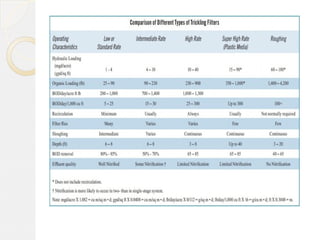
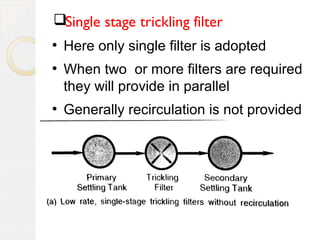
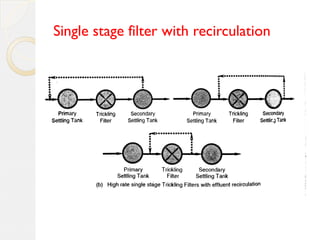
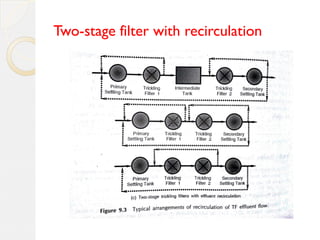
This document discusses different types of trickling filters classified by organic and hydraulic loadings or by the number of units used in series. Trickling filters are classified as low rate, high rate, intermediate rate, or roughing filters depending on loadings. They can also be single stage or double stage depending on the number of units used. Low rate trickling filters typically produce consistent effluent quality with varying influent. High rate trickling filters use recirculation to increase hydraulic loading and improve sloughing. Roughing filters are high rate filters that require low energy for treating high strength wastewater.