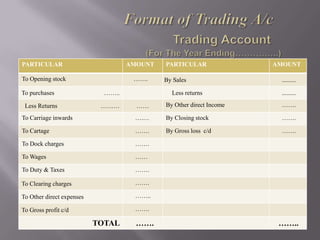
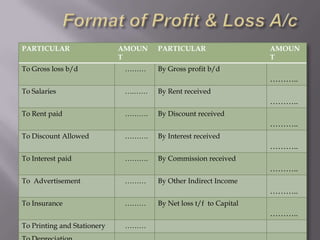
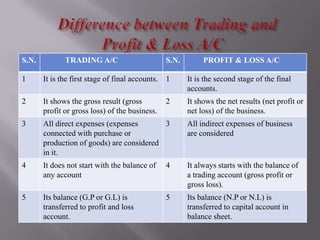
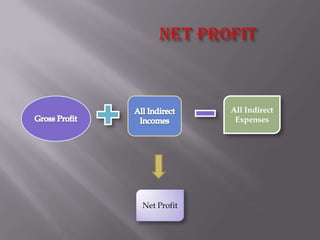
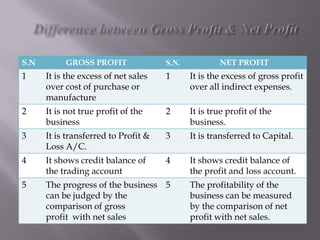
The document discusses trading accounts and profit and loss accounts. It defines trading accounts as the first stage of the income statement used to calculate gross profit or loss. Direct expenses and incomes are recorded. Profit and loss accounts are the second stage where indirect expenses are deducted from gross profit to determine net profit or loss, which is then transferred to the balance sheet. The key difference between gross and net profit is also explained, with gross profit only accounting for direct costs and net profit reflecting all expenses.