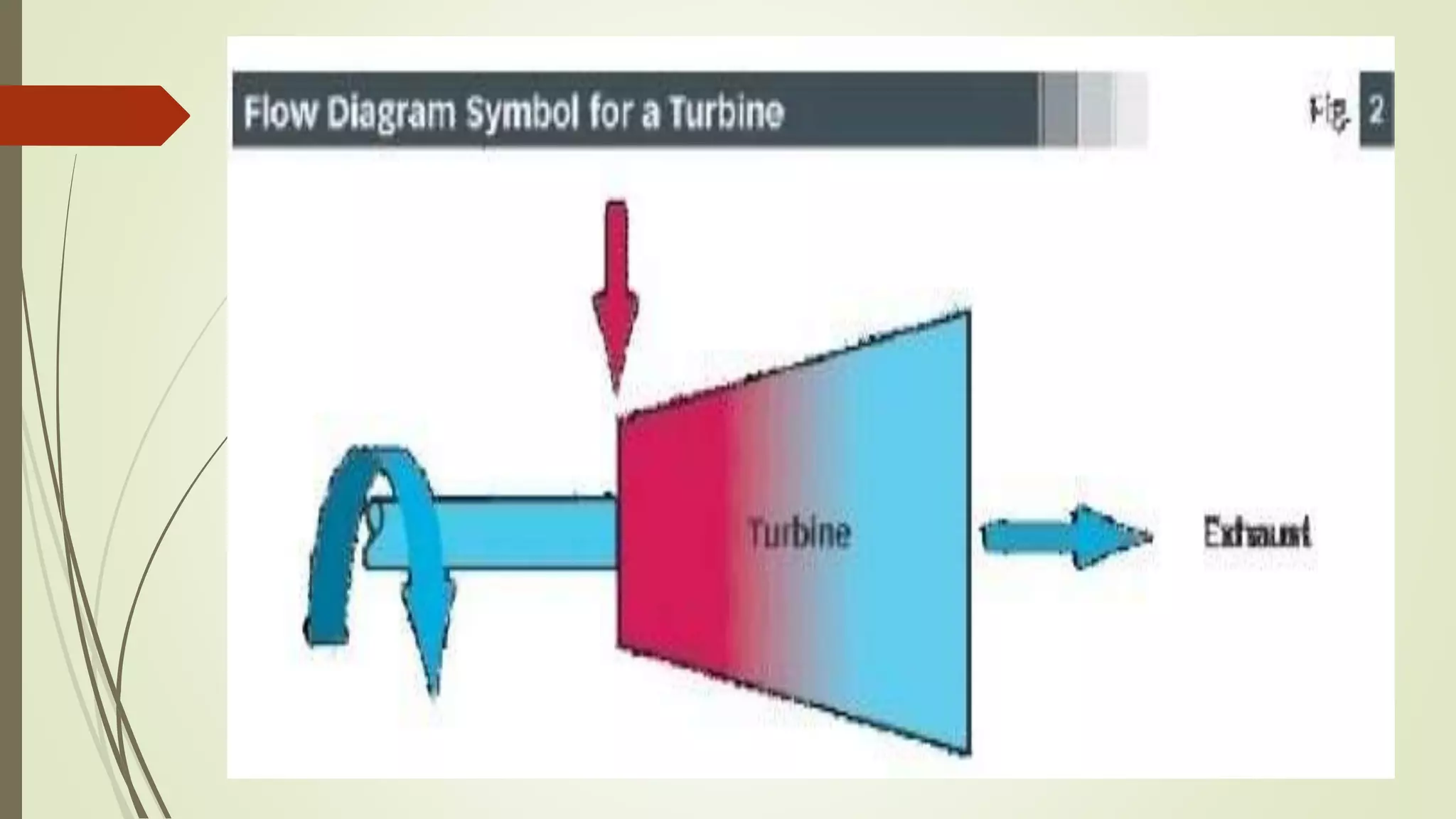
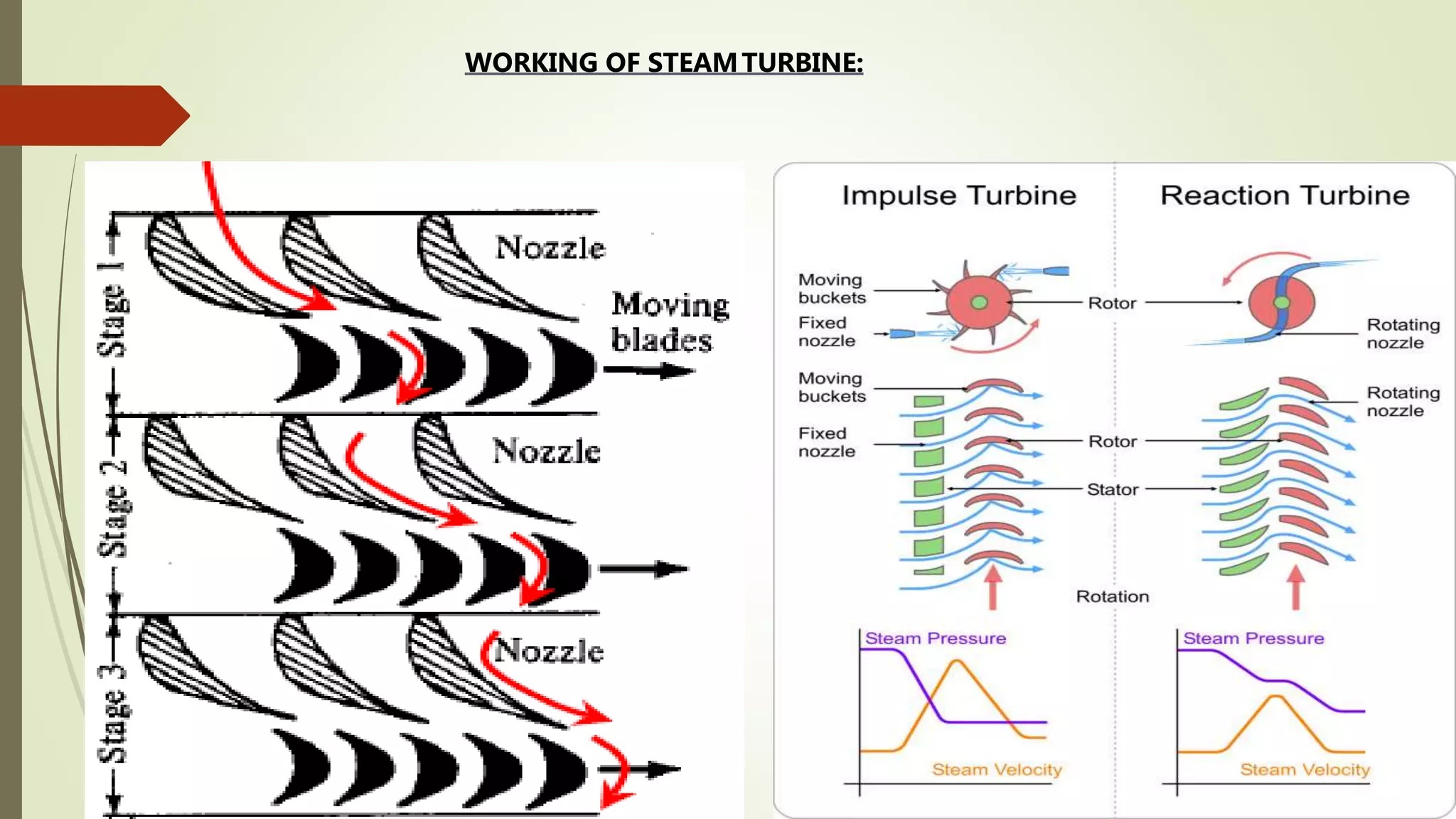
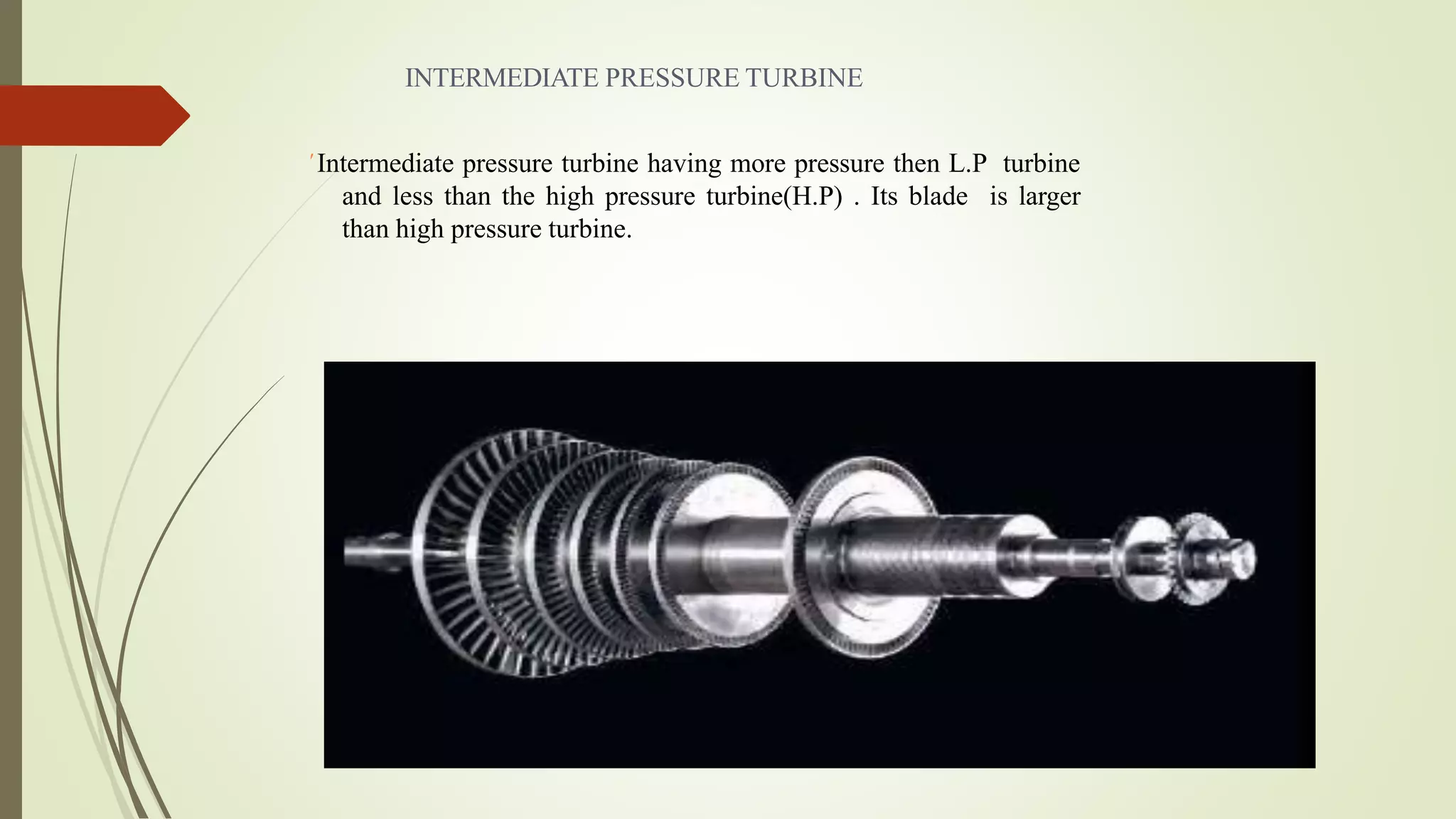
The document summarizes the vocational training report of Shakti Kumar Singh at BHEL Haridwar. It describes the various blocks at BHEL Haridwar involved in manufacturing power equipment. Block 3 focuses on heavy machinery, turbine assembly, blades and steam turbines. It explains the working of impulse and reaction steam turbines. Different types of turbine blades for high, intermediate and low pressure turbines are discussed along with their sizes. The conclusion states that BHEL is a major contributor to industries in India and the summer training gave insights into steam turbine manufacturing processes.