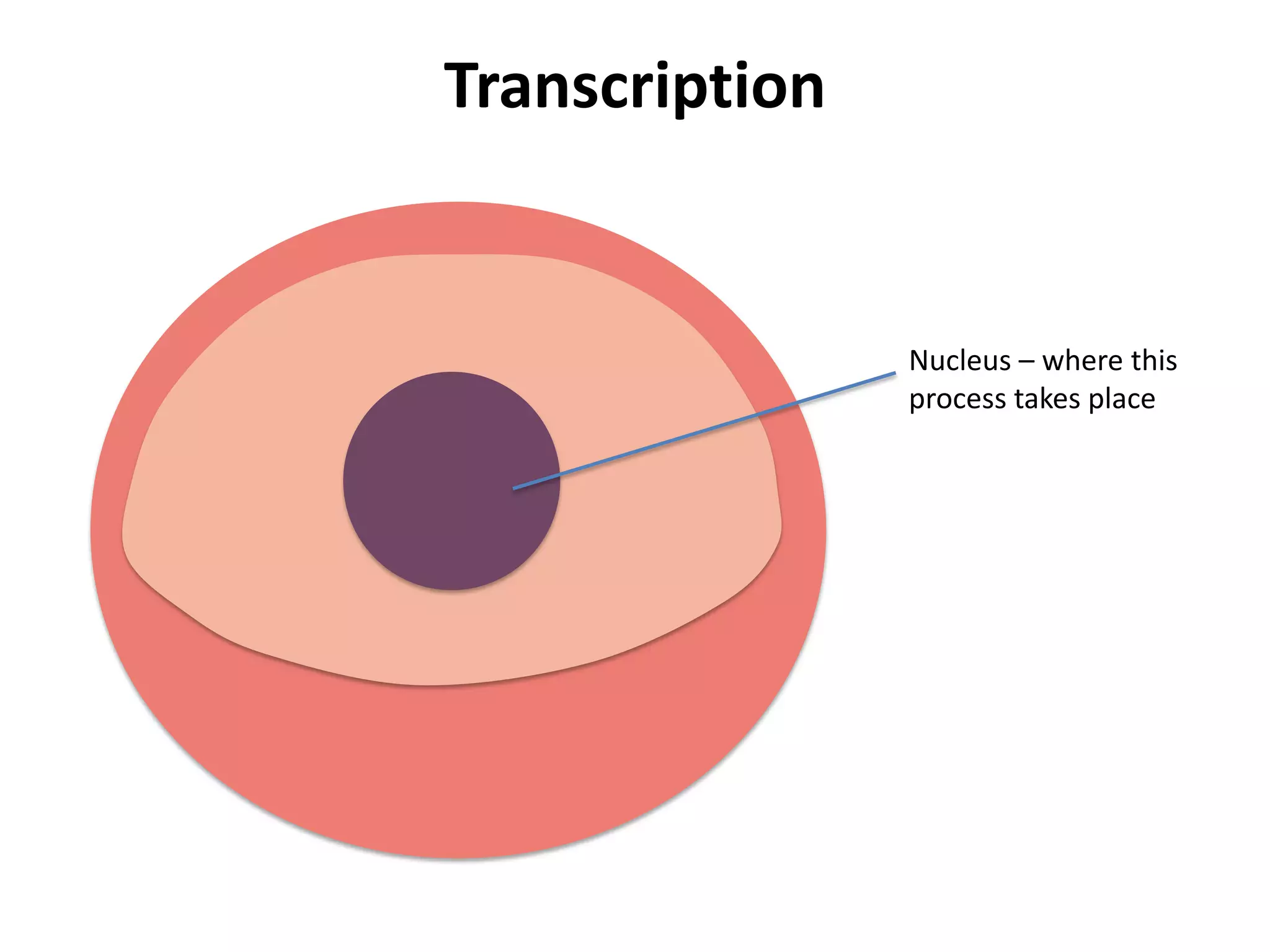
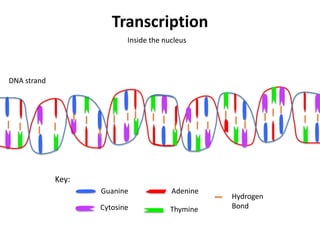
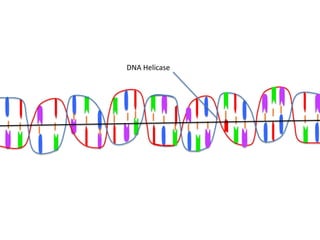
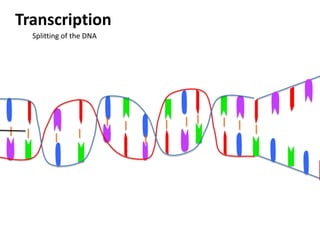
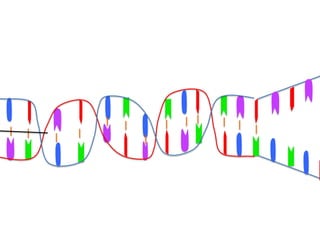
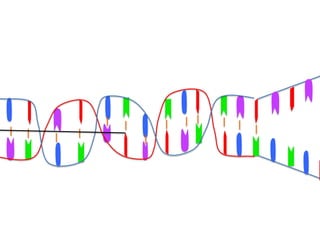
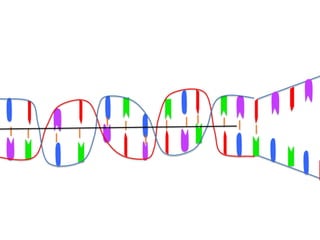
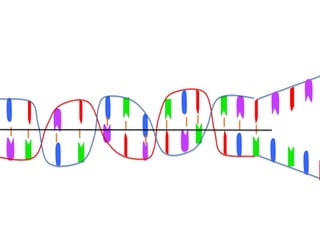
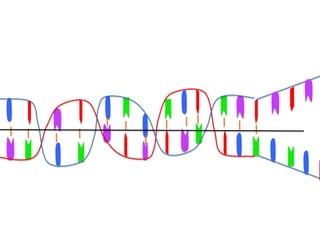
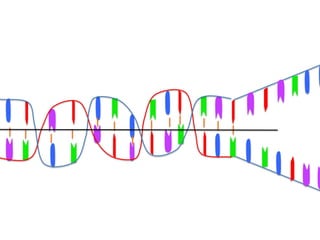
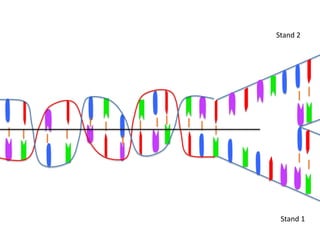
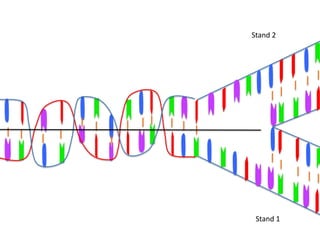
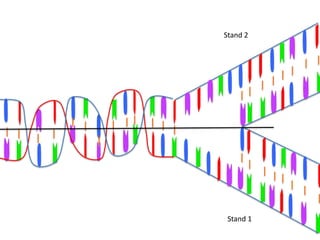
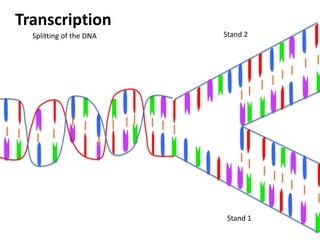
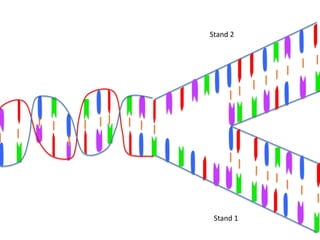
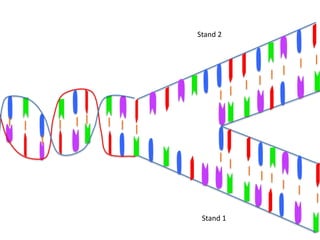
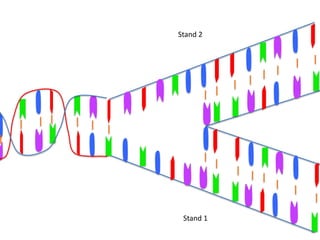
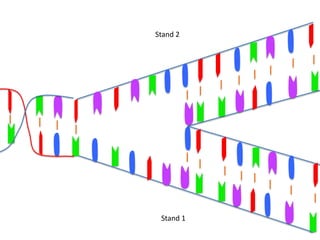
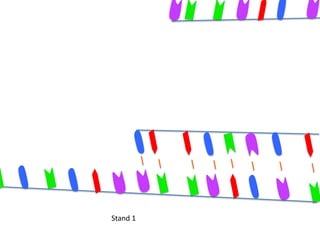
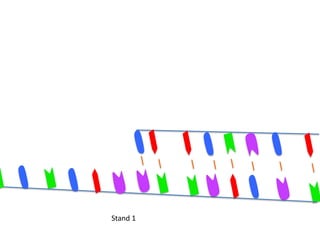
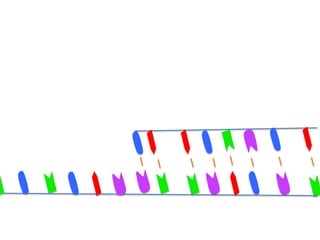
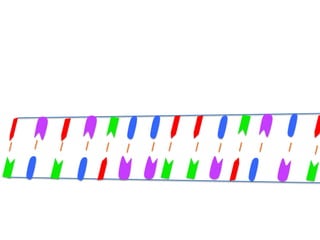
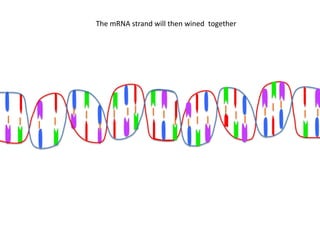
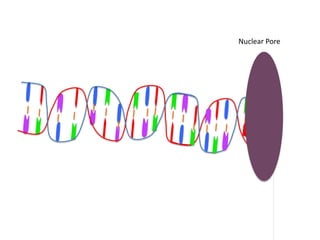
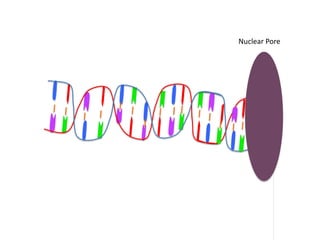
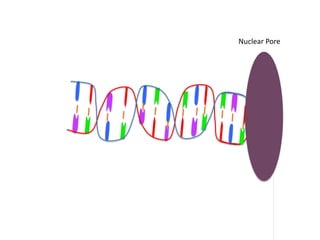
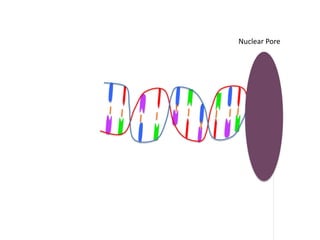
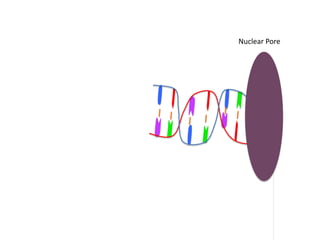
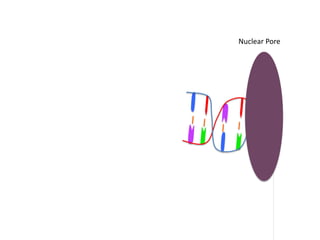
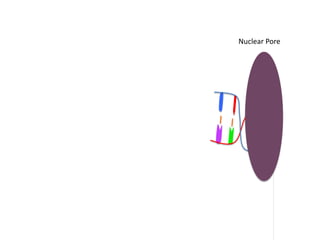
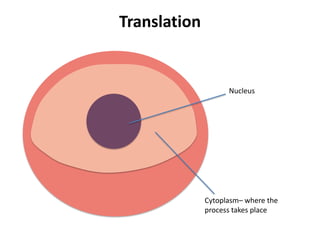
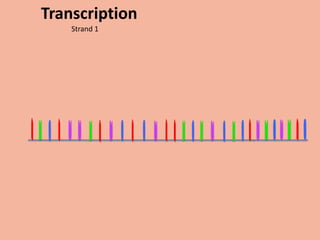
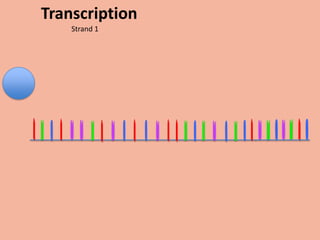
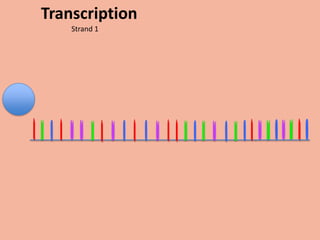
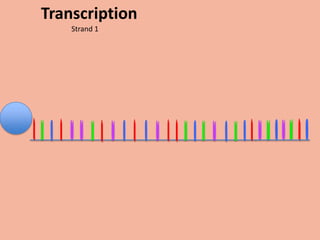
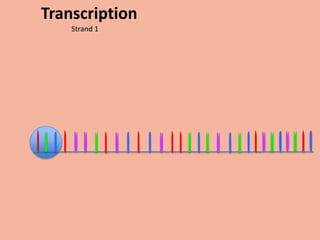
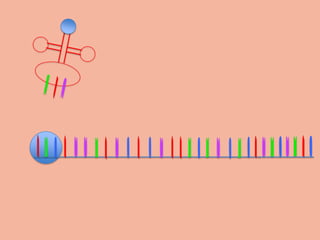
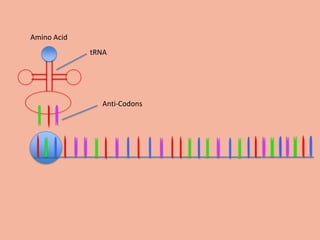
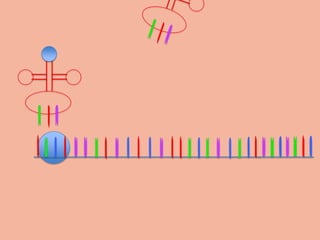
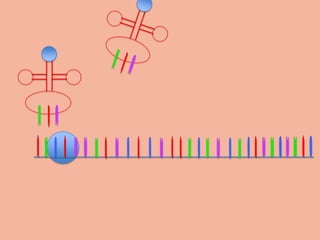
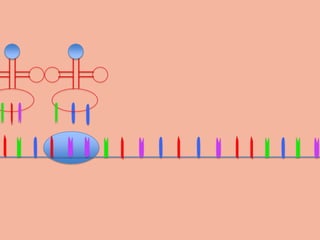
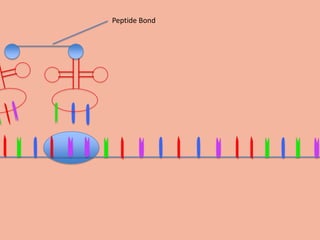
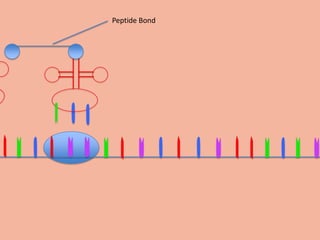
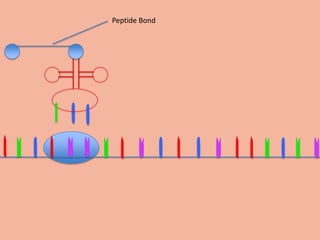
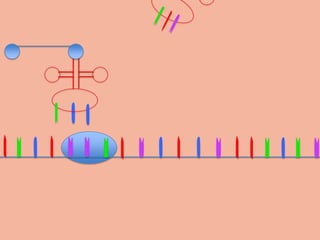
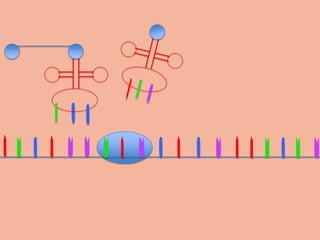
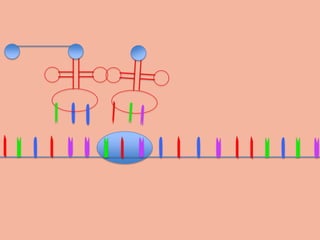
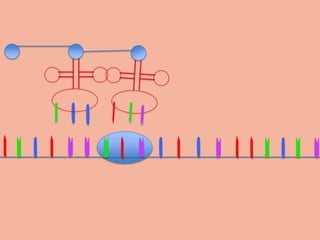
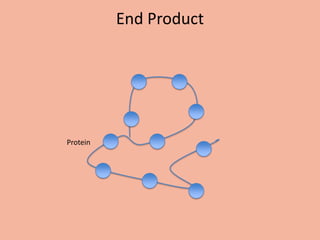
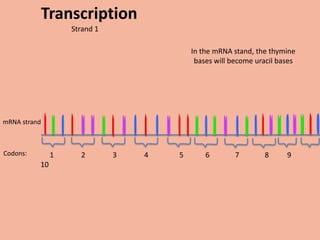
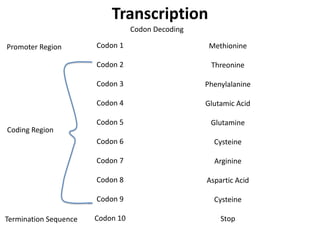
Transcription takes place in the nucleus and involves splitting DNA into two strands. One strand is used as a template to create a complementary mRNA strand. The mRNA strand exits the nucleus through nuclear pores. Translation takes place in the cytoplasm where ribosomes use the mRNA to assemble amino acids brought by tRNAs into a protein chain based on the mRNA codons. tRNAs match their anticodons to mRNA codons and add amino acids to form the protein.