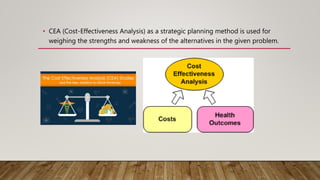
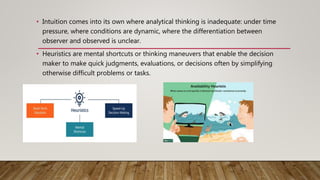
This document discusses the differences between strategic analysis and intuitive thinking. Strategic analysis is an analytical, rational process that involves researching a business and environment to formulate strategy. It uses tools like SWOT, PEST, CBA and CEA analyses. Intuitive thinking is a feeling or instinct that does not use facts or data. It is unconscious, rapid, and shared with animals. The document provides attributes of each approach and asks the reader to categorize words and phrases as exclusively describing intuitive thinking or strategic analysis.