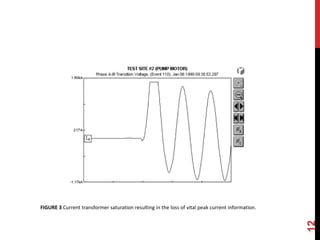
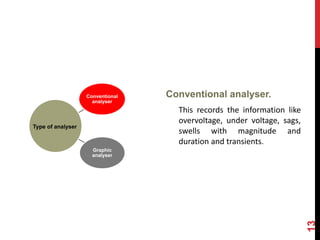
The document provides an overview of transient disturbances in electrical systems, indicating they are brief changes in voltage and current caused by factors like switching operations and faults. It discusses transient disturbance analyzers, which are advanced devices used to capture and analyze these short-duration events, emphasizing their importance in assessing potential damage to equipment. Additionally, the document distinguishes between conventional and graphic analyzers for recording and presenting various forms of electrical disturbances.