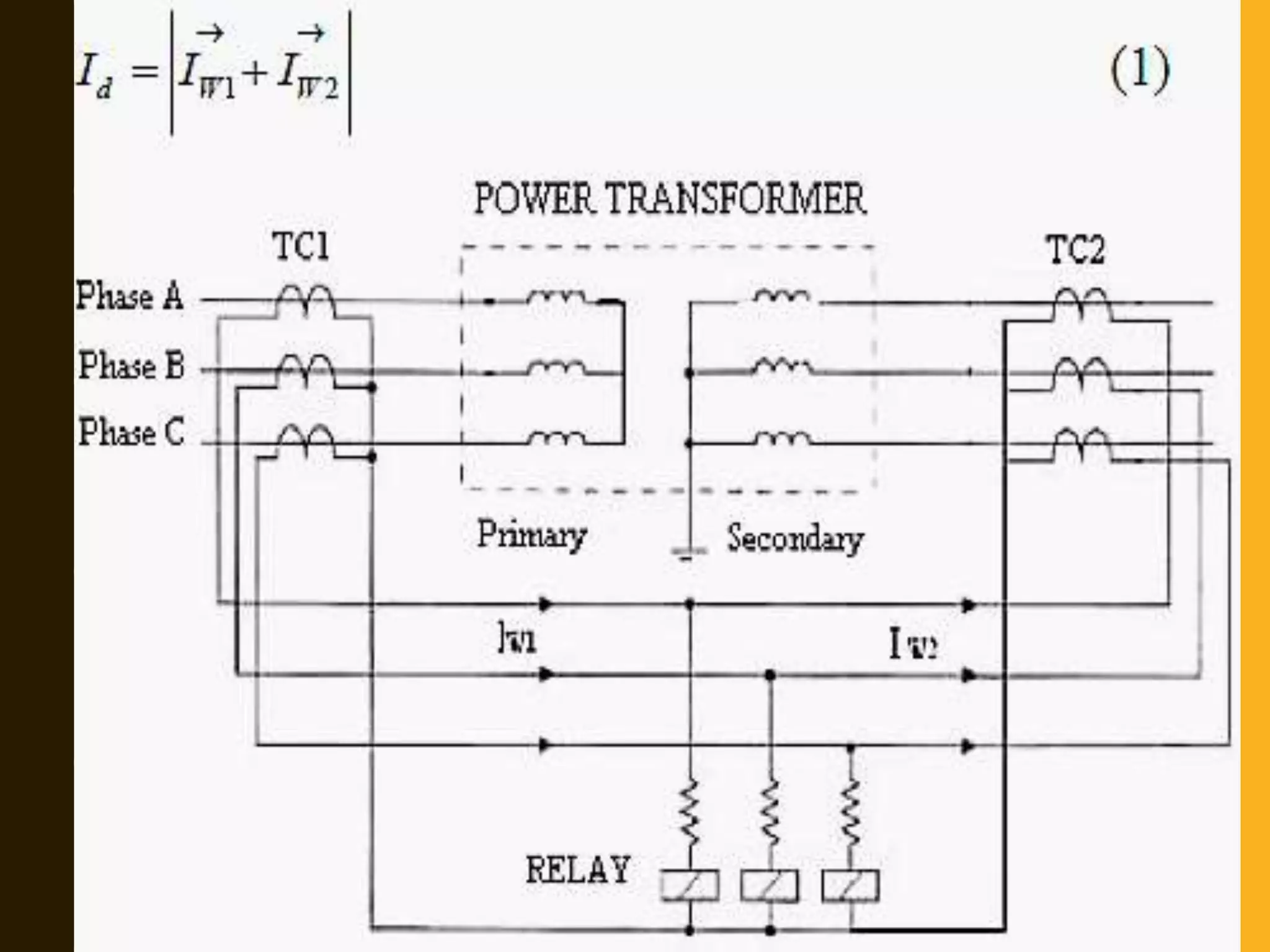
This document discusses transformer protection methods. It describes various types of faults that can occur in transformers, including internal short circuit faults and incipient faults, as well as external faults. The document then outlines several protection methods for transformers, including percentage differential protection, Buchholz relays, protection against magnetizing inrush current, overheating protection, and overfluxing protection. Videos are provided that explain how Buchholz relays and transformer inrush current work.