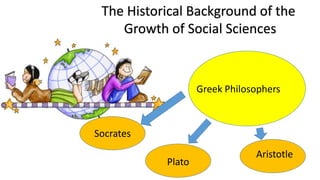
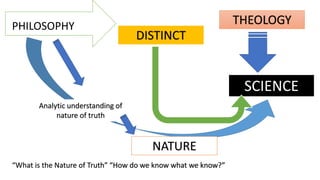
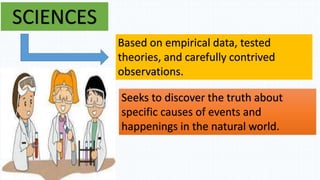
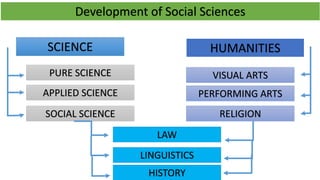
The document discusses the historical development of social sciences from ancient Greek philosophers to modern times. It notes that early study of society was based in philosophy and theology. The scientific revolution starting in the 16th century led to a more empirical and secular approach to understanding the natural world and society. Key figures like Descartes, Kant, and Weber advocated using reason and rigorous analysis over religious dogma. The rise of universities also supported the growth of social sciences. Early social thinkers studied topics like the dissolution of feudalism, trade, and the rise of individualism. Disciplines like sociology, anthropology and political science later emerged with scholars like Comte, Marx, Boas, and Malinowski making important contributions and helping establish