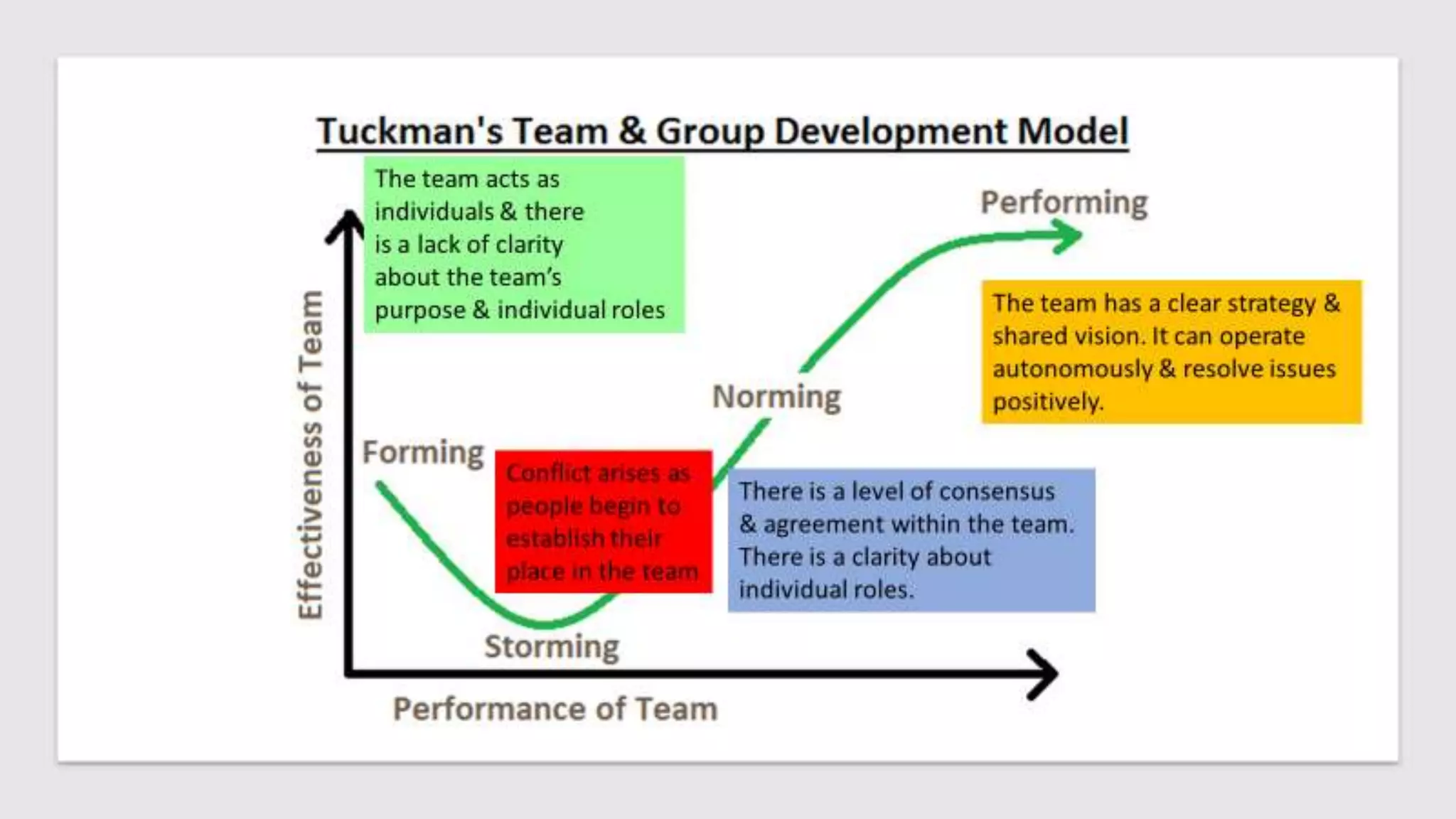
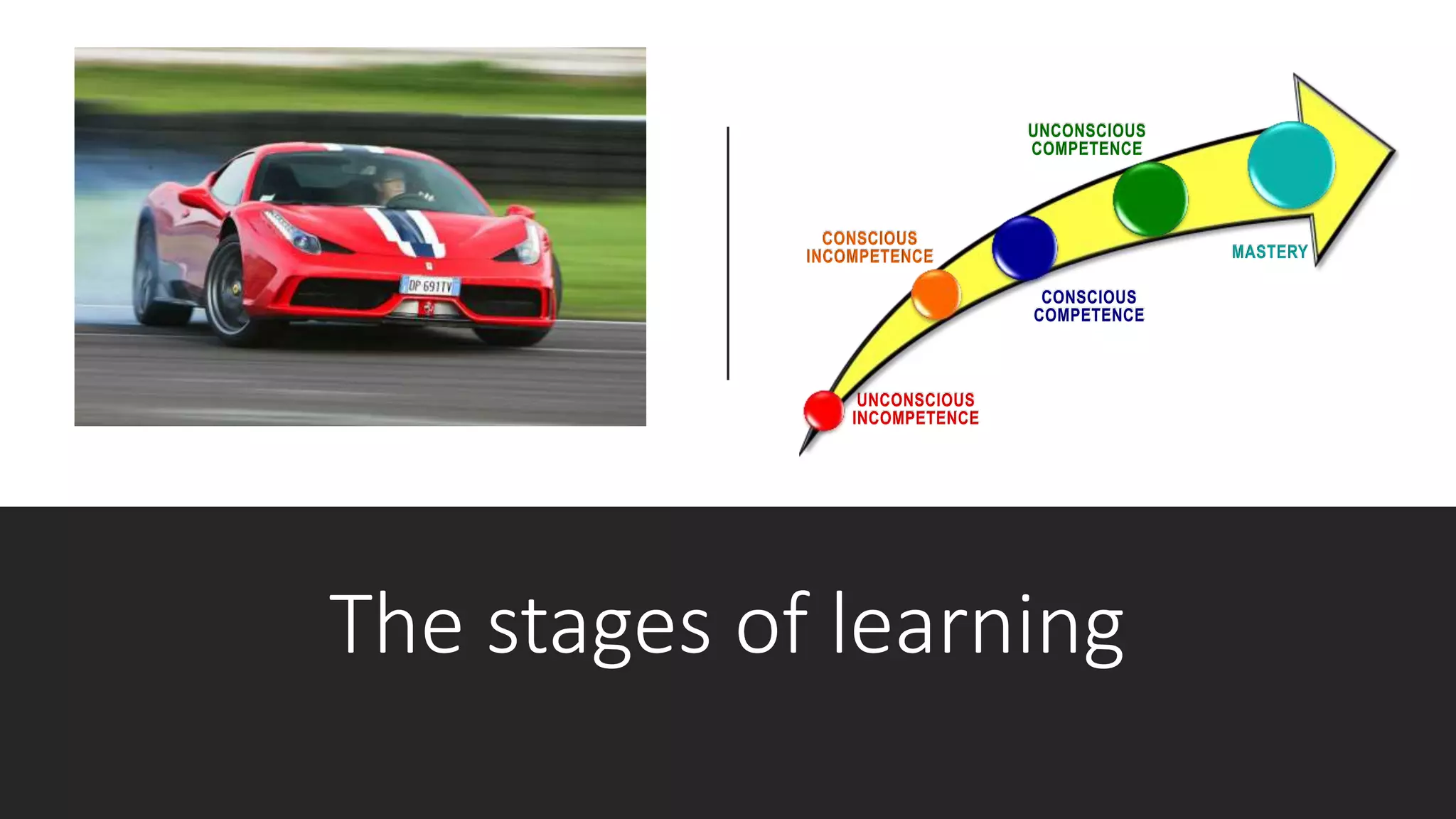
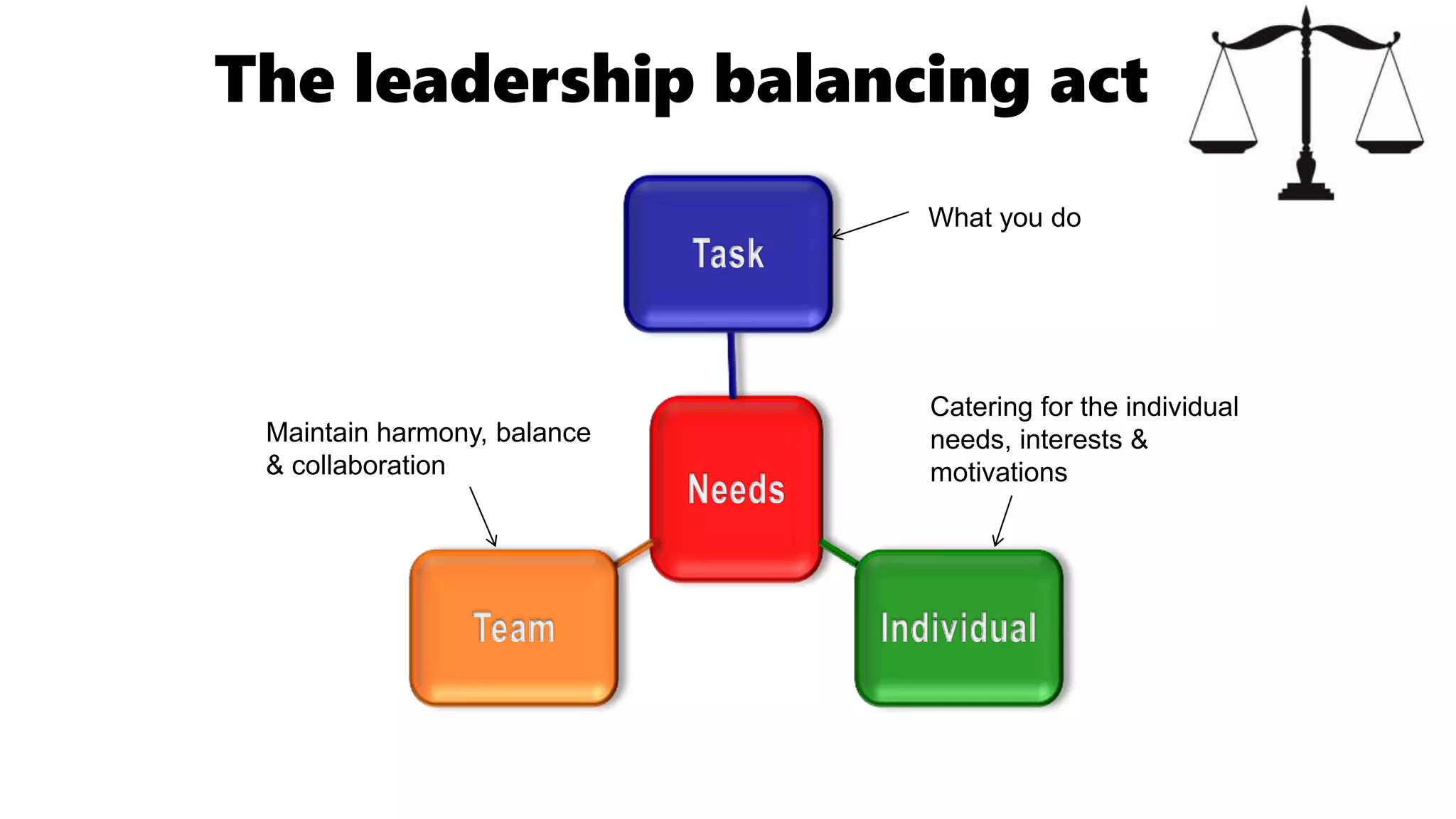
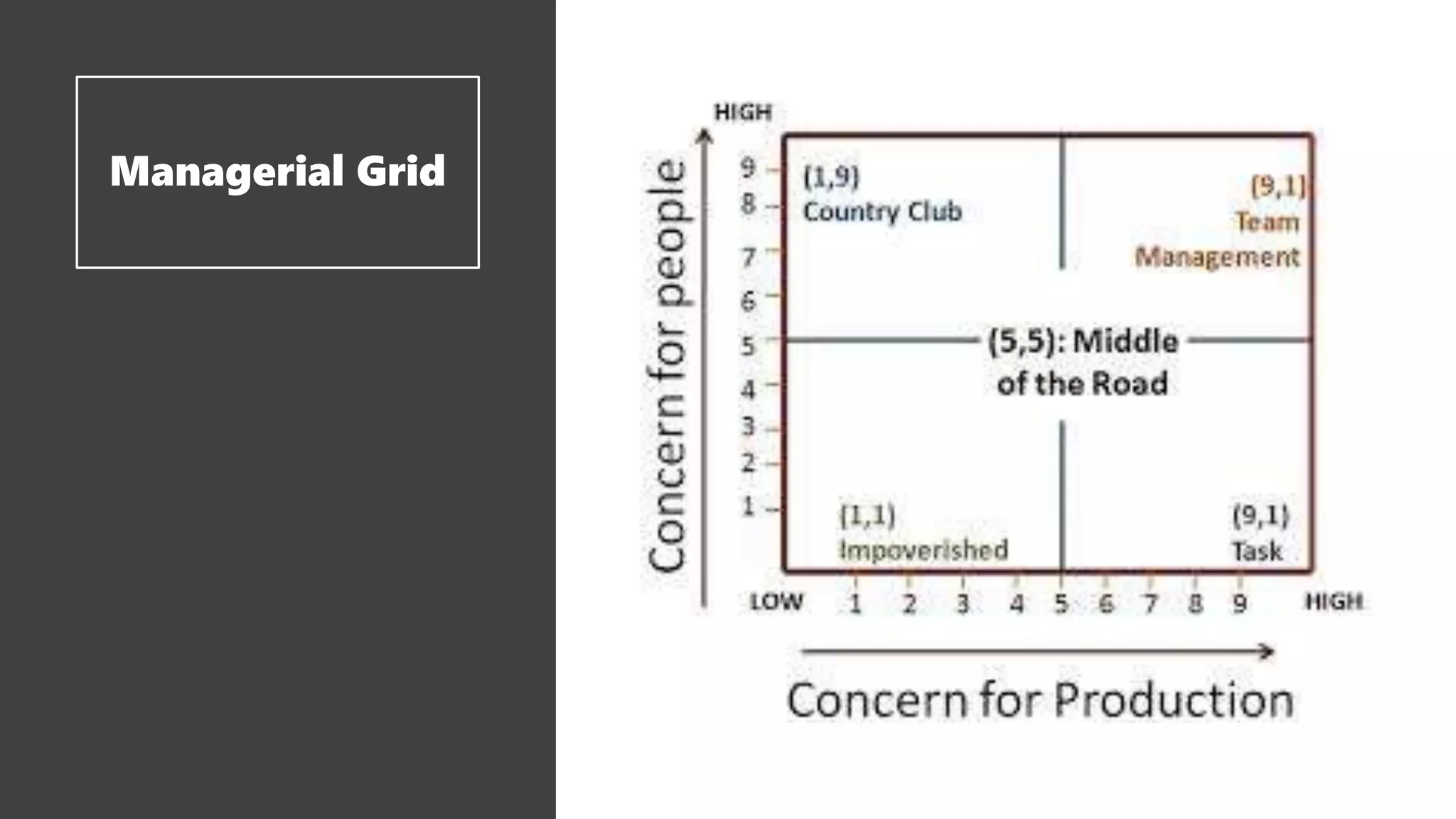
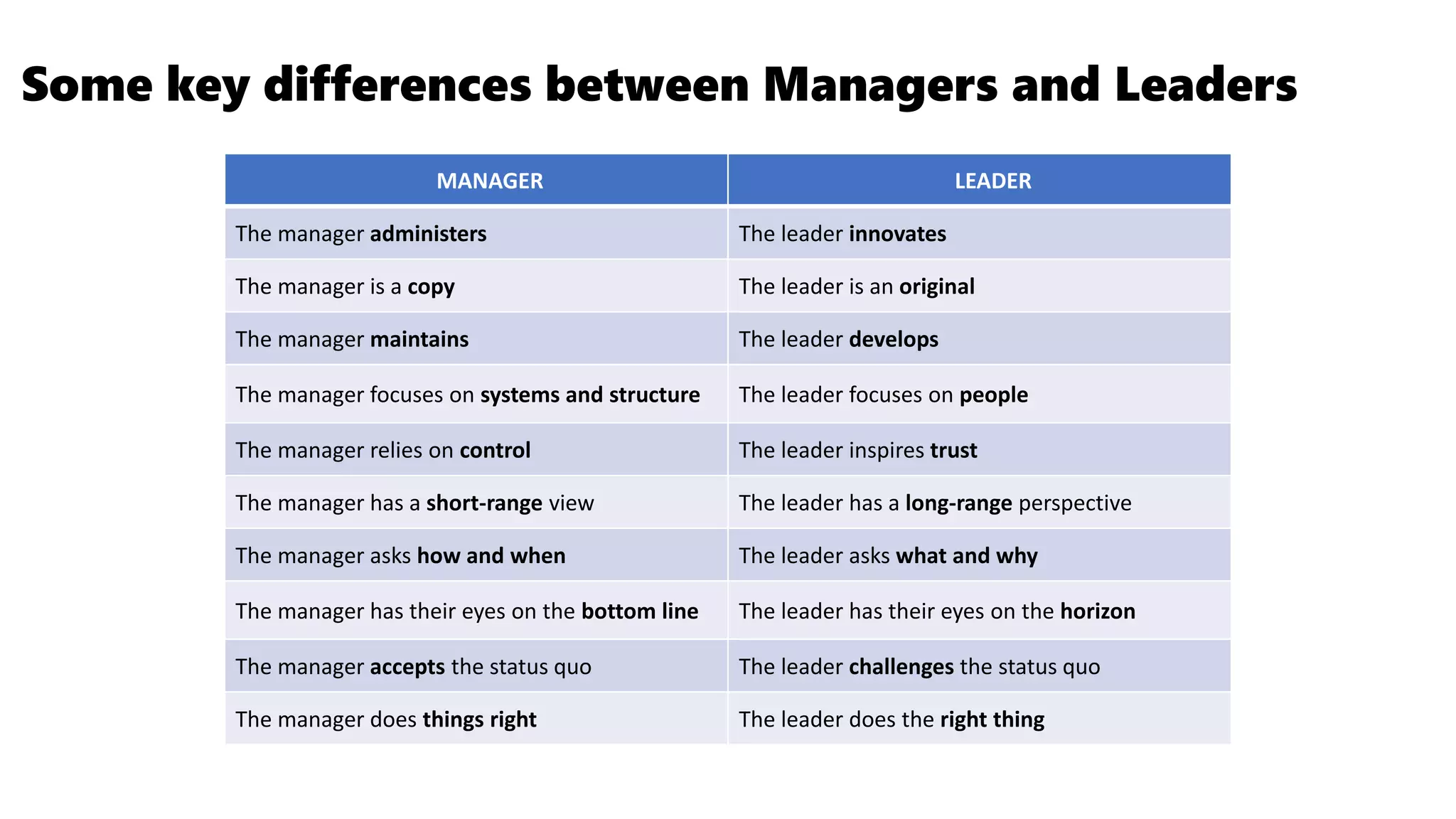
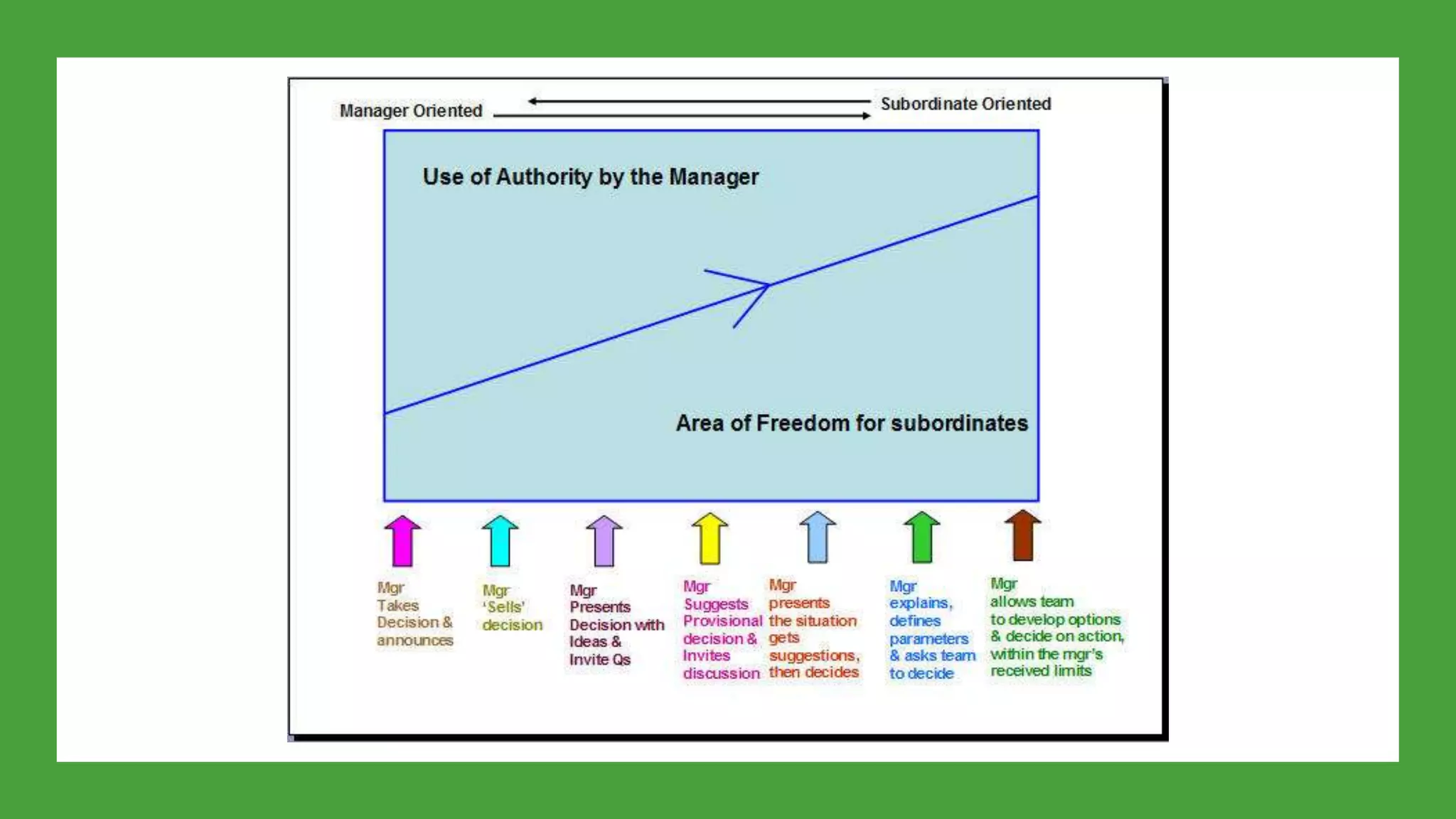
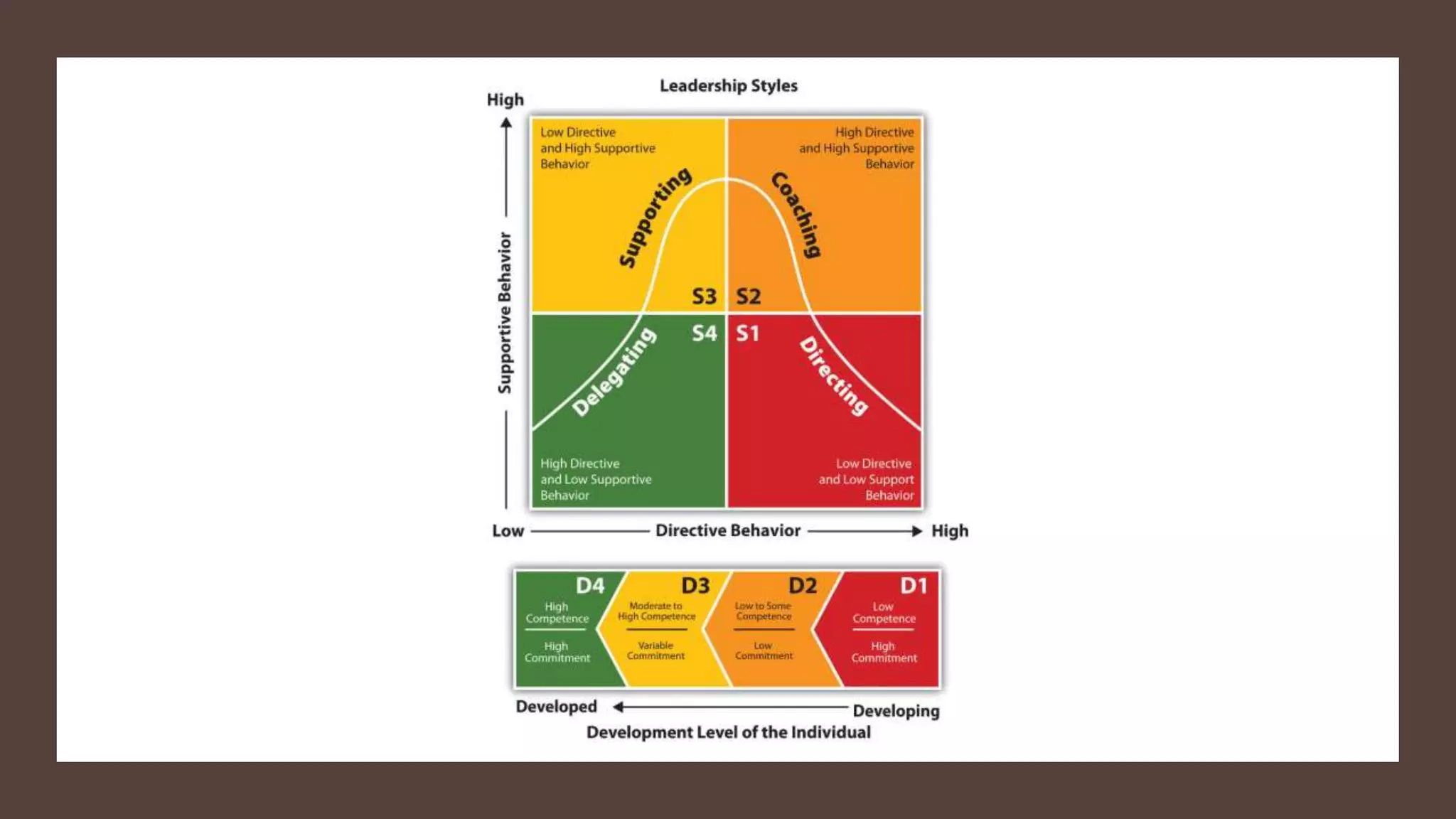
This document outlines the key points from a training course on tools for leading teams. The course covers characteristics of high-performing teams, stages of team development, tools for leading teams, roles in teams, managing conflict and developing team culture. It discusses defining competence, balancing task and relationship focus, different leadership styles, and differences between managers and leaders. It emphasizes being flexible in leadership approach and applying the tools in practice.