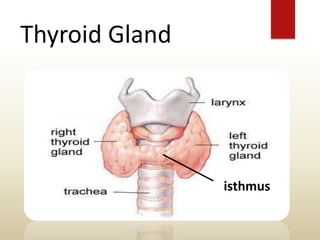
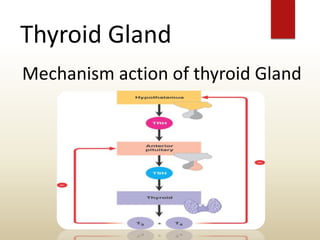
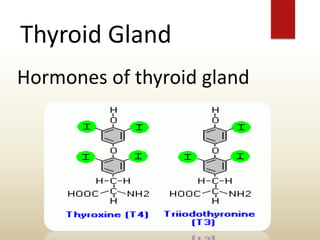
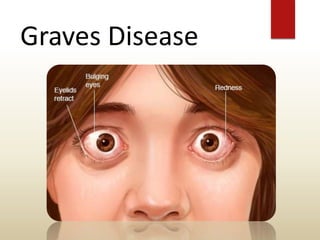
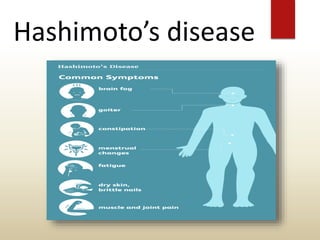
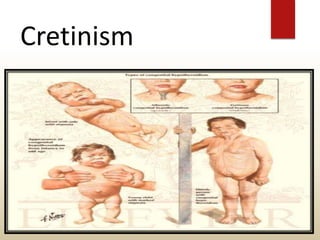
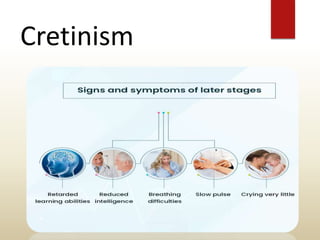
The document provides an overview of the thyroid gland, including its anatomy, hormones, and physiological functions, as well as disorders like hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. It discusses various conditions related to thyroid dysfunction, such as Graves' disease and Hashimoto's disease, along with their symptoms and treatments. Prevention strategies and treatment options for thyroid-related disorders are also outlined.