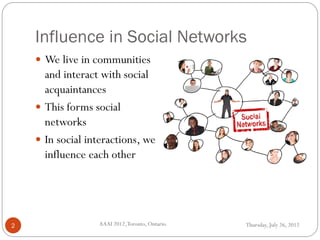
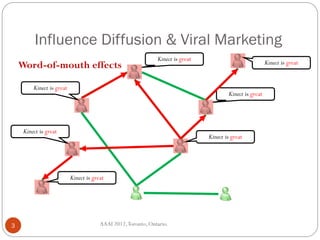
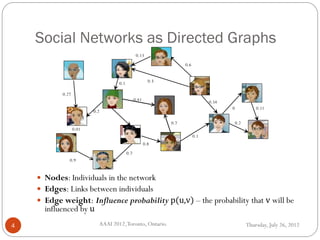
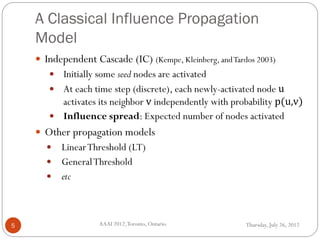
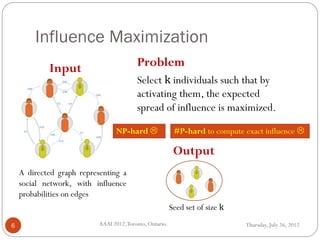
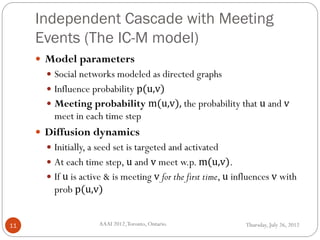
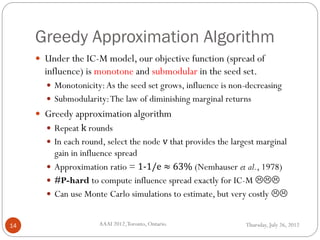
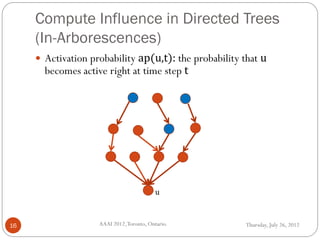
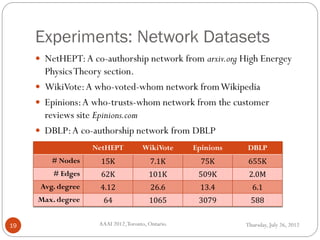
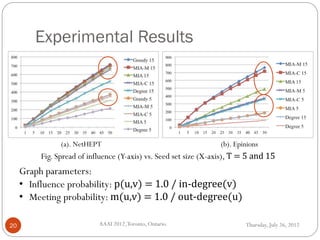
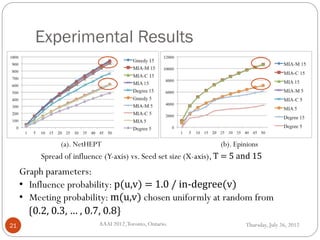
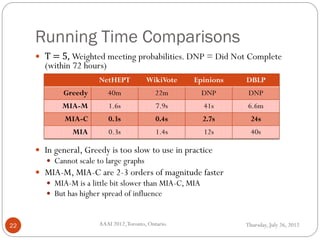
The document discusses time-critical influence maximization in social networks, specifically extending the classical independent cascade model to account for meeting events and time constraints. It addresses the complexities and computational challenges involved in maximizing influence spread within a limited time, presenting new heuristics and algorithms for efficient implementation. The findings highlight the significance of temporal aspects in influence diffusion, with experiments demonstrating the algorithms' performance on various network datasets.