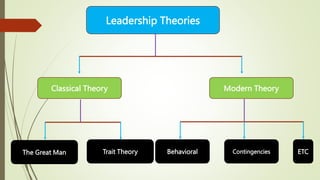
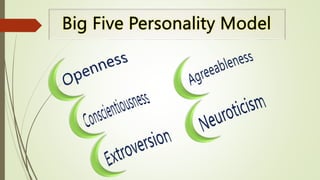
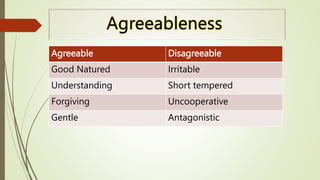
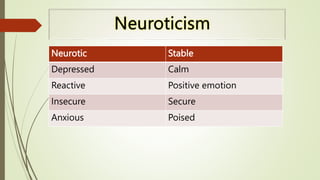
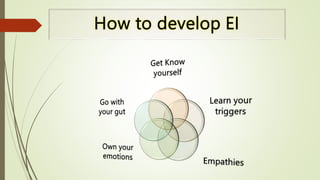
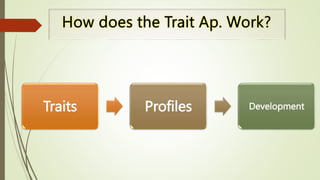
The document outlines the trait theory of leadership, which proposes that effective leaders possess certain innate personality traits and characteristics. It discusses early theories like the Great Man Theory that leaders are born with traits that make them leaders. Later trait theories attempted to identify common traits of leaders, such as intelligence, self-confidence, and sociability. The document also discusses how the Big Five personality model and emotional intelligence relate to leadership traits. It notes strengths of the trait theory in identifying benchmarks for leadership, but also criticisms around situational effects and difficulty measuring traits.