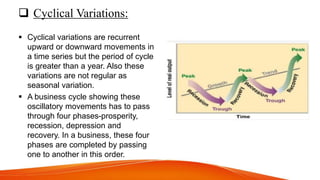
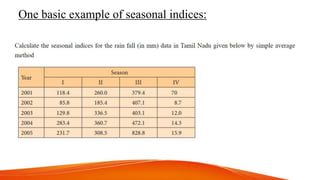
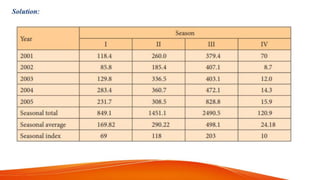
The document discusses time series analysis and seasonal indices. It begins with definitions of time series and their key components: secular trend, seasonal variation, cyclical variation, and irregular variation. An example is given of seasonal indices using monthly sales data, where the seasonal index is calculated by dividing the monthly sales by the 12-month moving average. Seasonal indices are used to smooth time series data and aid in predicting future values by accounting for typical seasonal fluctuations. The document provides an overview of time series components and the basic use of seasonal indices.