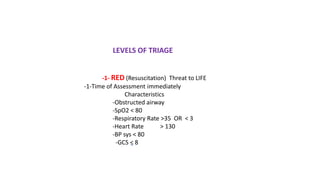
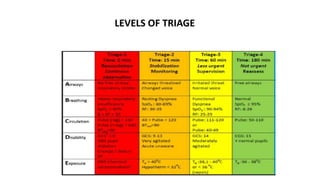
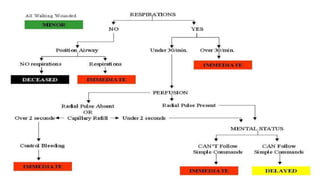
This document discusses triage, which is the process of sorting patients based on the urgency of their medical condition. It defines triage and outlines its objectives of identifying patients, prioritizing their needs, and directing them to the appropriate care provider. It describes different types of triage including simple, advanced, continuous integrated, and reverse triage. It also discusses under and over triage. The document outlines levels of triage from red to green based on the severity of the patient's condition. Finally, it discusses the role and characteristics of EMTs in effectively performing triage.