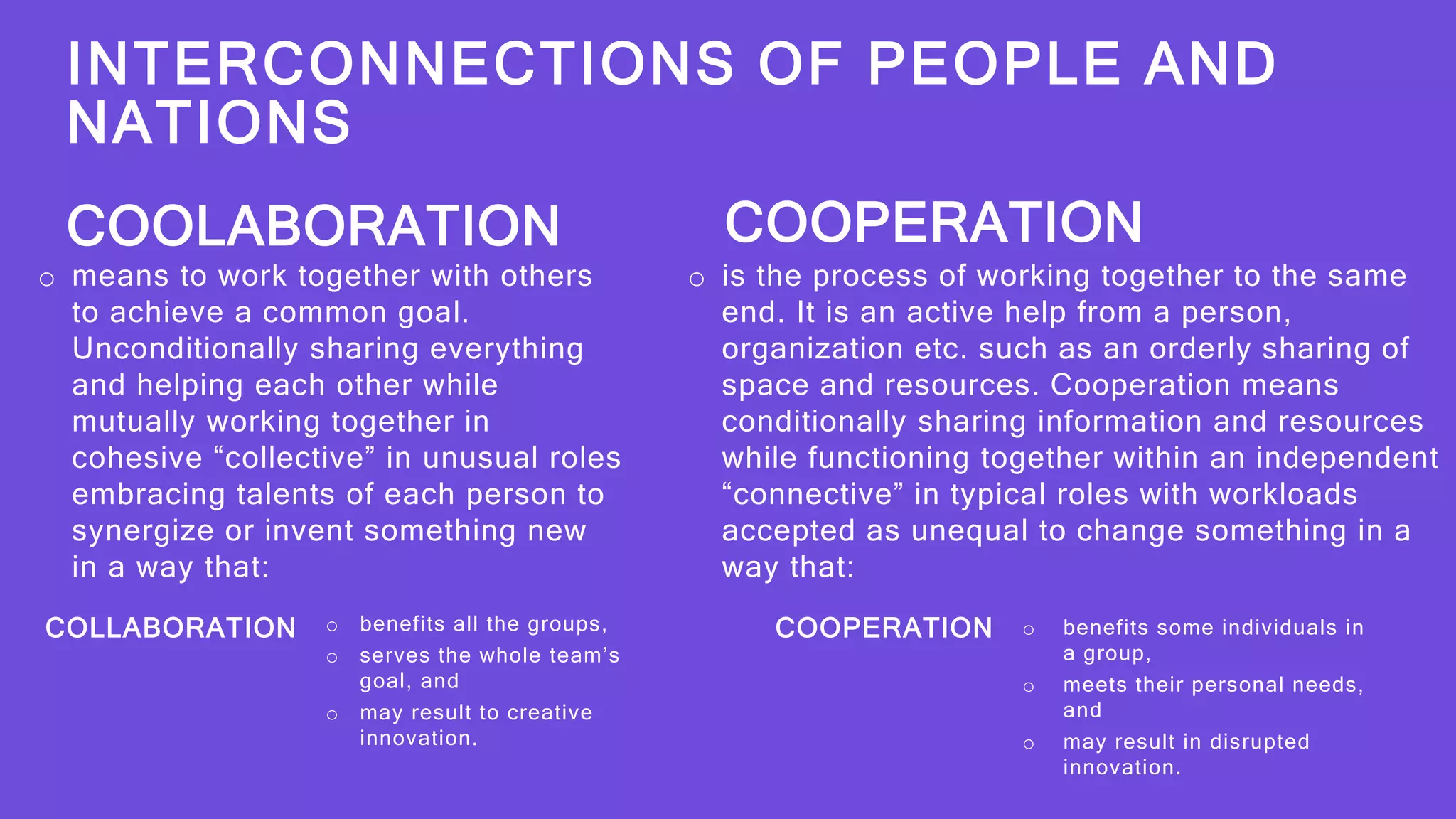
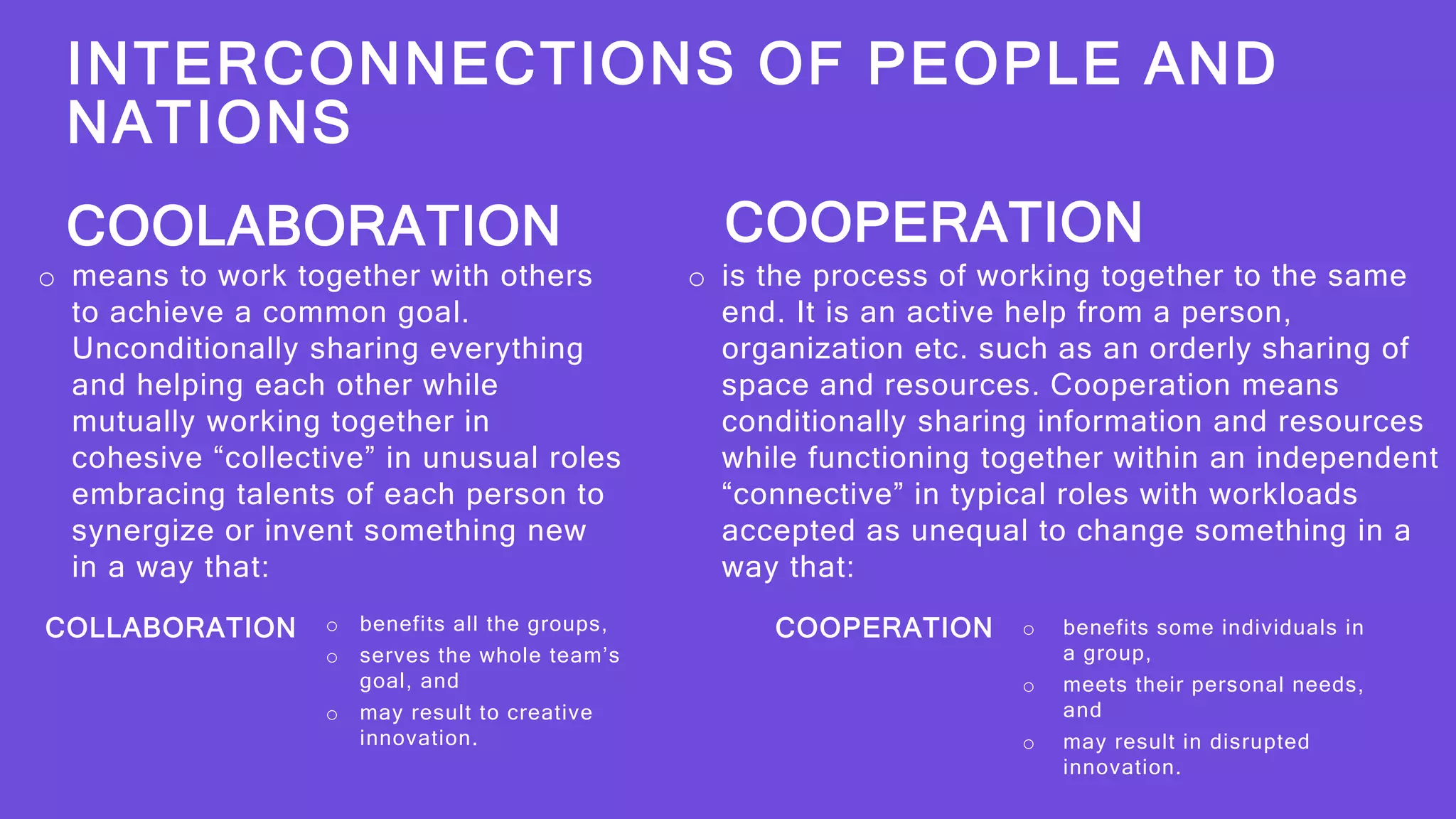
This document discusses various aspects of globalization including economic, social, political, financial, technological, and ecological globalization. It defines each type and provides examples. It also discusses the interconnectedness of people and nations through globalization and the need for collaboration and cooperation to achieve interconnectedness. Key terms discussed include labor, social globalization, financial integration, World Trade Organization, financial globalization, people, nation, cooperation, political globalization, ecological globalization, and technological globalization.