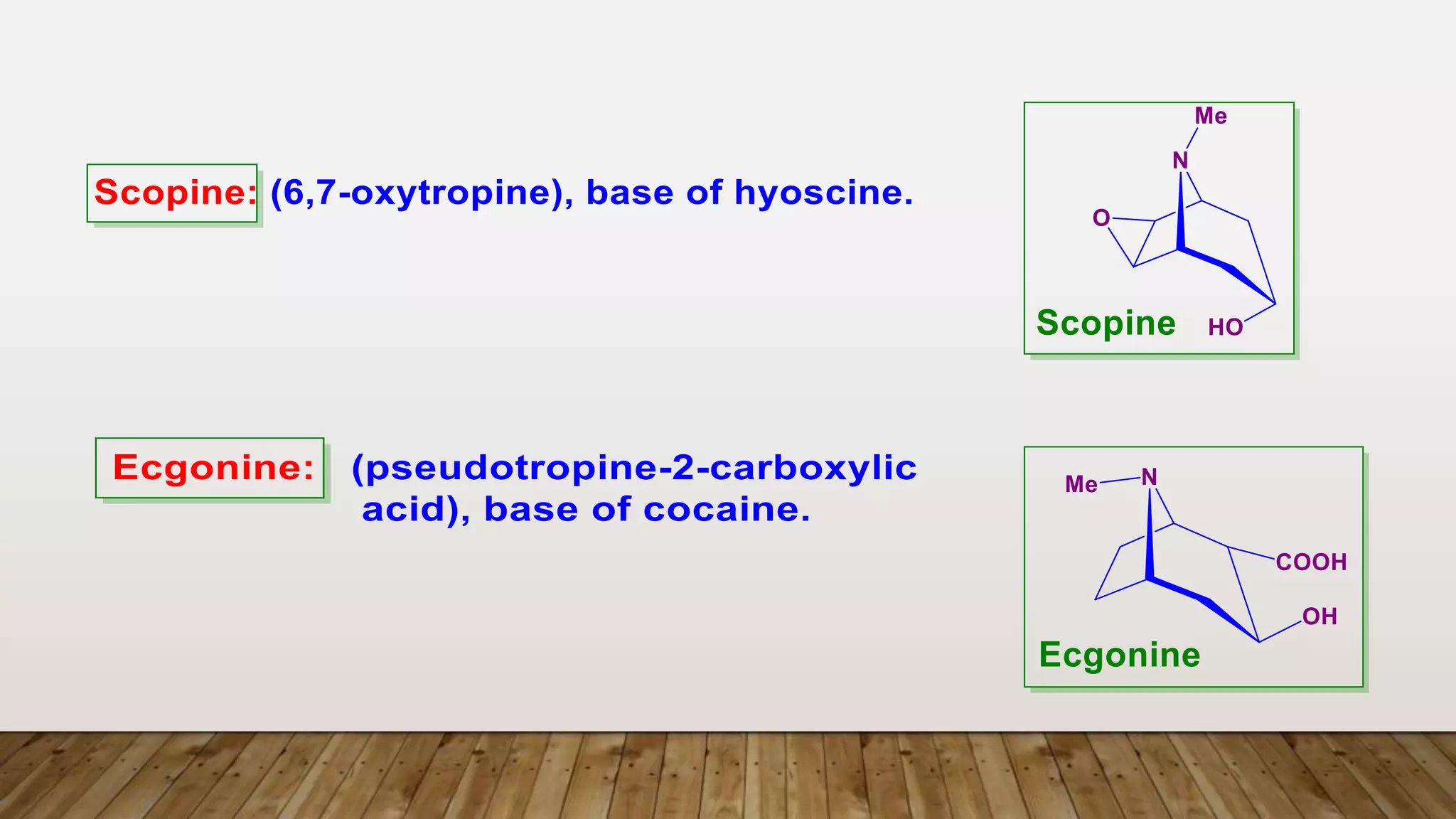
1) Ecgonine derivatives (2-carboxy-tropine). [base of Cocaine]
e.g. Cocaine, Cinnamyl Cocaine and a- and b-Truxillines.
2) Psudotropin derivatives e.g. Tropacocaine and Velerine.
3) Pyrrolidine derivatives e.g. Hygrine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jchskpost1ubjrsfqapi-5-tropane-akaloids-230329212835-f4fe7f85/75/5-Tropane_Akaloids_-pptx-32-2048.jpg)