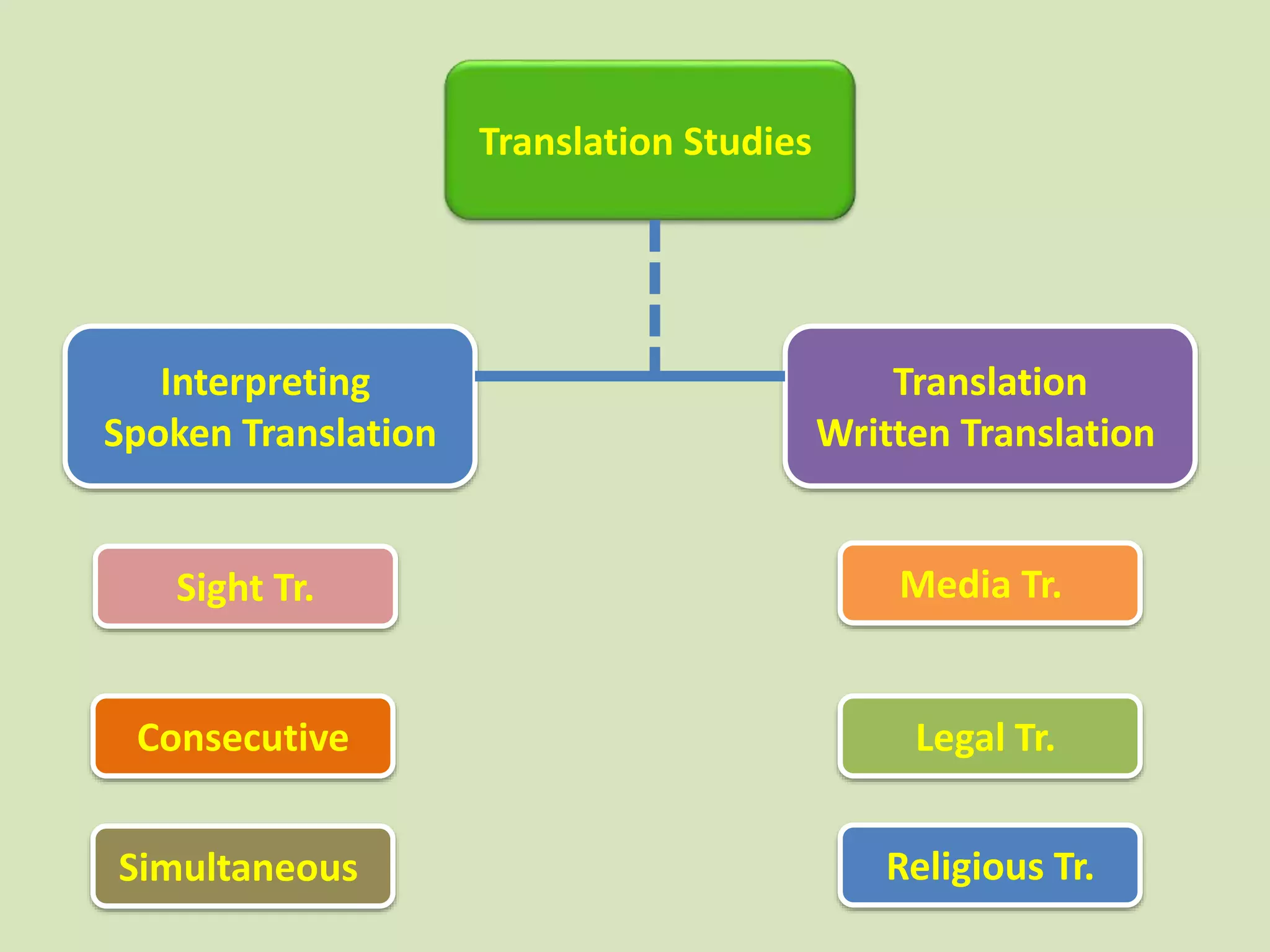
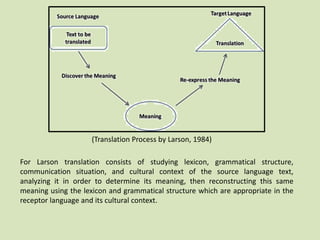
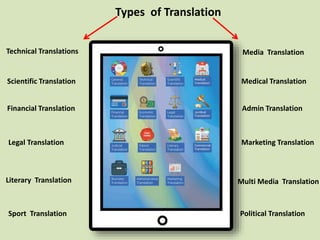
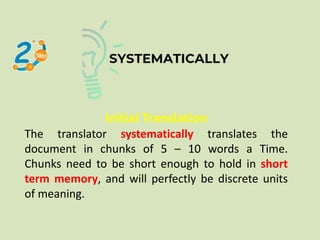
This document discusses different definitions and perspectives of translation. It defines translation as substituting text from one language to an equivalent text in another language. Translation is also defined as replacing a written message from one language to another while maintaining the same meaning. Additionally, translation involves studying elements of the source language text like lexicon, grammar, culture to determine meaning, then reconstructing that meaning using appropriate elements of the target language and its culture. The document also outlines various types of translations like technical, scientific, literary, and media translations. It provides an overview of the translation process including initial analysis of the text, translating in short chunks, accuracy checking, taking a break, and final polishing. Essential translator skills are also listed.