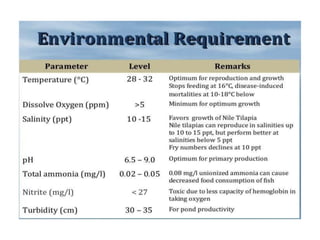
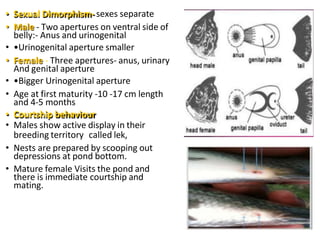
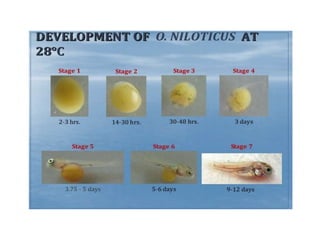
Tilapia breeding is important for global aquaculture production and food security. Nile tilapia is the most commonly farmed species due to its fast growth, high reproduction rates, and ability to thrive in various environments. Tilapia can be bred through mixed-sex or mono-sex culture. Mono-sex male culture is preferred for commercial farms since males grow larger. Methods to produce male-only populations include manual sexing, hybridization with other species, hormone treatment of fry, and genetic manipulation. Hormone treatments typically involve feeding fry diets supplemented with steroids like 17-alpha methyltestosterone.