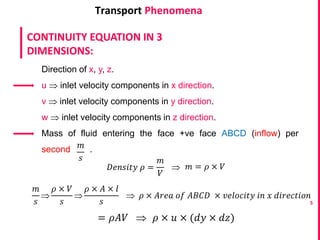
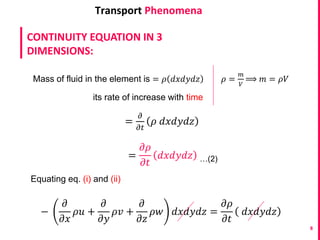
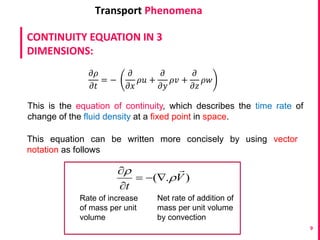
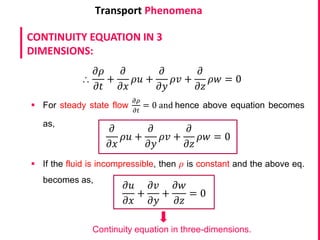
This document discusses the continuity equation in three dimensions. It begins by stating that the continuity equation is based on the principle of conservation of mass. It then presents the mathematical form of the continuity equation in three dimensions, showing how it accounts for the rate of increase of mass in an infinitesimal fluid element equaling the net rate of mass flow into and out of the element. The document provides explanations and derivations of the terms in the three-dimensional continuity equation. It concludes by noting some simplified forms of the equation under certain conditions like steady state or incompressible flow.