The document outlines Bangladesh's 7th Five Year Plan from 2016-2020. Some key points:
- The plan aims to accelerate economic growth to 8% annually while empowering citizens through job creation, skills development, and access to credit.
- Major goals include reducing poverty and inequality, boosting sectors like manufacturing, exports, and infrastructure development.
- Targets also focus on human development through education, health, water and sanitation improvements.
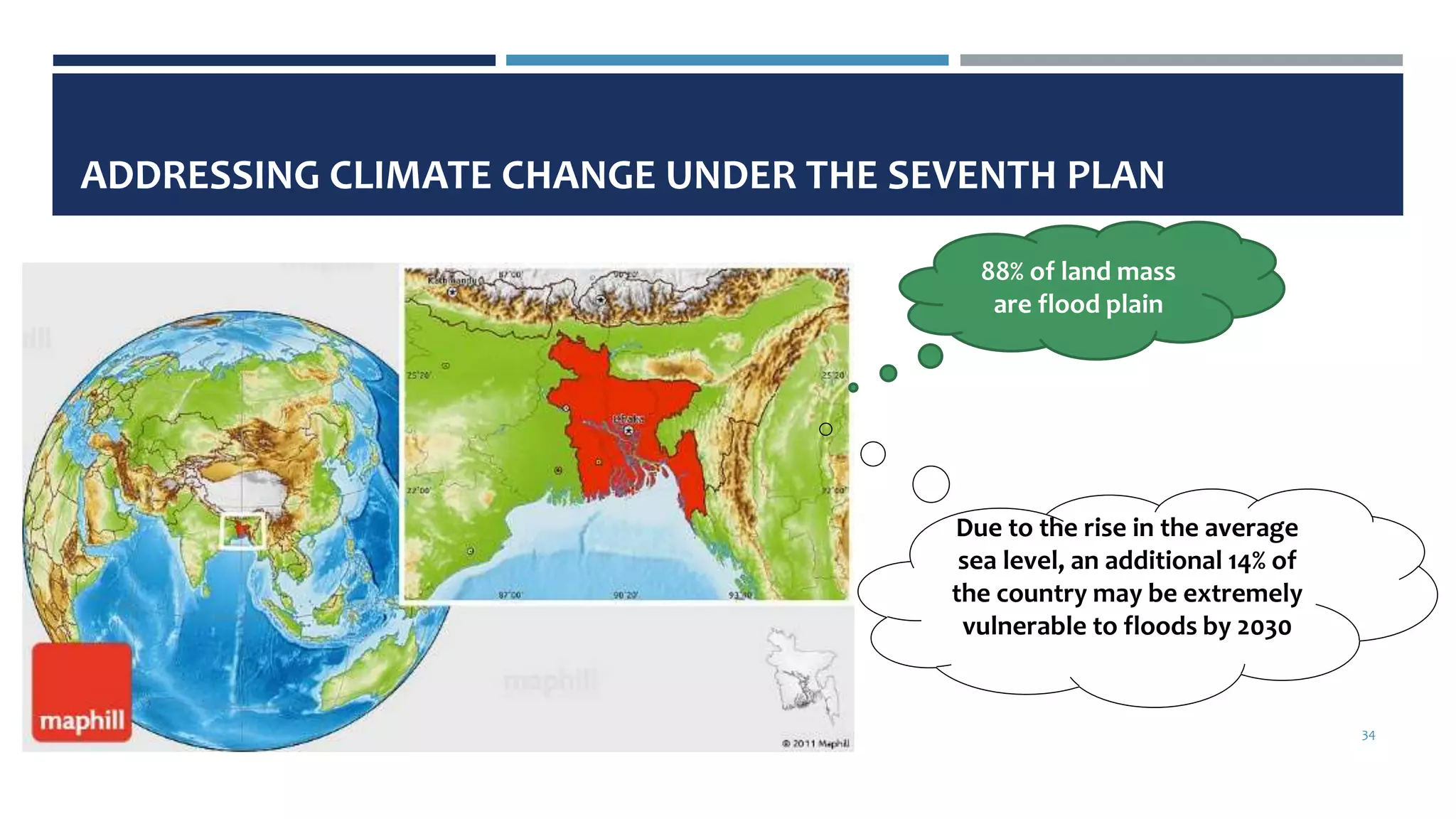
- The plan emphasizes sustainable and inclusive development, urban transition management, and building resilience against climate change and disasters.