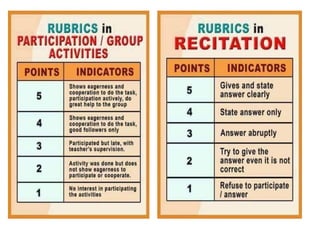
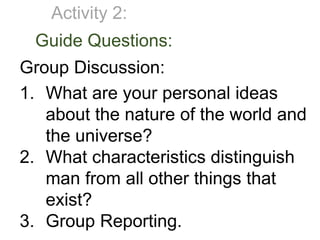
The document discusses the topic of doing philosophy. It provides instructions for classroom activities where students will be split into groups and discuss philosophical questions. It also summarizes some of the key questions and methods used in philosophy, such as questions about reality, certainty, ethics, and the tools philosophers use like systematic doubt, argumentation, and thought experiments.