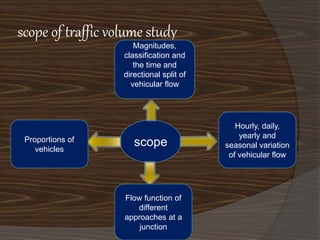
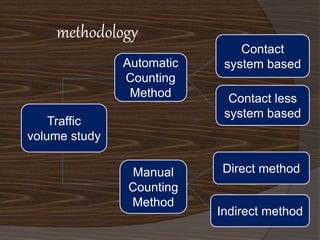
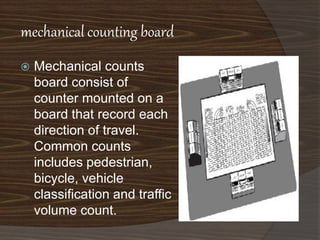
This document discusses a presentation on a traffic volume study. It outlines the objectives, scope, methodology, data collection, and purposes of conducting a traffic volume study. The study aims to count vehicle volumes, types, and flows over time to help with transportation planning, design, and management. Methodologies include manual counting methods using hand counters or video review as well as automatic methods using sensors to detect vehicle presence and classify types.