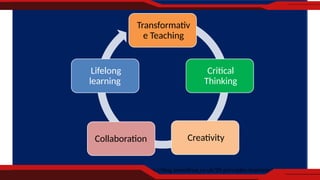
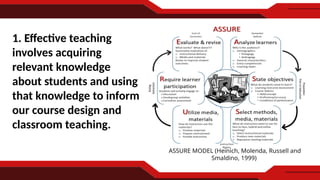
The document discusses transformative teaching, emphasizing the integration of research-based knowledge and principles to enhance learning outcomes for students. It presents the Philippine Professional Standards for Teachers (PPST) as a framework for effective teaching and outlines various domains essential for teacher competency. The author advocates for student-centered, collaborative, and experiential learning methods that promote critical thinking and real-world applications in education.