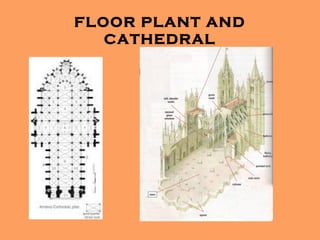
Gothic art developed in Western Europe from the 12th to 16th centuries, coinciding with changes in medieval society. The most characteristic Gothic architecture featured cathedrals with pointed arches, vaulted ceilings, flying buttresses, and large windows to let in light. Gothic sculpture became more naturalistic and expressive, often depicting religious themes. Painting evolved from illuminated manuscripts to panels and frescoes with livelier colors and perspective. Overall, Gothic art marked a shift from the heavy Romanesque style through lighter, brighter designs that spread across Europe.