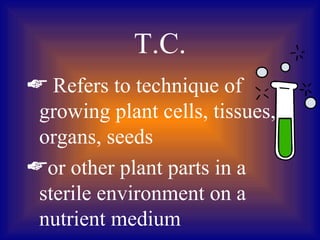
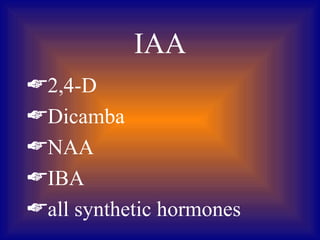
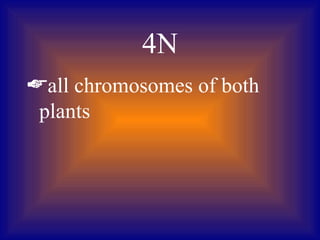
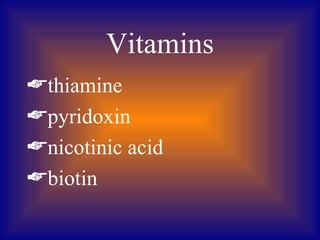
Plant tissue culture involves growing plant cells, tissues, or organs in a sterile nutrient medium. Key developments included the discovery that single plant cells could be cultured in 1902, the role of growth regulators in the 1930s, and the development of techniques like protoplast fusion and genetic engineering in the 1970s-1980s. Successful tissue culture involves explant preparation, multiplication of cultures, rooting, and transplantation to the greenhouse. Various methods can be used to introduce foreign DNA, including Agrobacterium infection, microinjection, and electroporation.