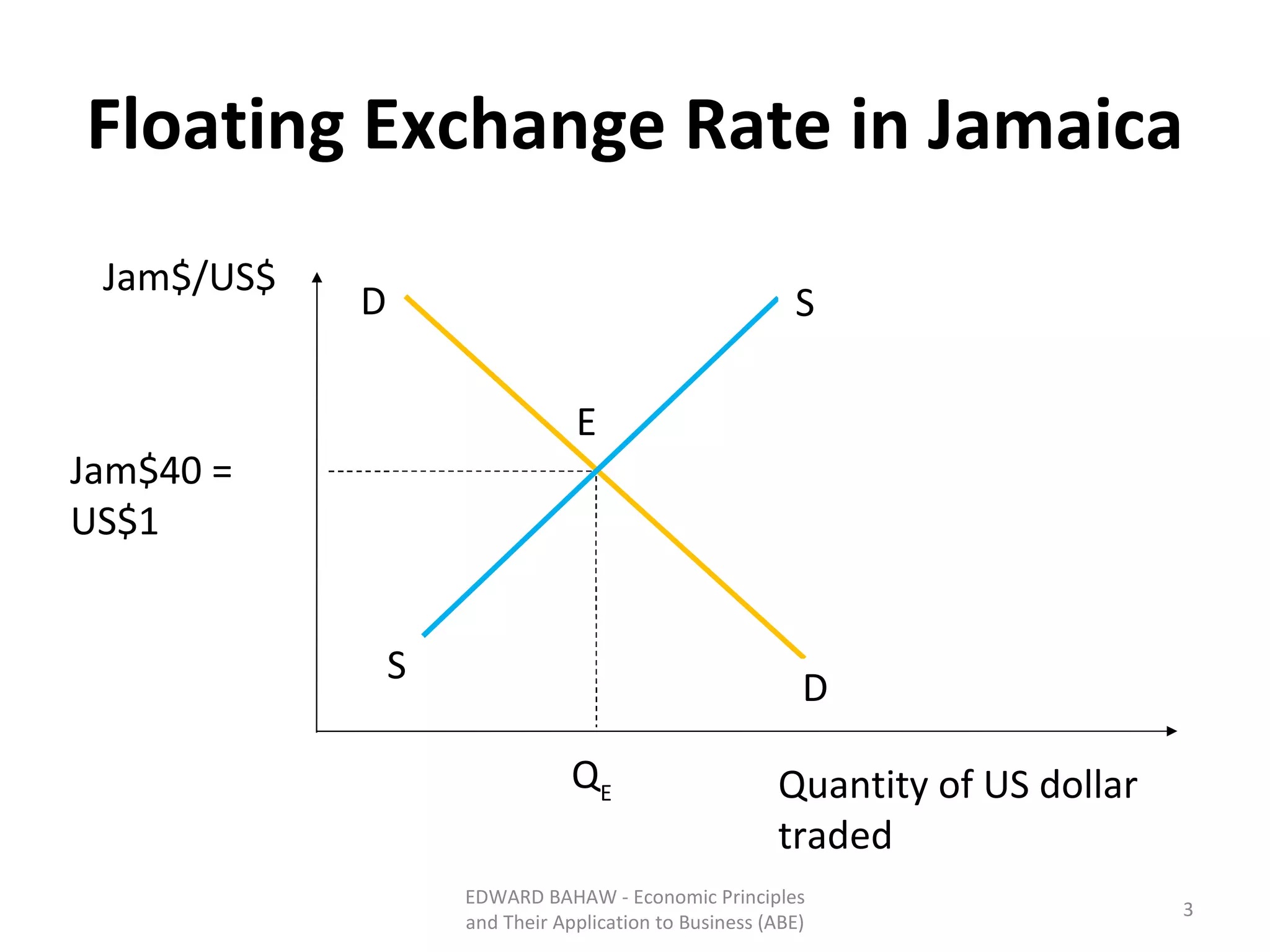
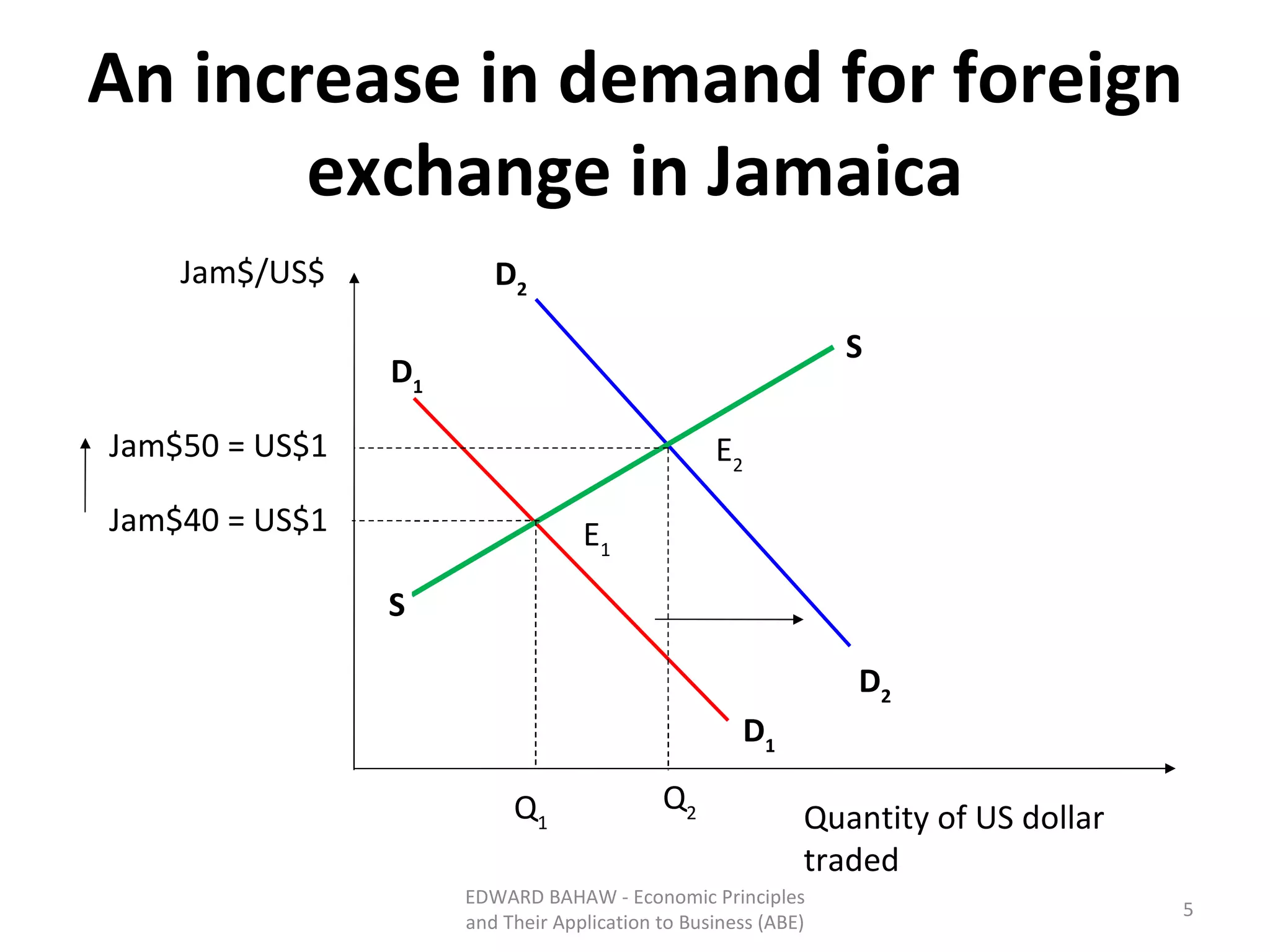
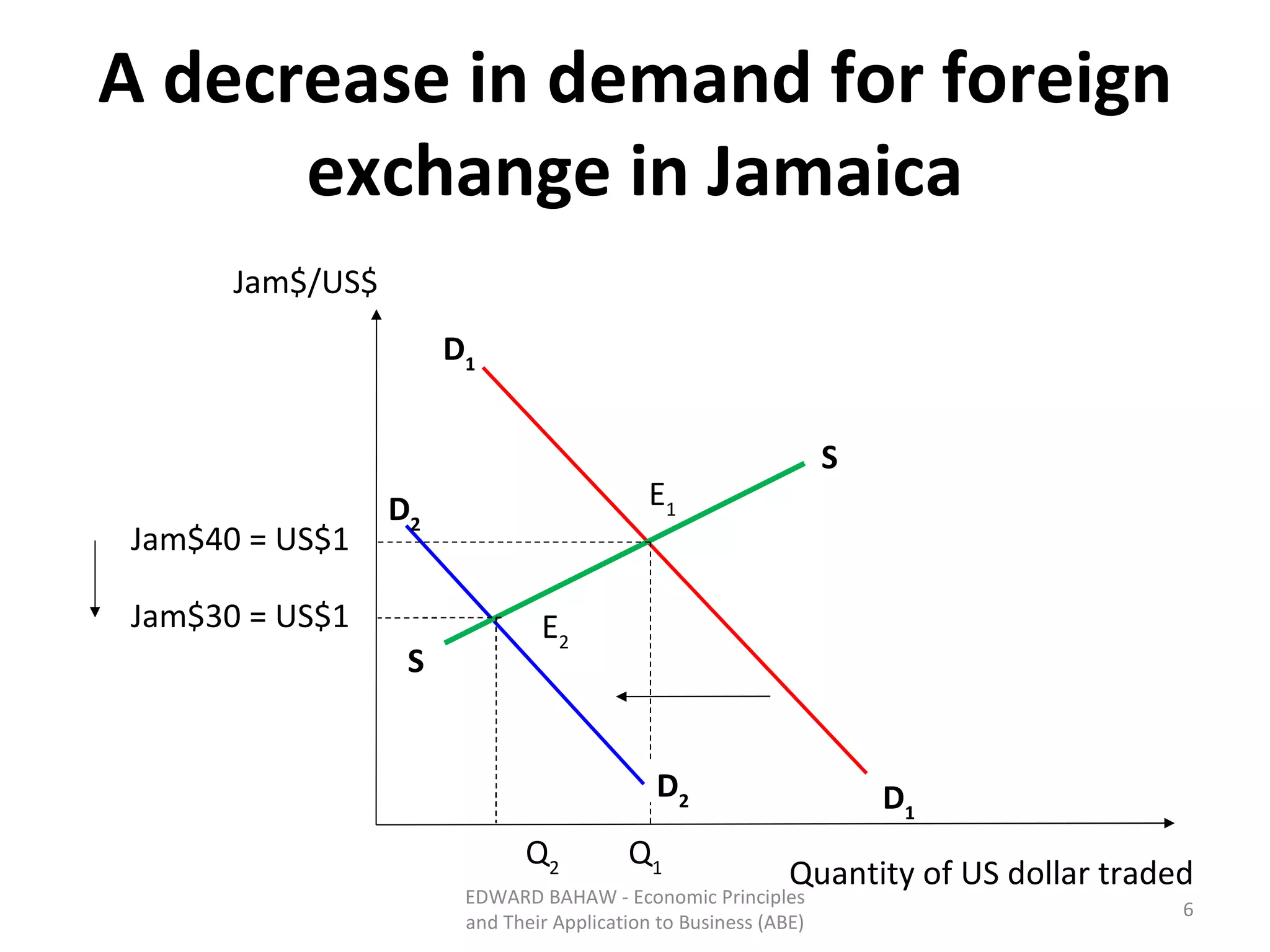
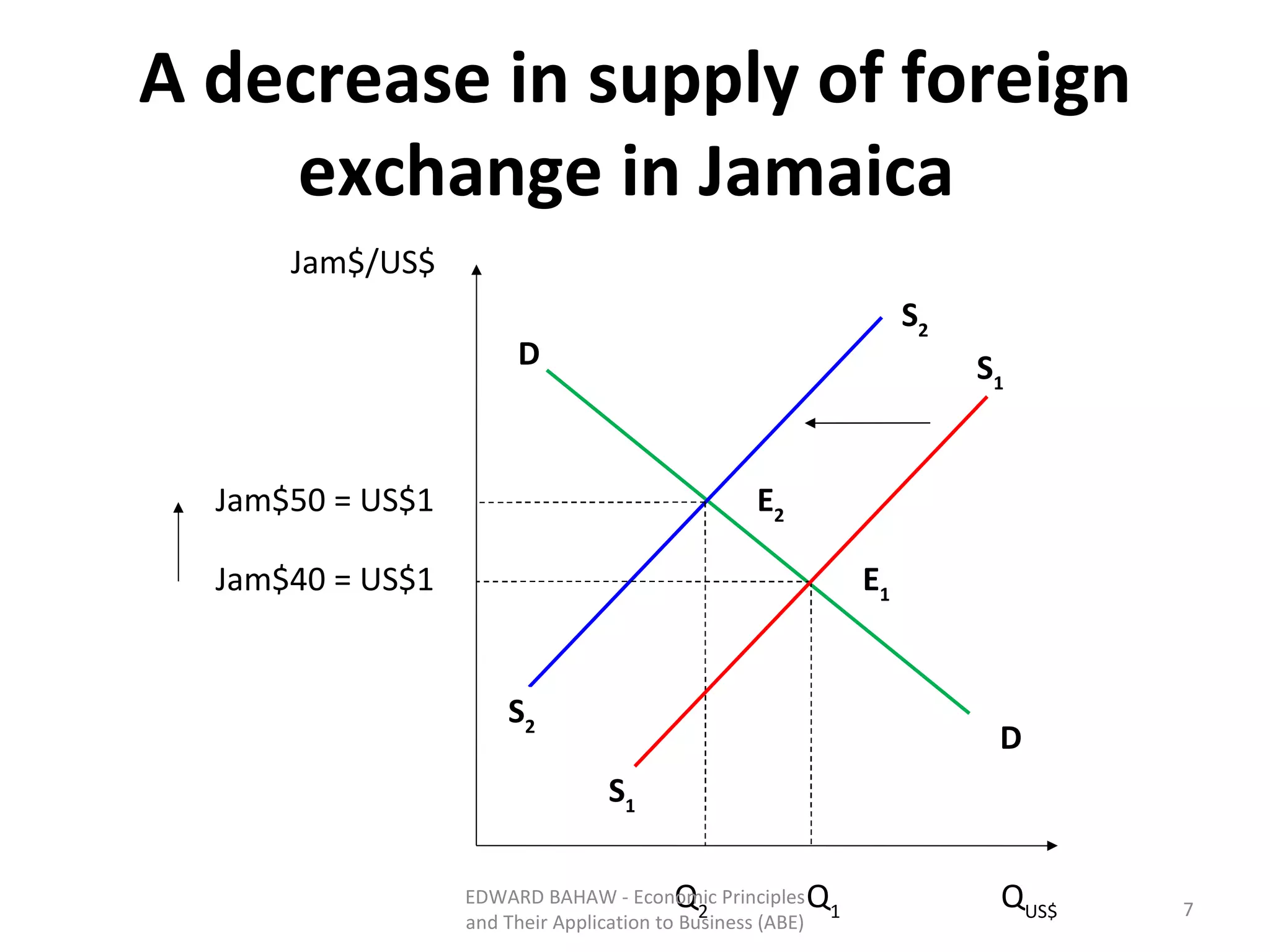
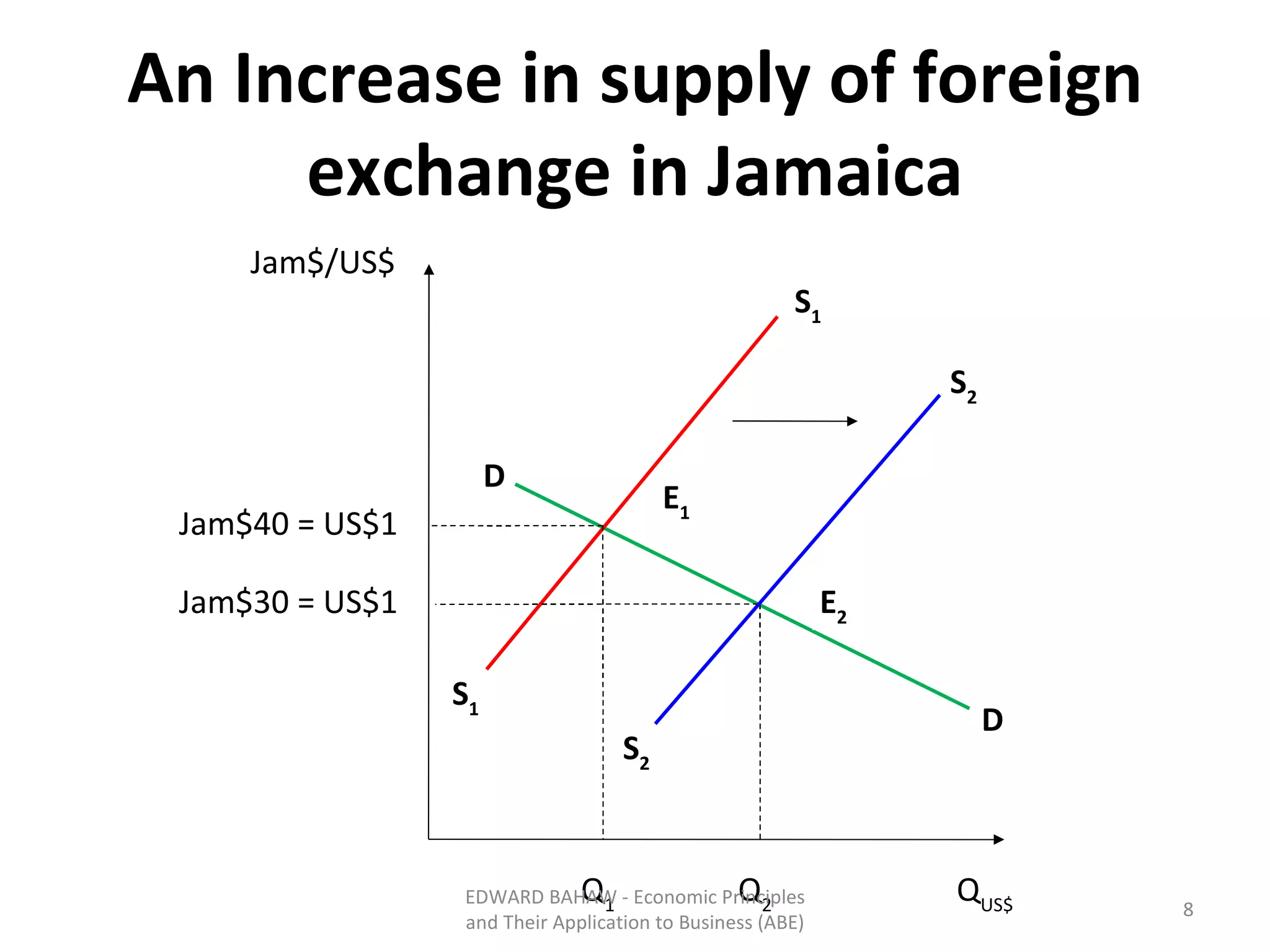
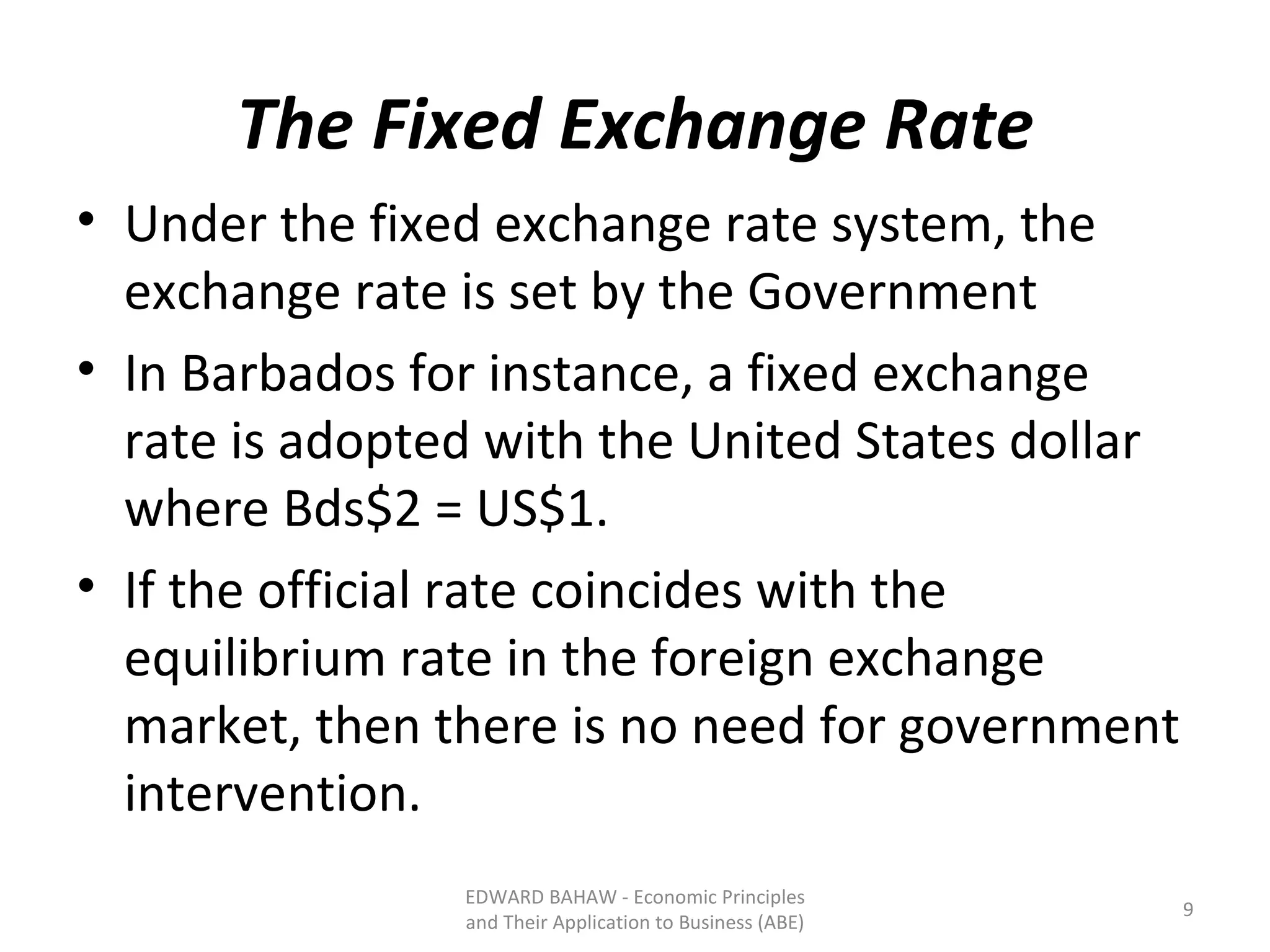
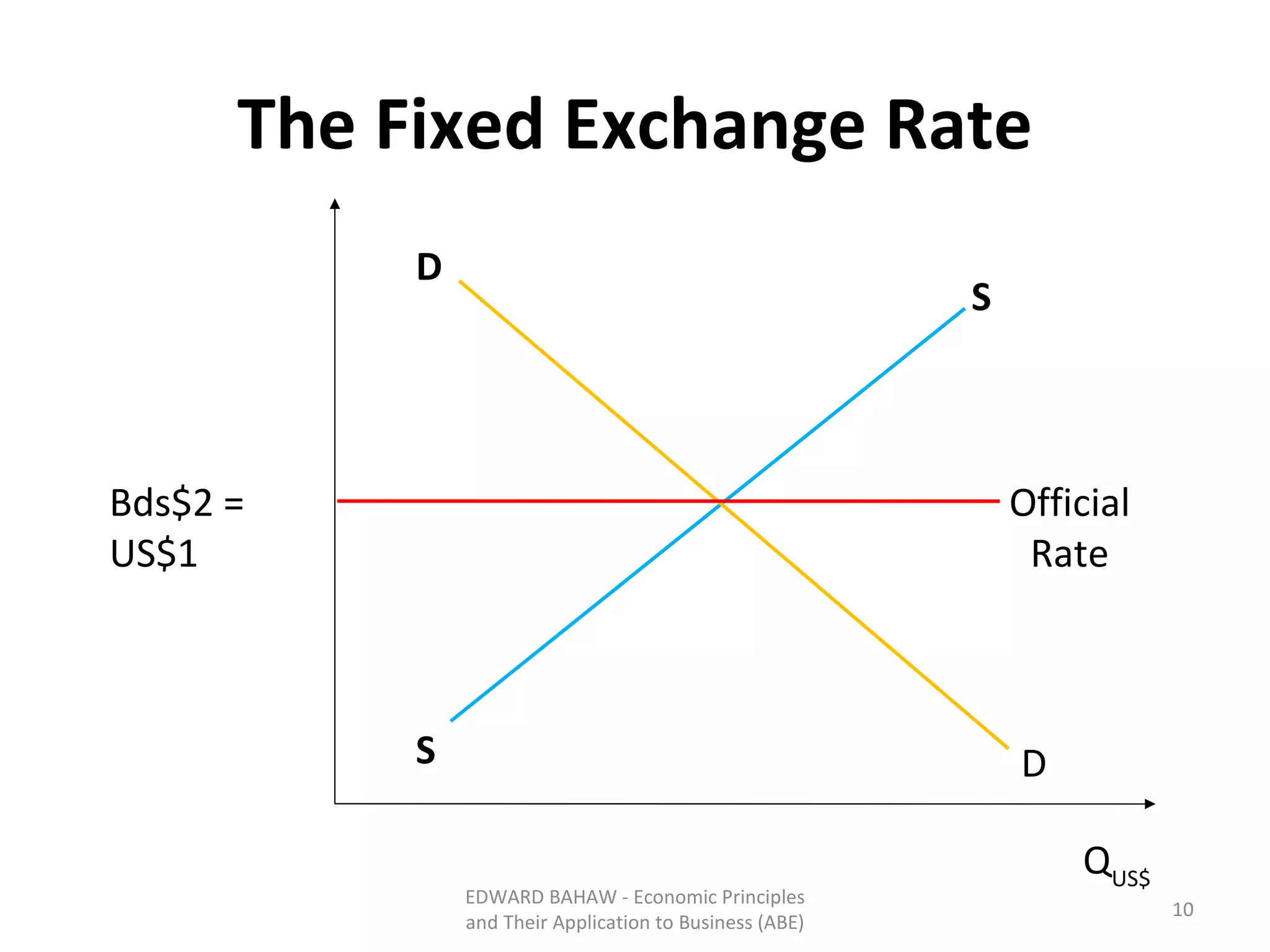
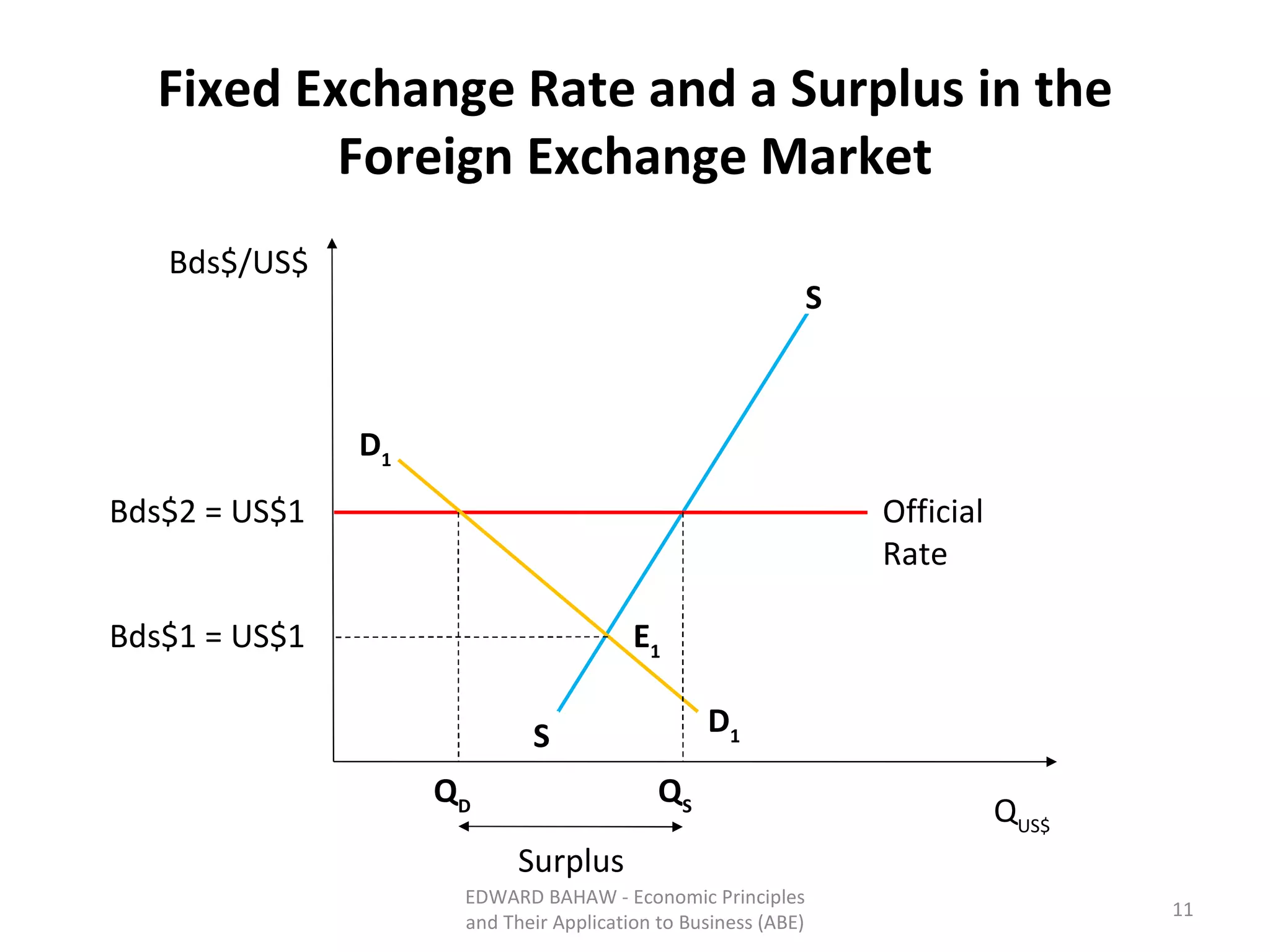
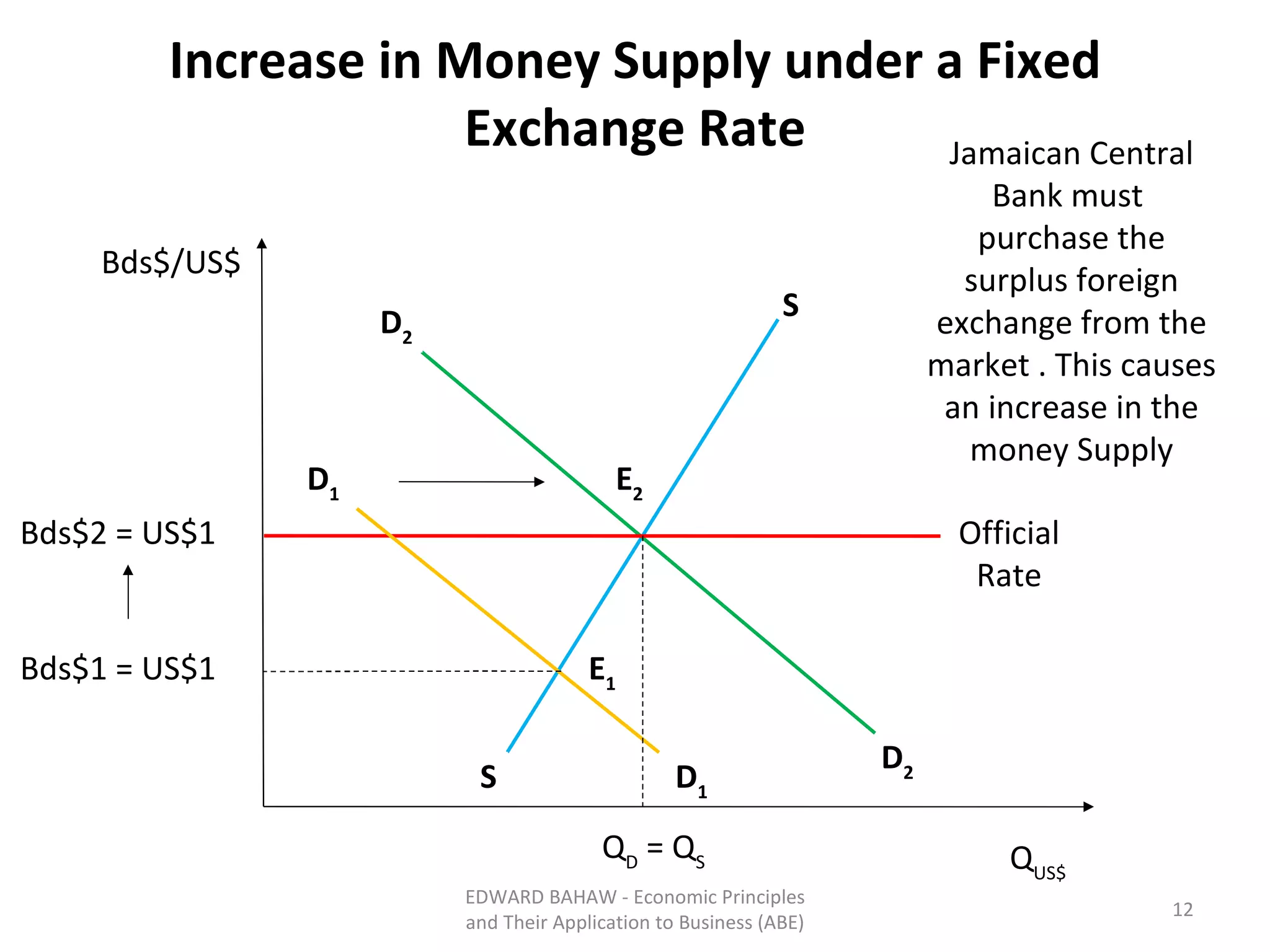
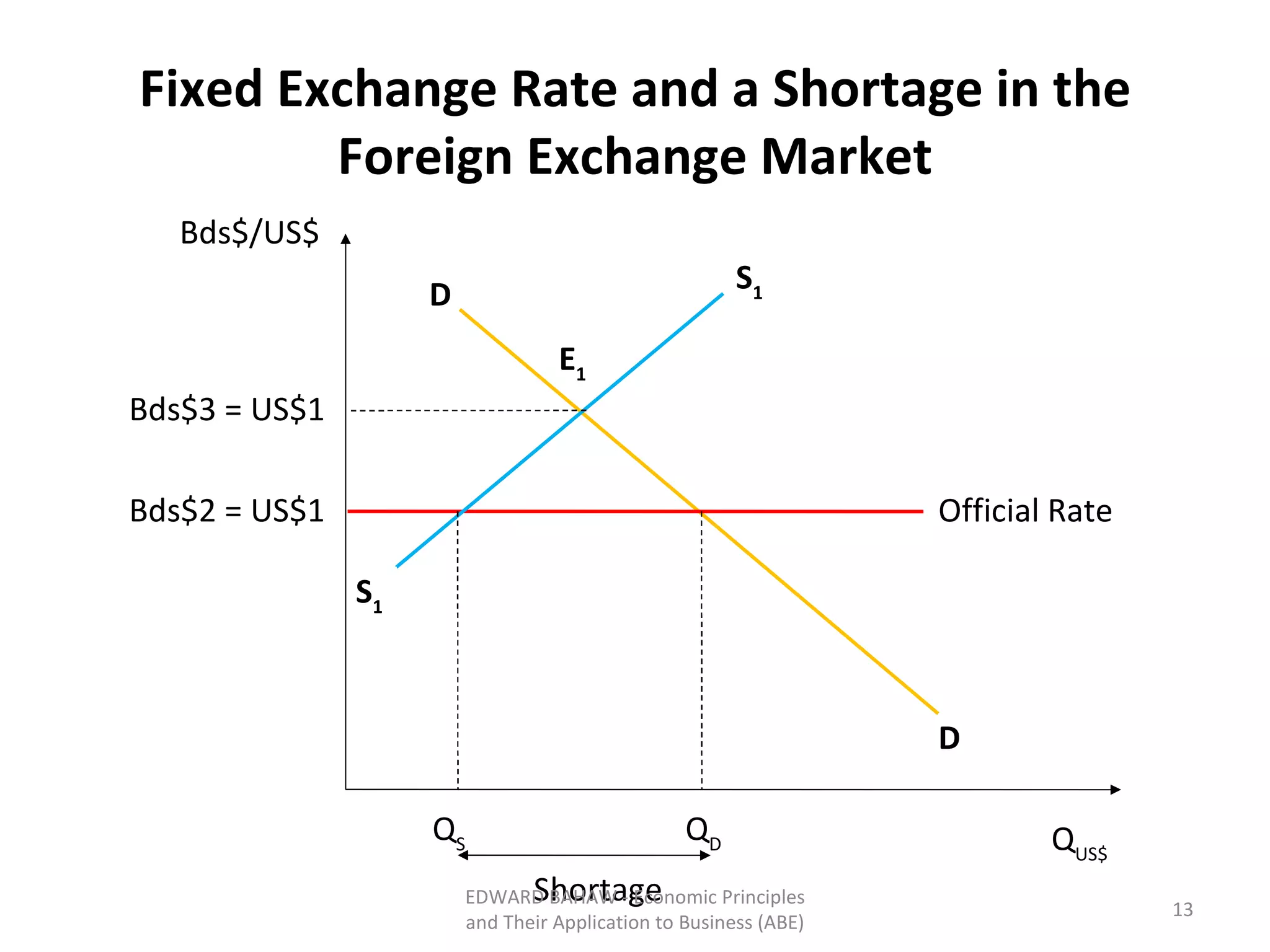
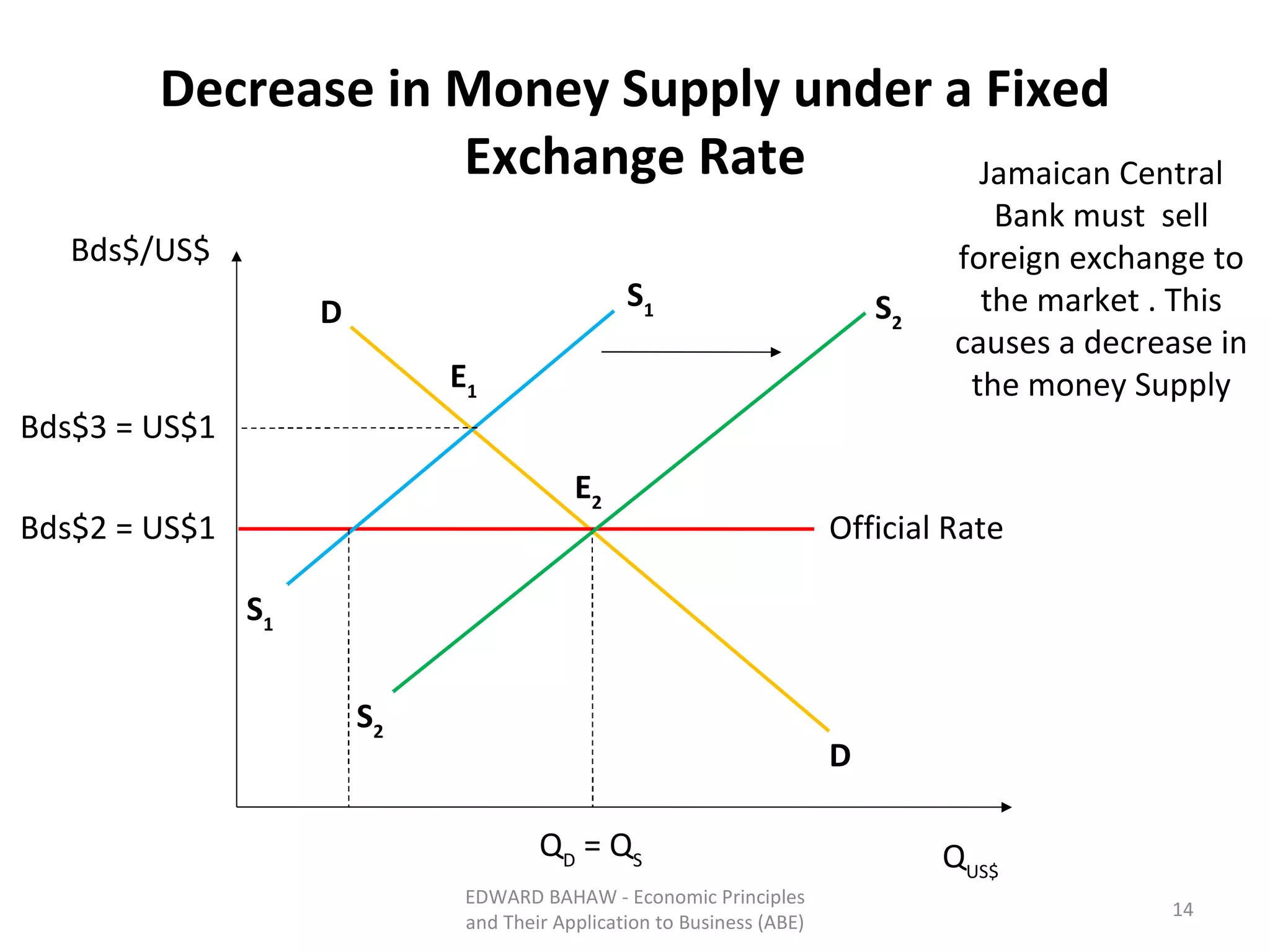
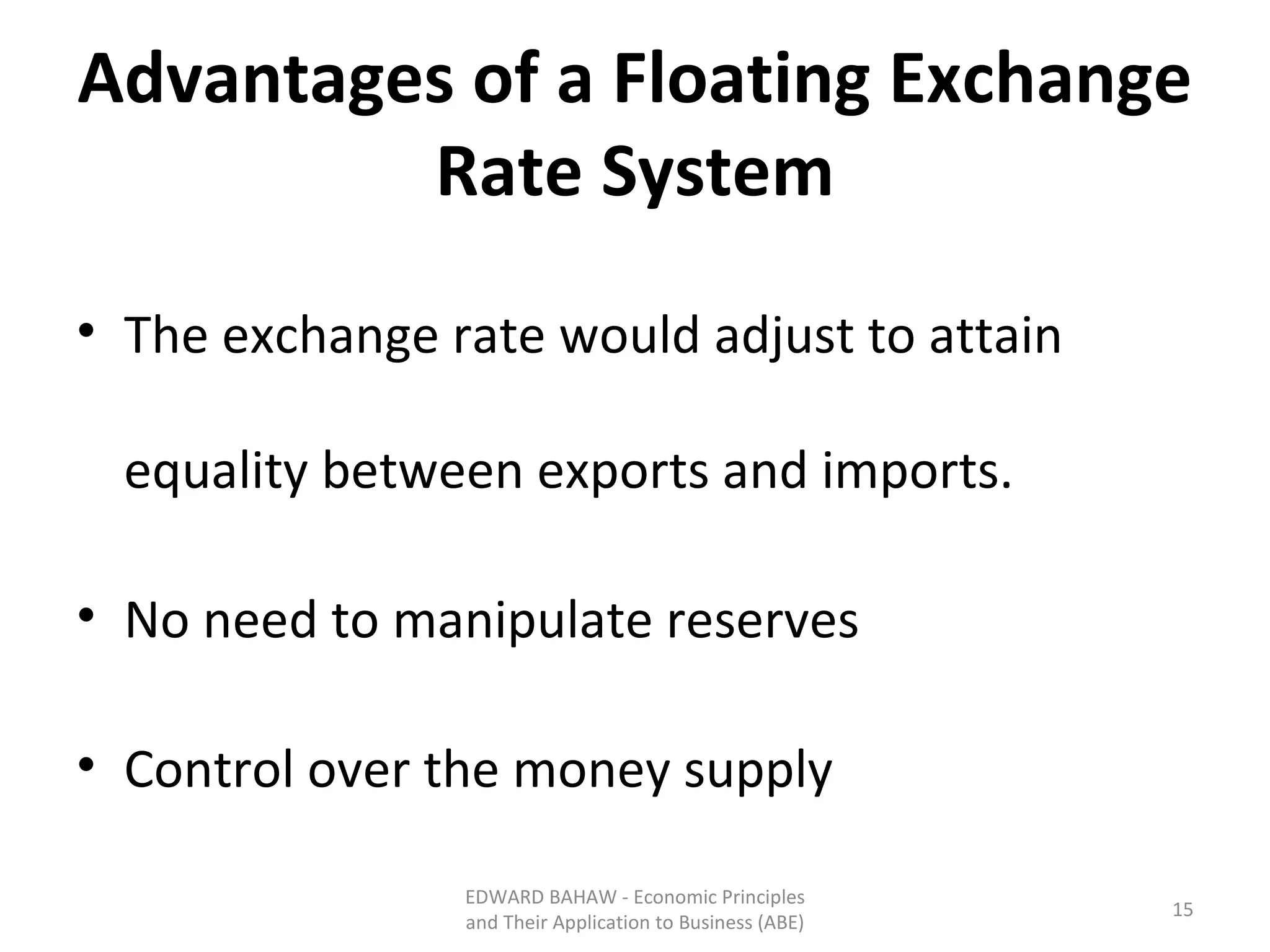
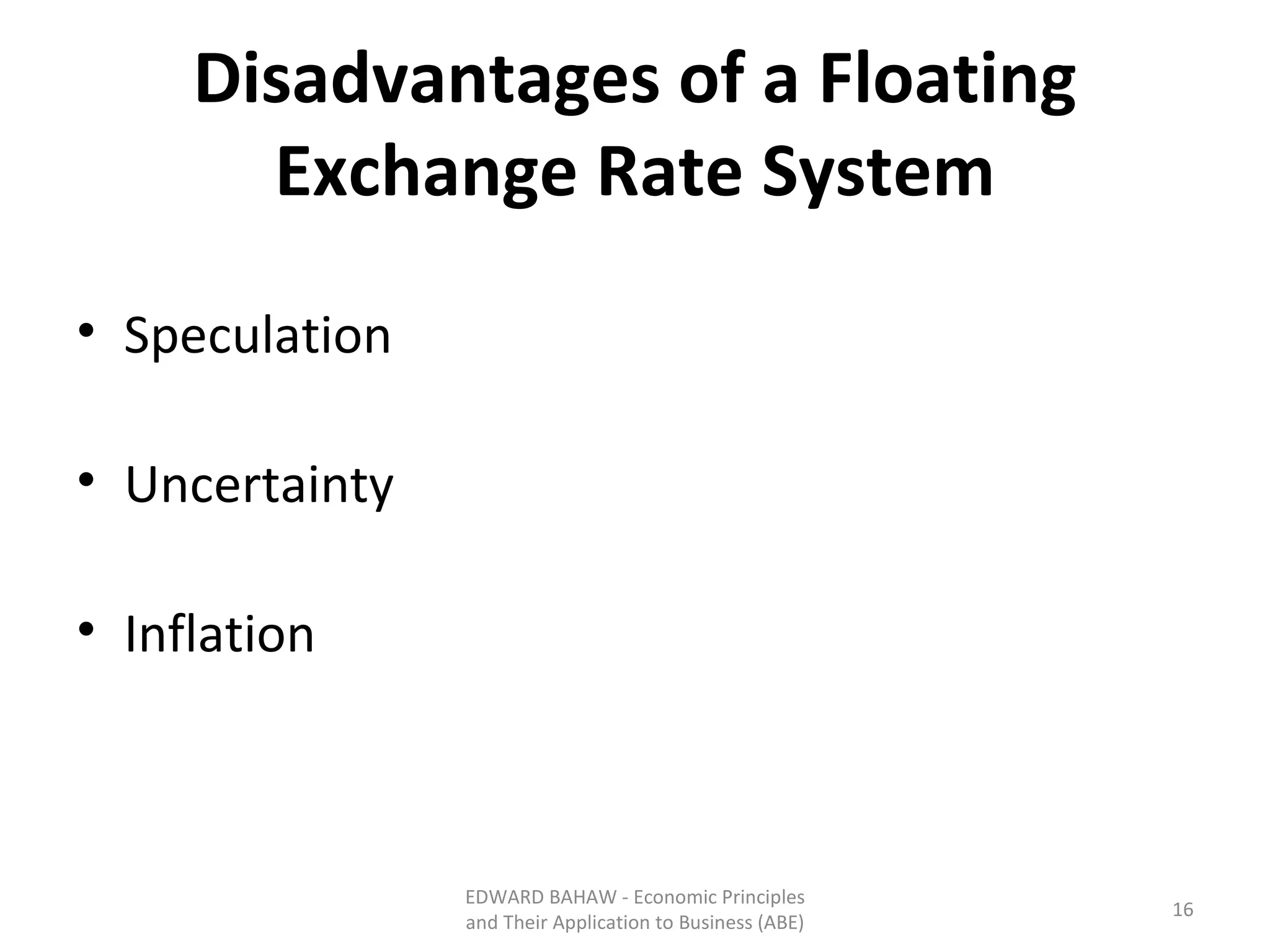
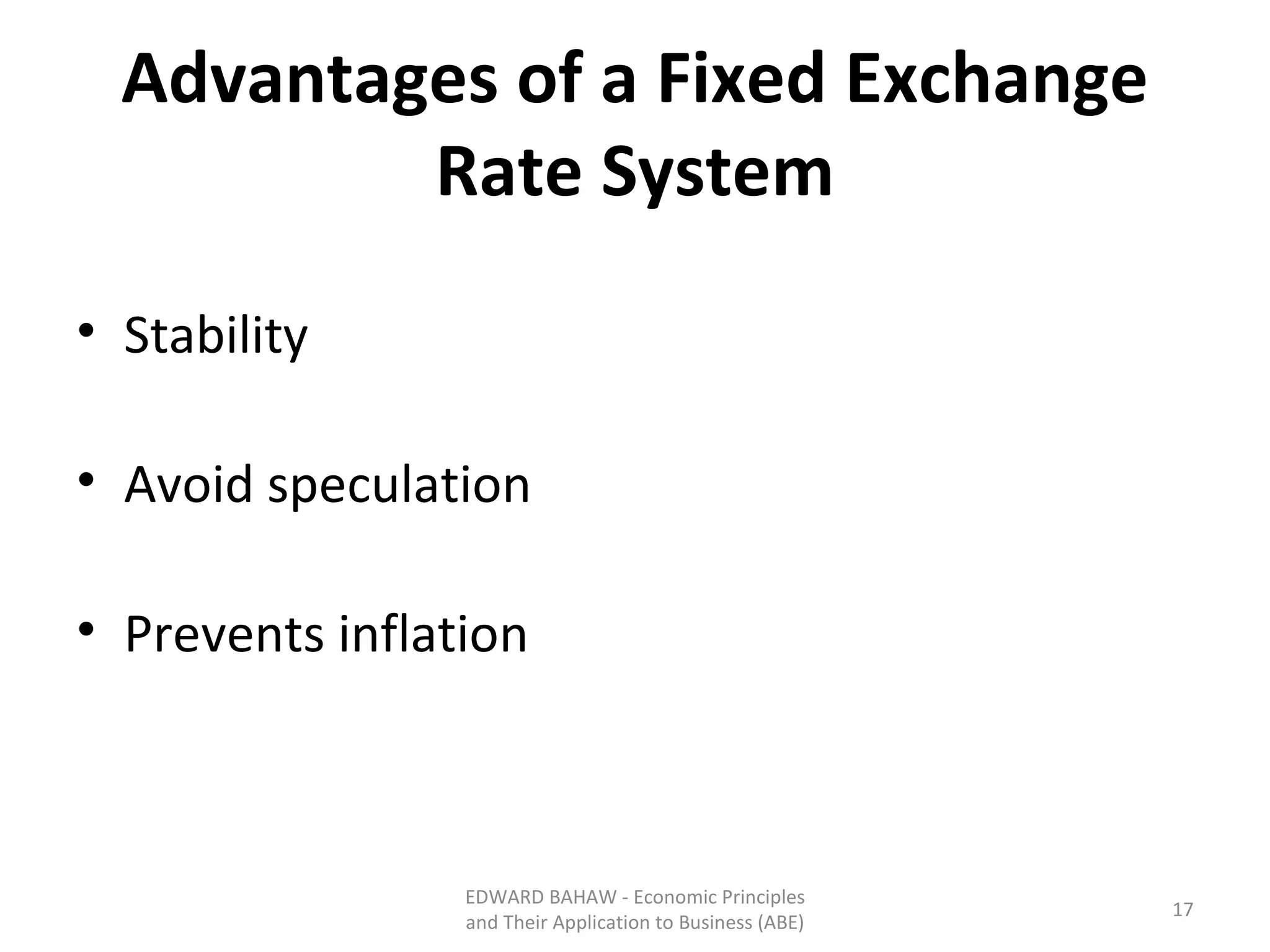
Under a floating exchange rate system, the exchange rate between currencies is determined by foreign exchange market forces of supply and demand. Under a fixed exchange rate system, a government sets the exchange rate. When there is a surplus of foreign exchange under a fixed system, the central bank must purchase the surplus to increase the money supply. When there is a shortage, the central bank must sell foreign exchange to decrease the money supply. The document discusses the advantages and disadvantages of fixed and floating exchange rate systems for businesses and governments.