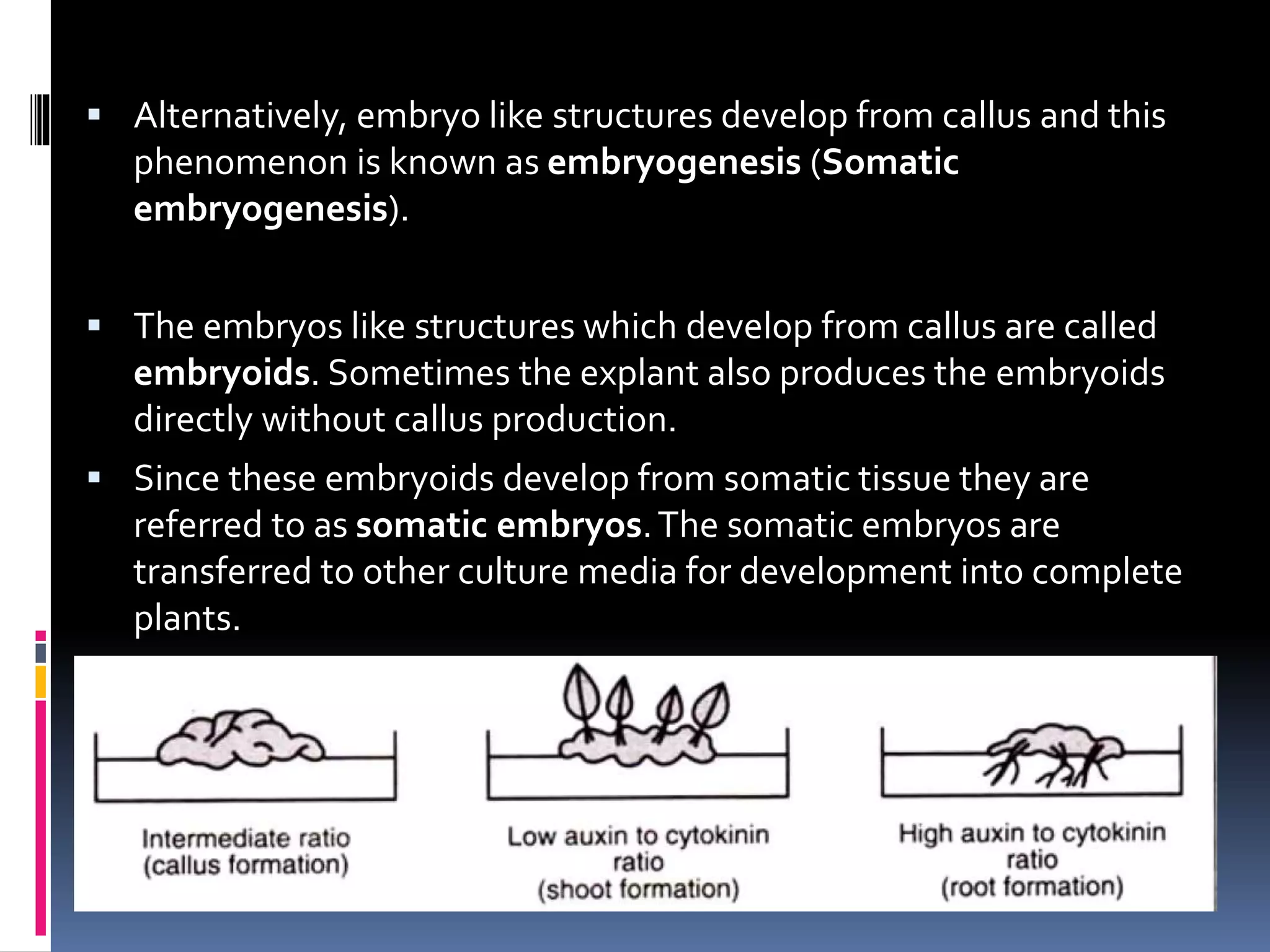
This document provides an introduction to plant tissue culture. It describes how plant parts can be grown in vitro in artificial nutrient media. The key aspects covered are the types of explants used, applications of plant tissue culture, essential operations, techniques like callus and suspension cultures, steps involved like preparation of media, sterilization, incubation, and acclimatization of plants. Common components of nutrient media and roles of plant hormones are also summarized.