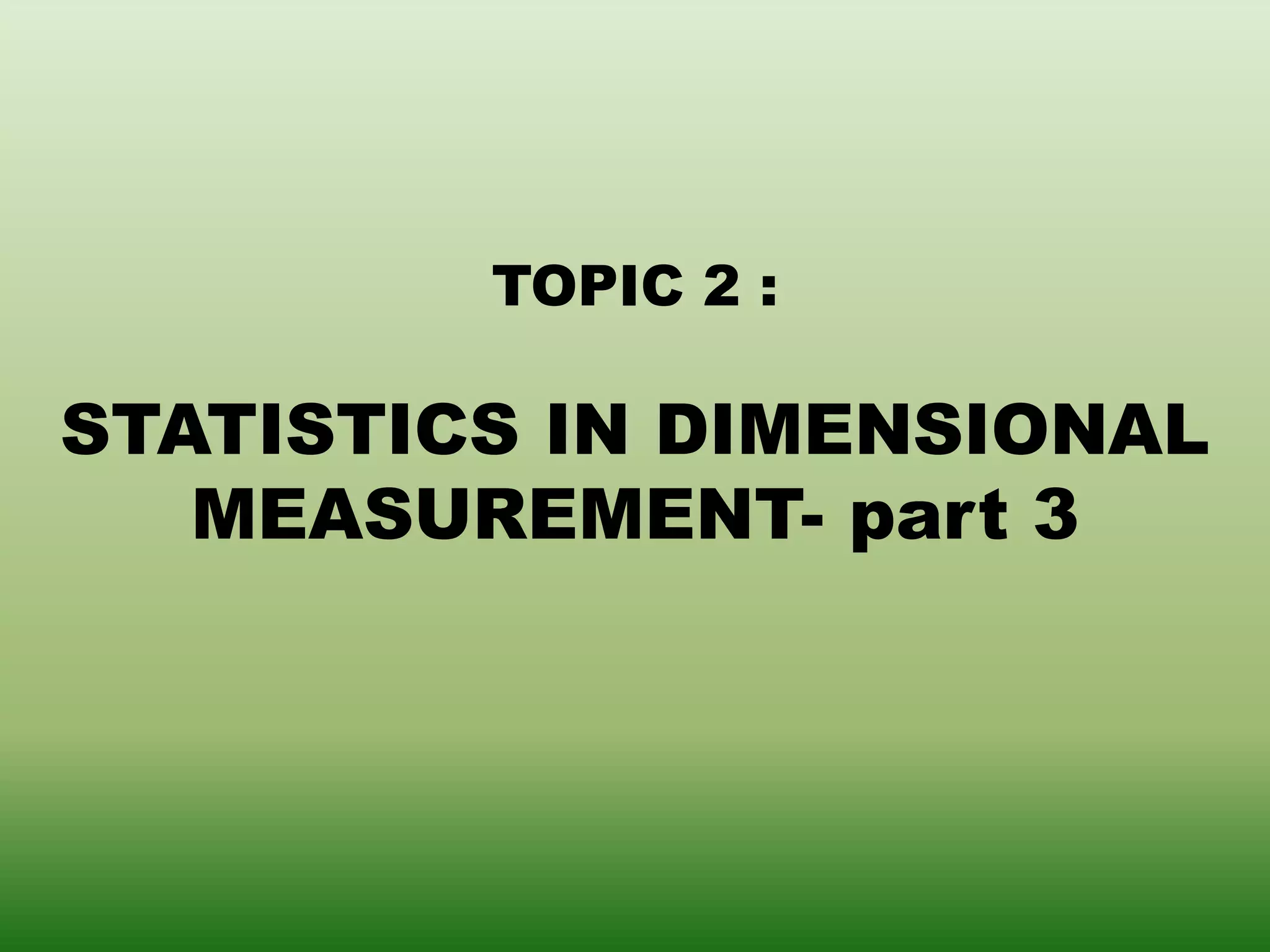
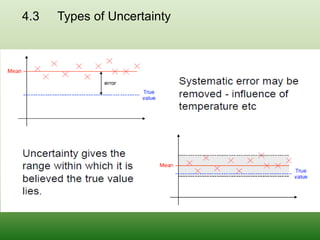
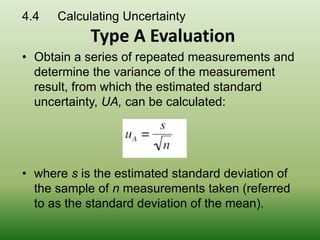
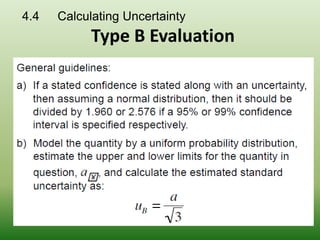
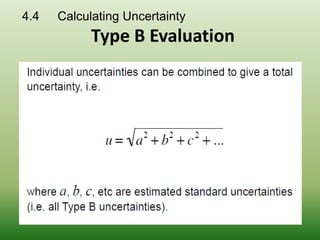
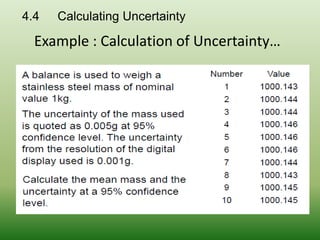
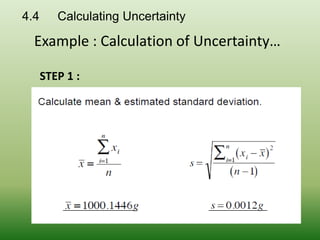
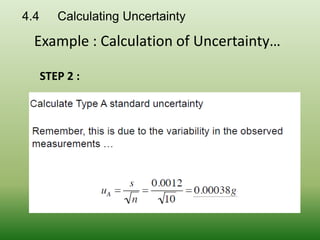
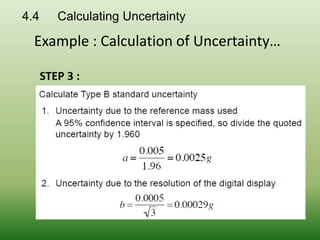
This document discusses errors and uncertainty in measurement. It defines error as the difference between an individual measurement and the true value. Errors can be random or systematic. Sources of error include the measuring instrument, the item being measured, the measurement process, and environmental factors. There are two types of uncertainty - type A which is evaluated statistically from repeated measurements, and type B which is evaluated from other sources like specifications or published data. Calculating uncertainty involves identifying sources of uncertainty, estimating individual uncertainties, and combining them to obtain an overall measurement uncertainty.