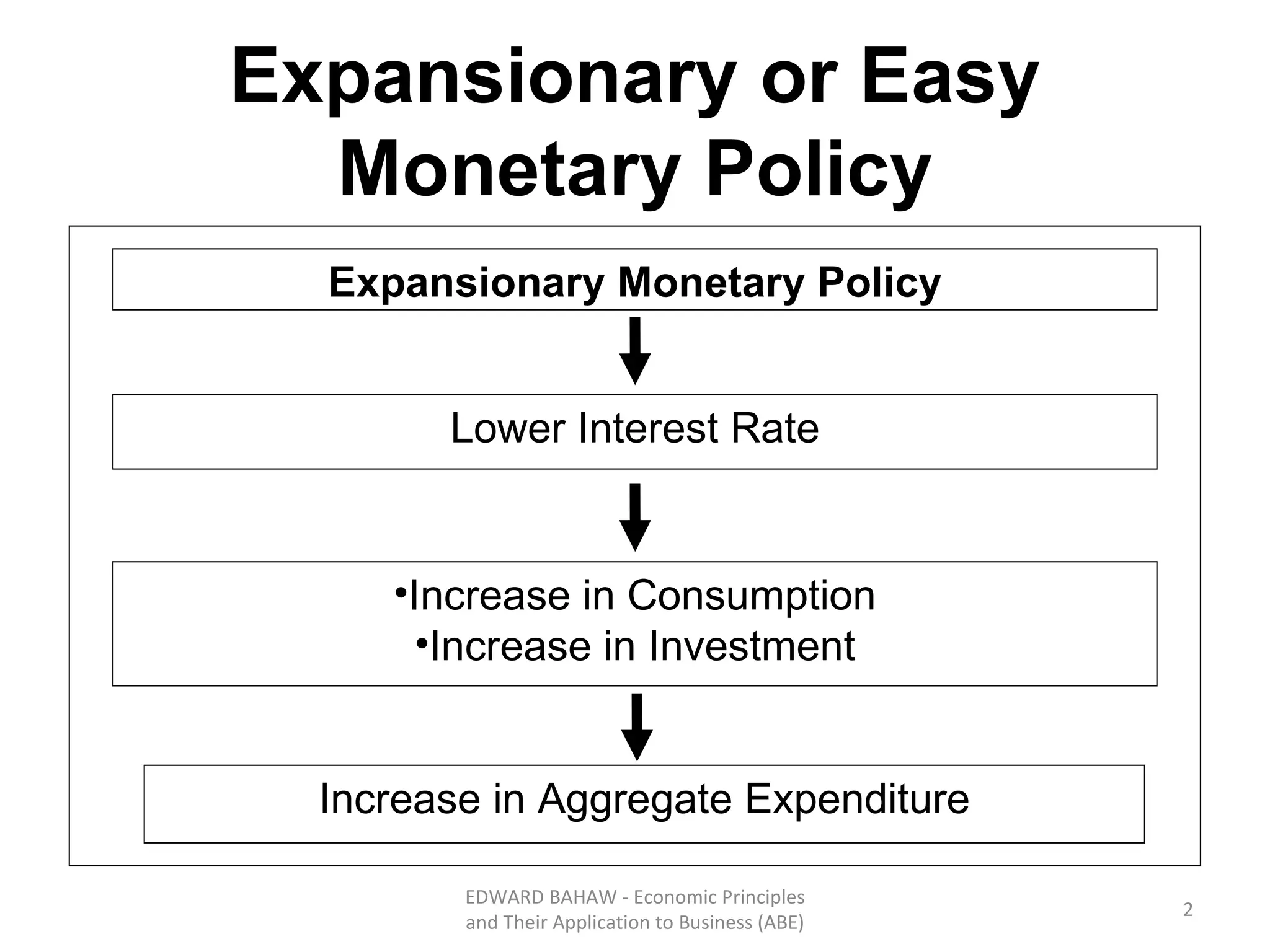
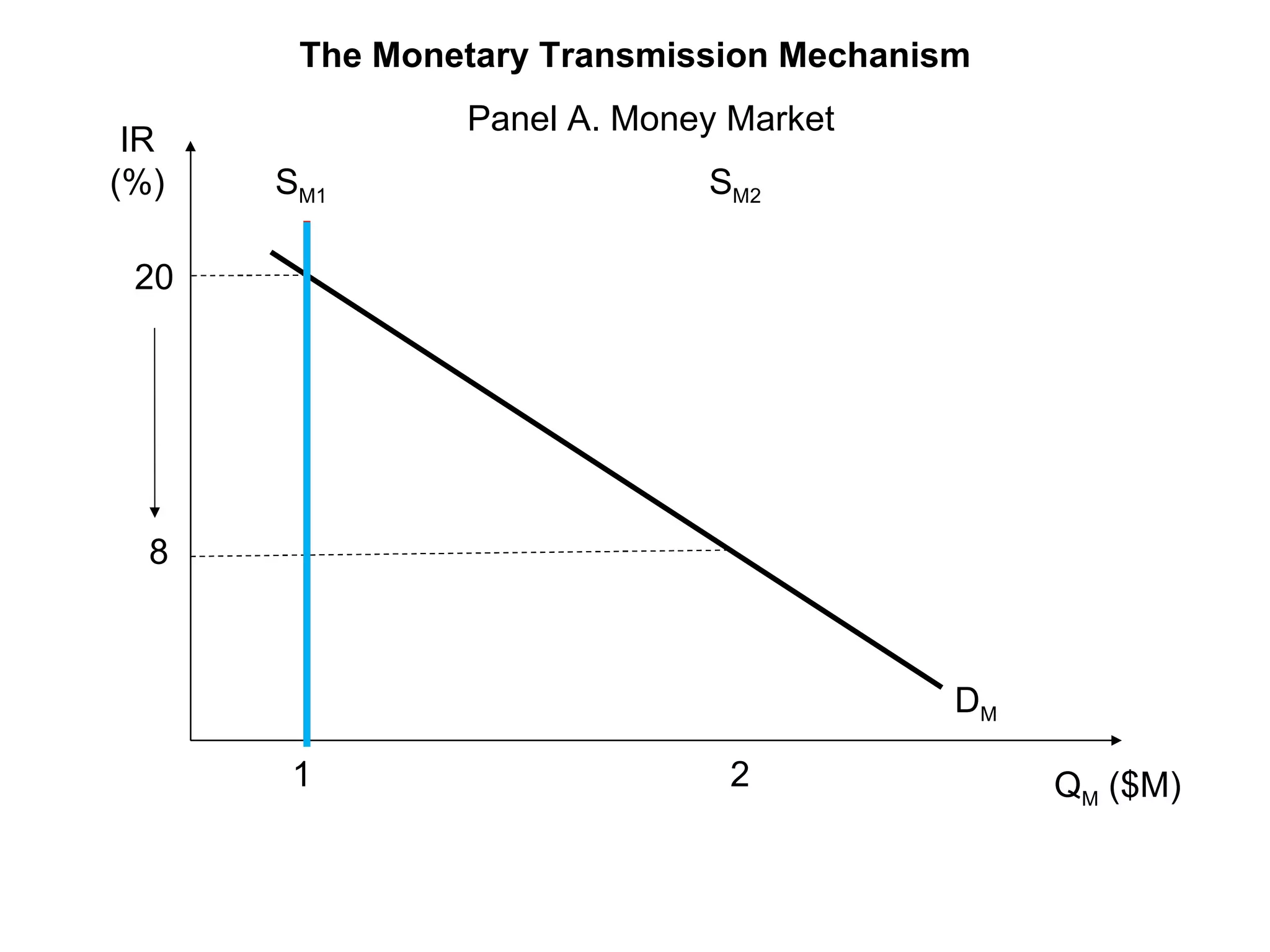
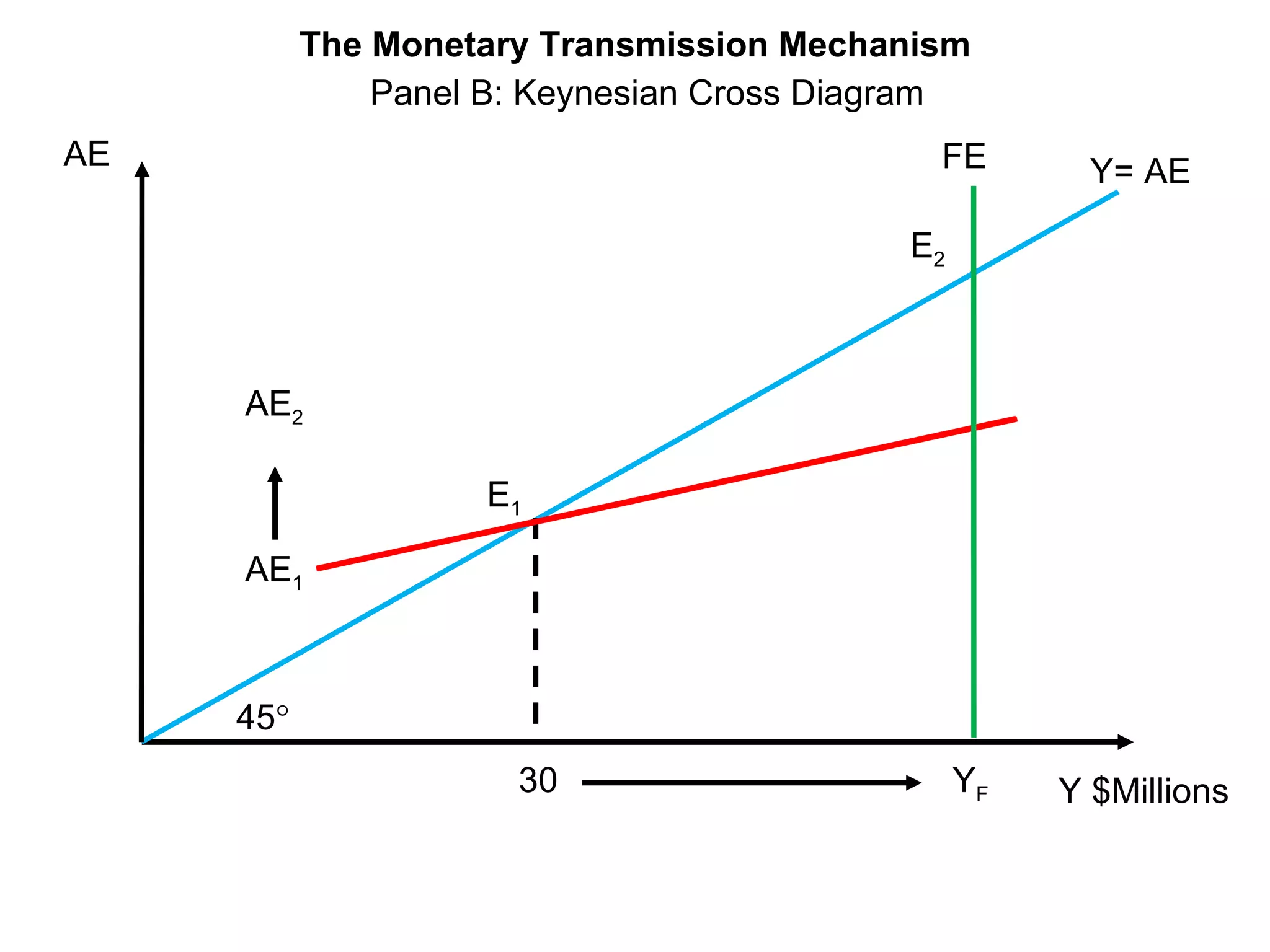
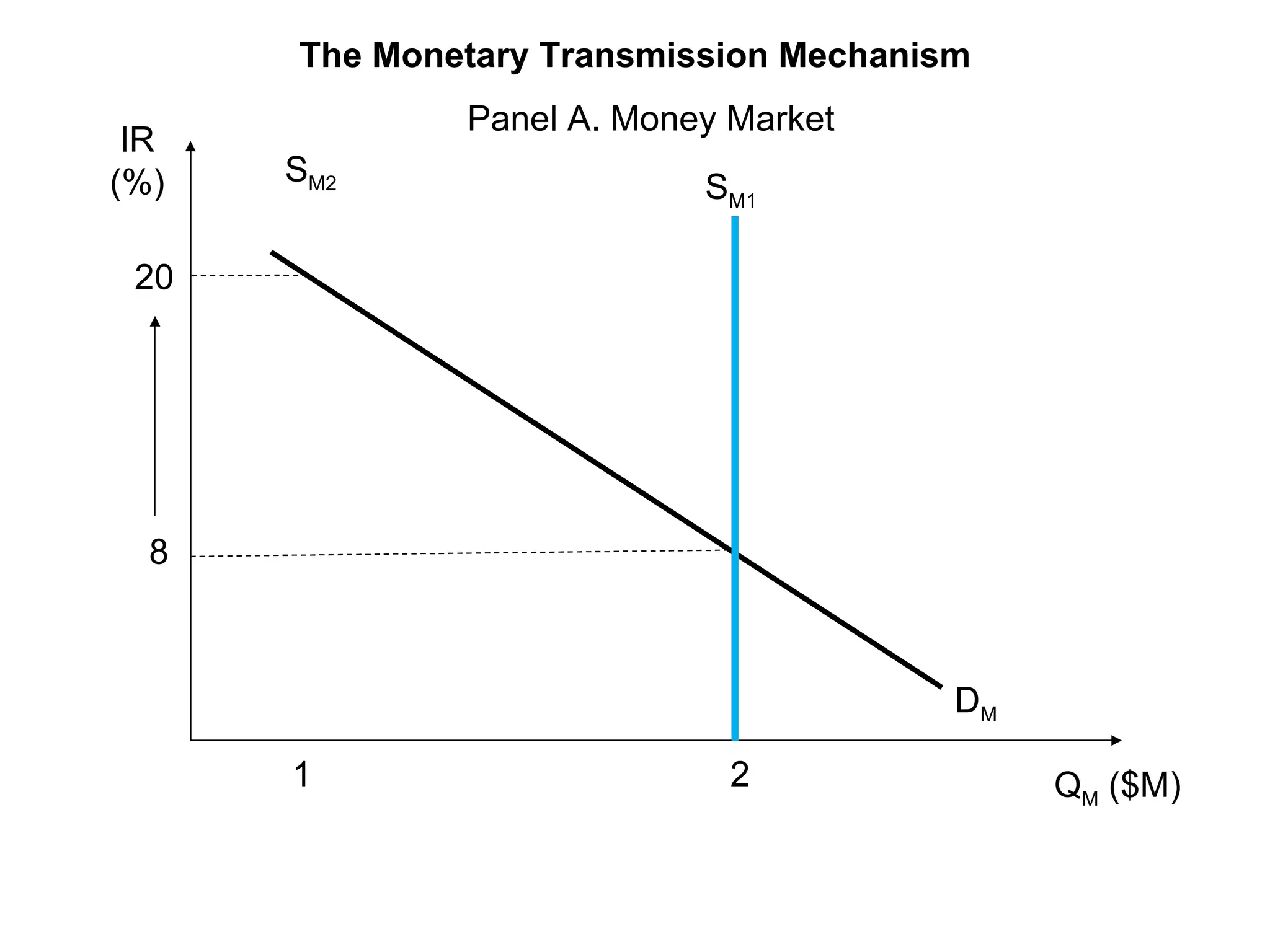
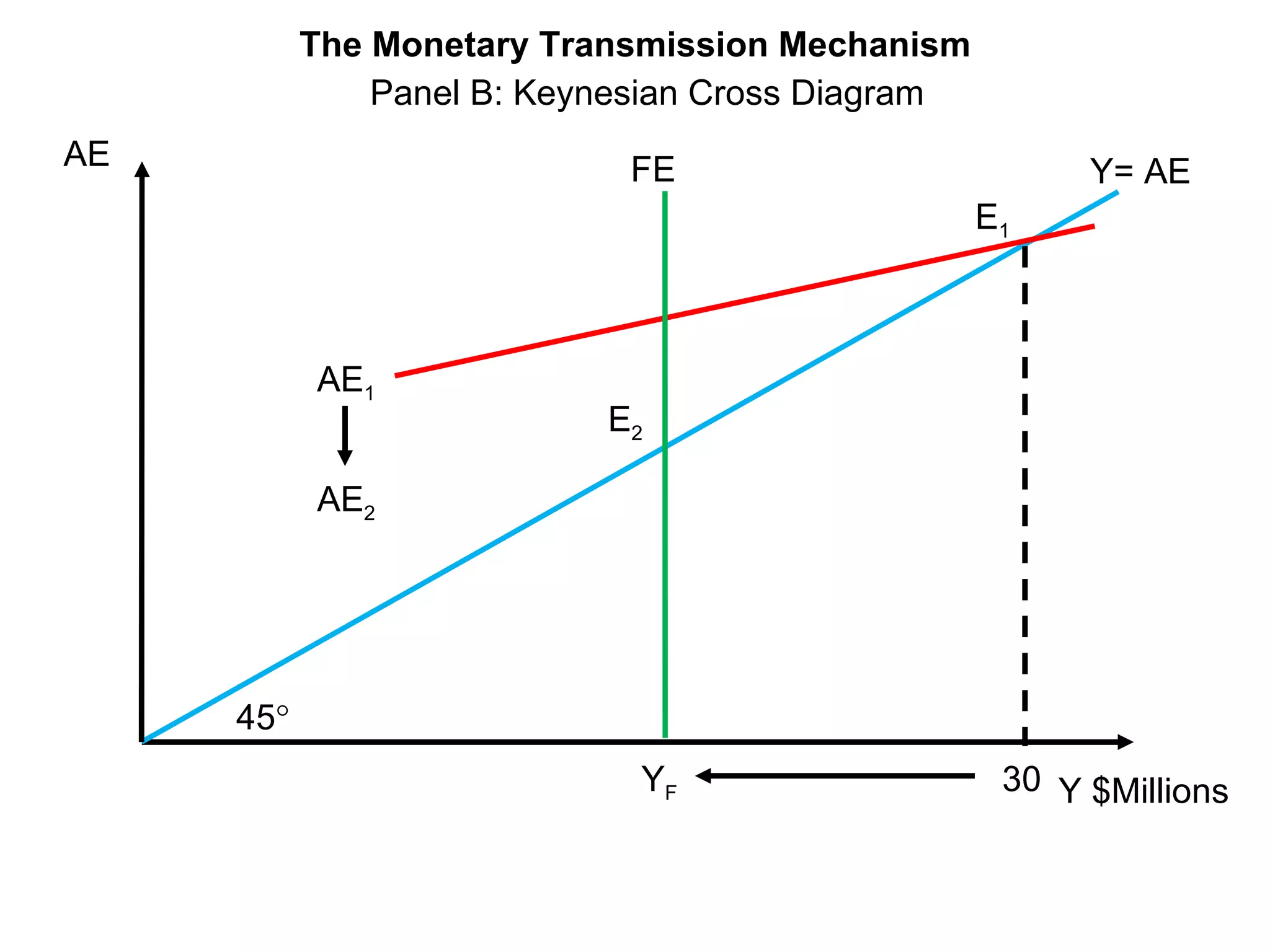
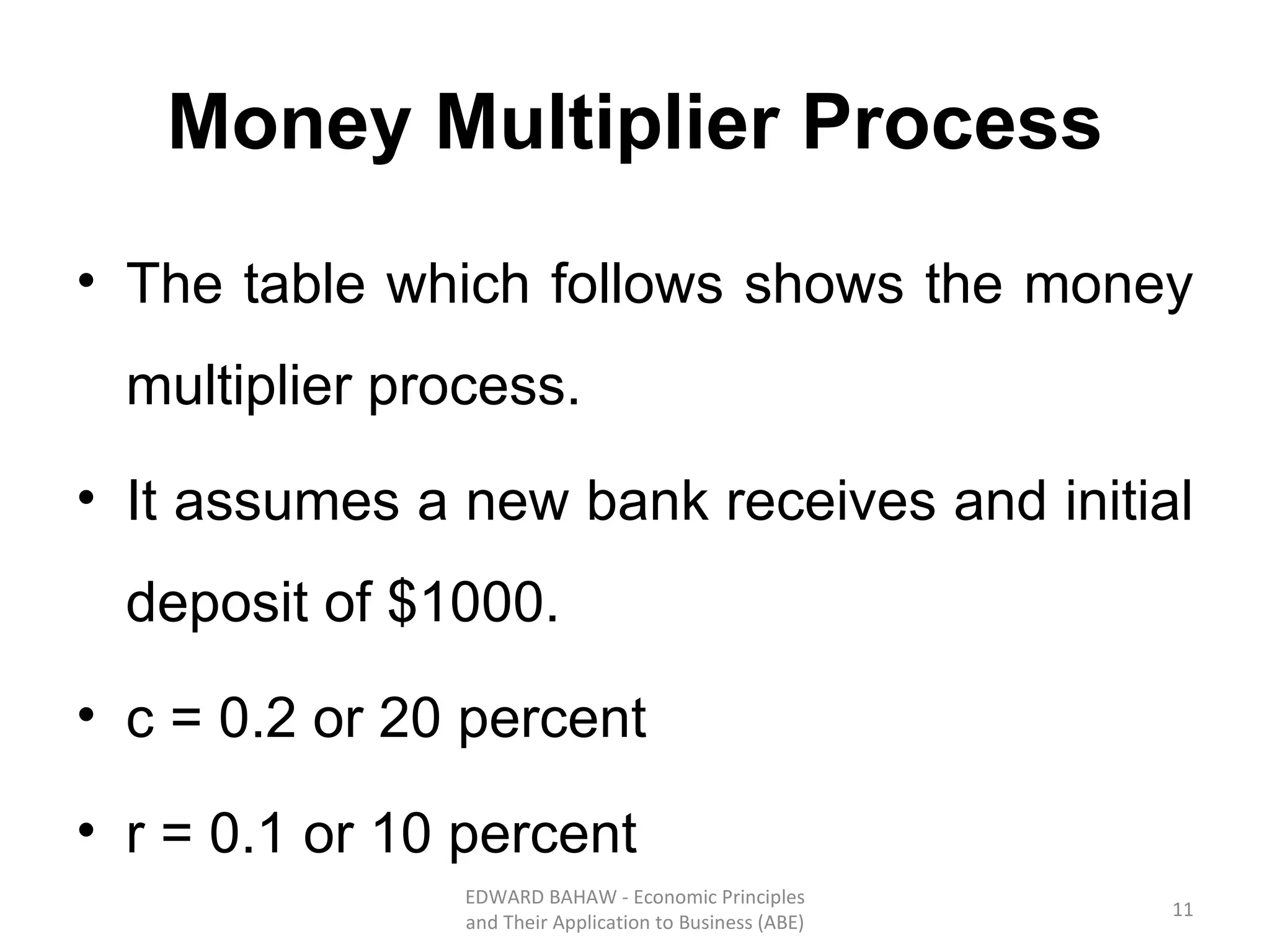
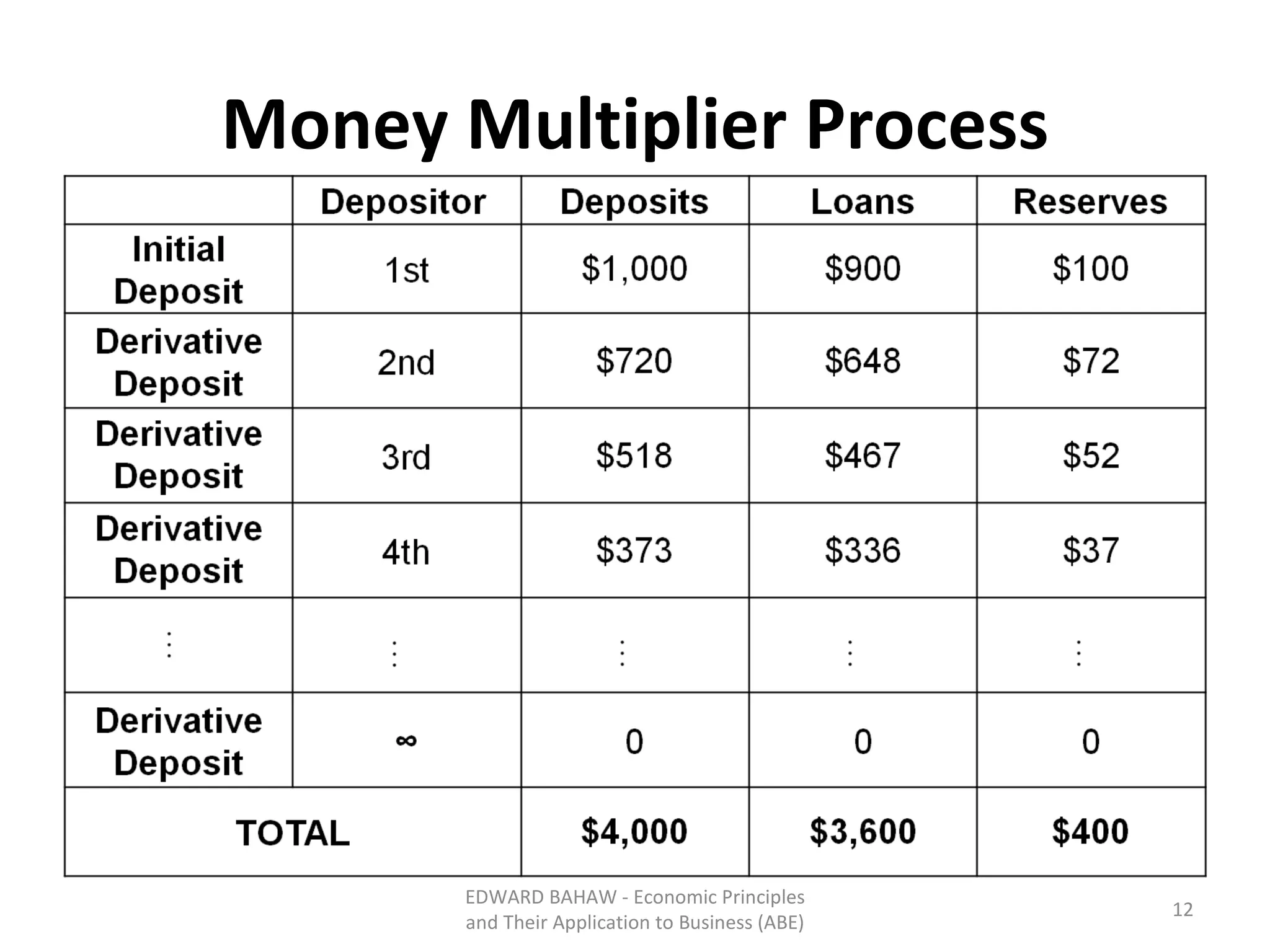
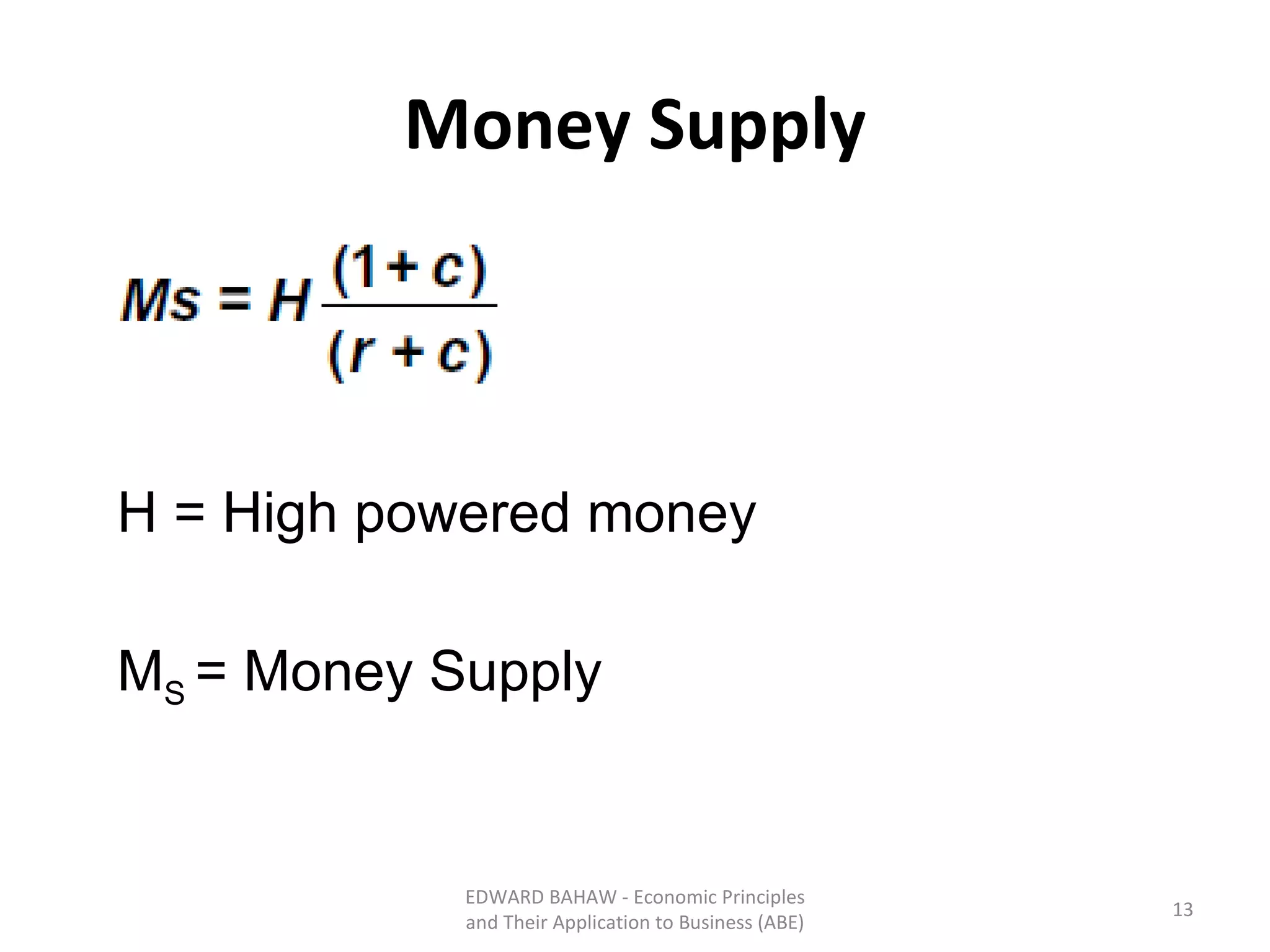
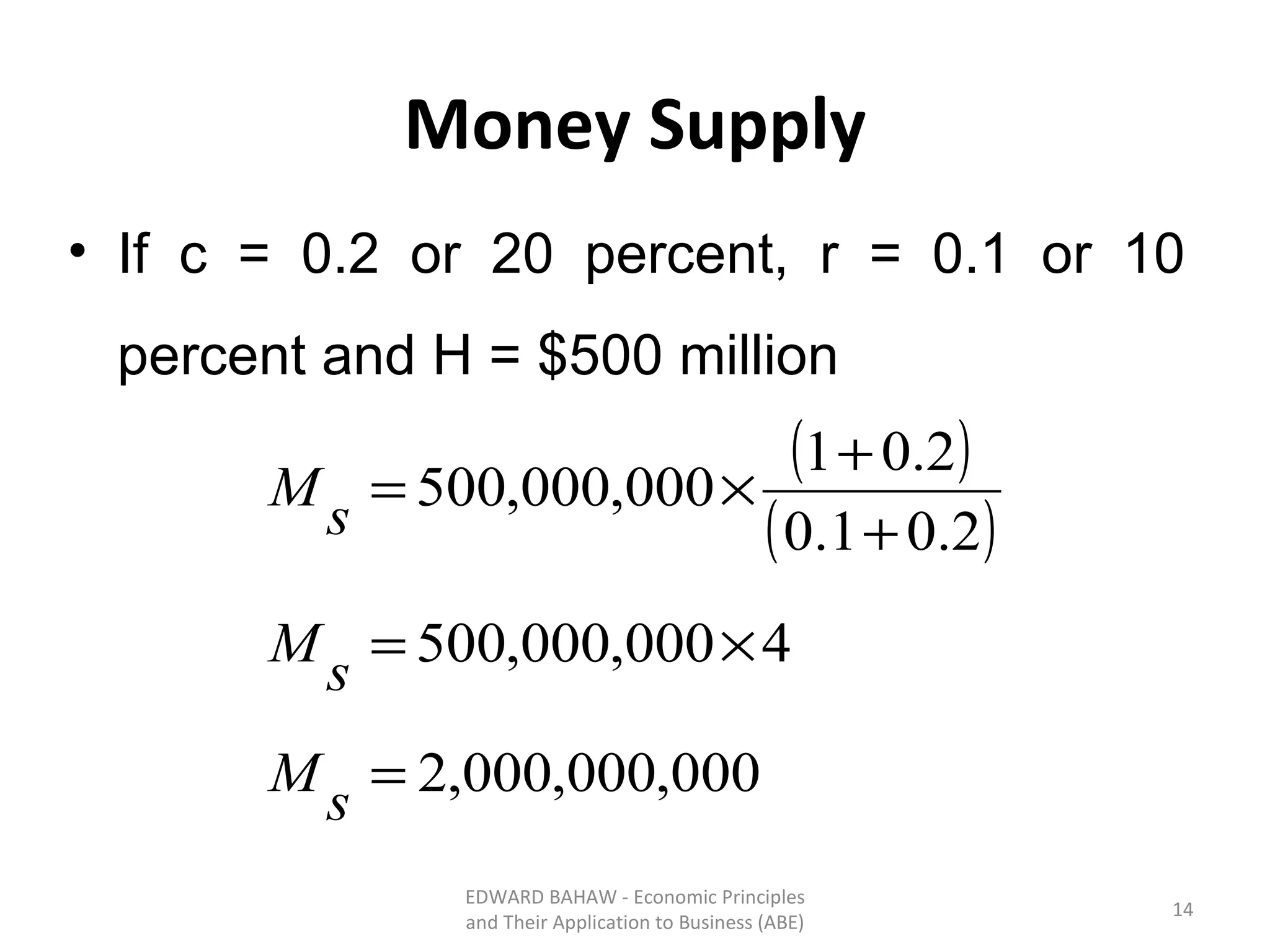
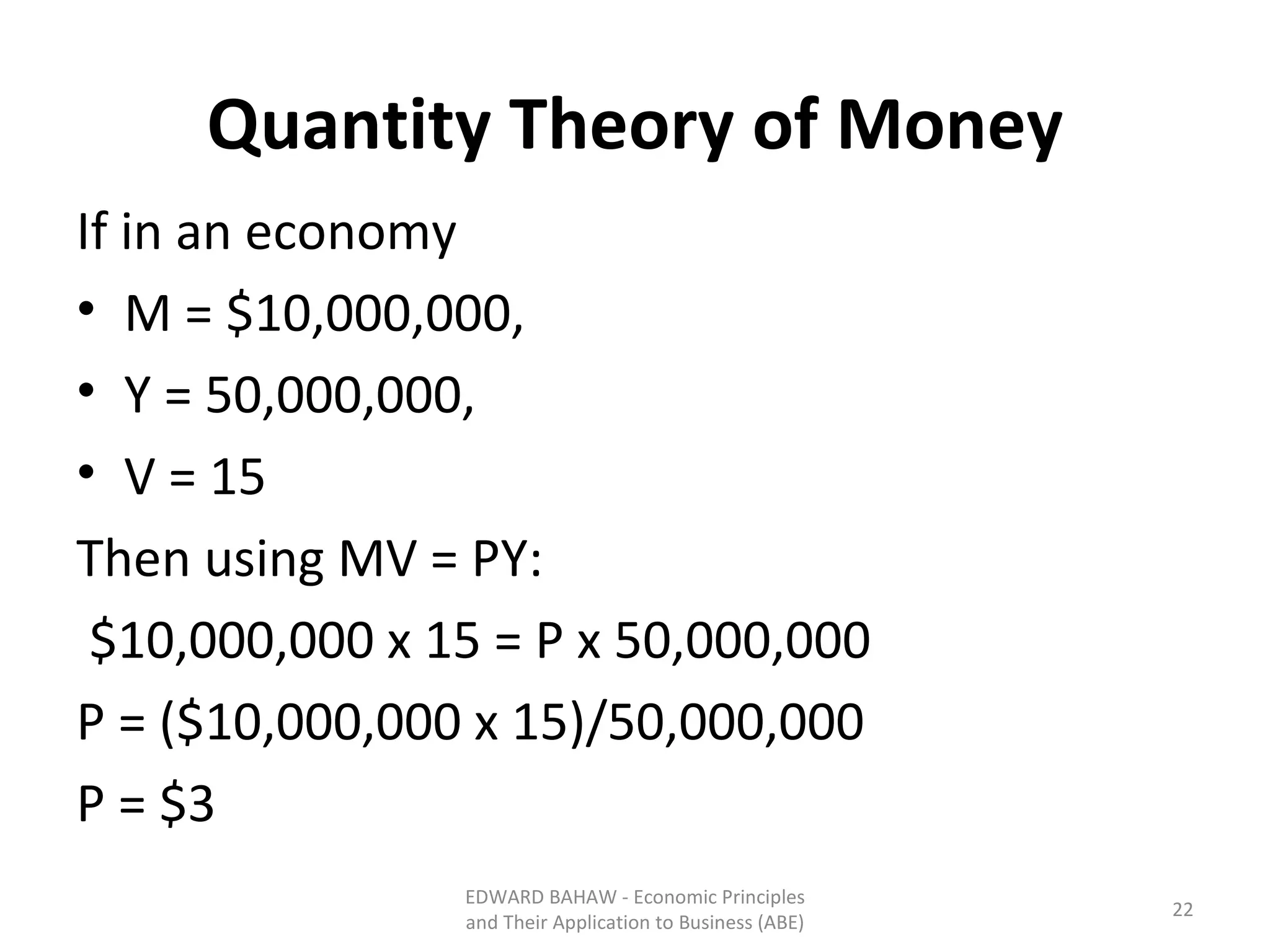
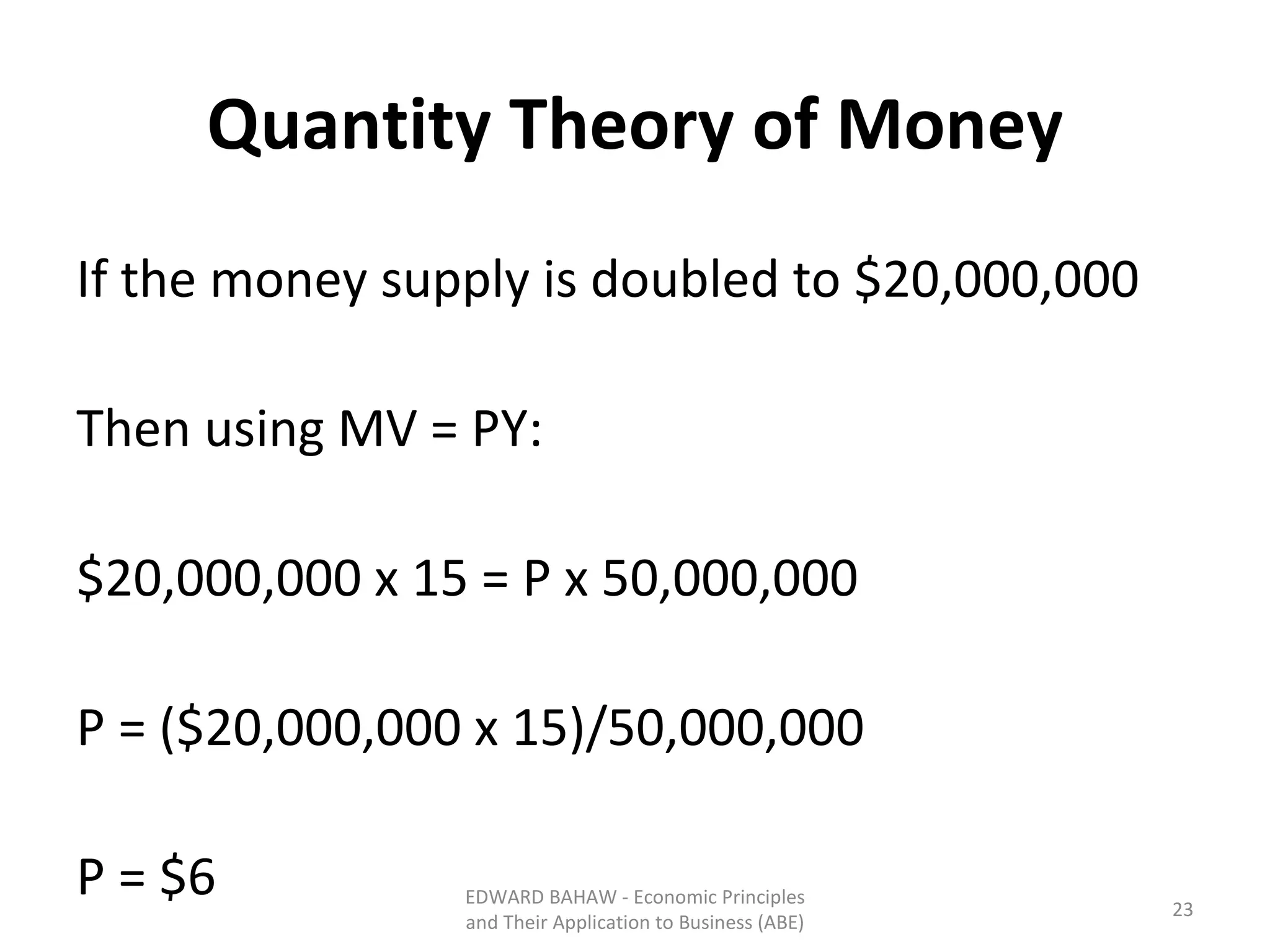
The document discusses monetary policy tools used by central banks to influence the money supply and interest rates. It explains that expansionary monetary policy involves lowering interest rates through tools like lowering reserve requirements, engaging in open market operations, and reducing policy rates. This increases money supply and aggregate demand. Contractionary policy does the opposite through higher interest rates. The quantity theory of money is also covered, showing how increasing the money supply directly increases price levels in an economy.