1) Acute limb ischemia is a sudden decrease in blood flow to a limb that threatens viability and requires urgent treatment. It has an incidence of about 1.5 cases per 10,000 people per year.
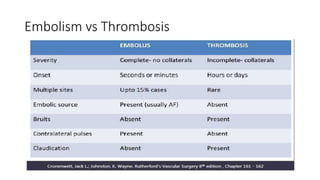
2) Causes include arterial embolism (from cardiac or arterial sources), native arterial thrombosis, arterial thrombosis after intervention, and arterial injury.
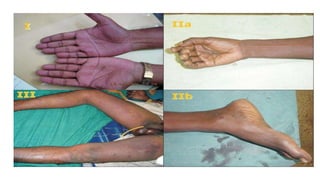
3) Diagnosis involves history, physical exam assessing pain and function, and imaging tests like Doppler ultrasound and angiography.
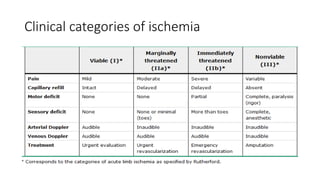
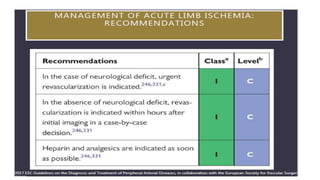
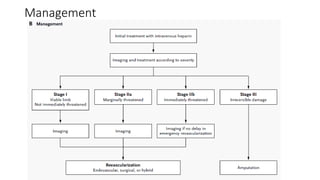
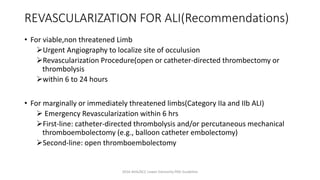
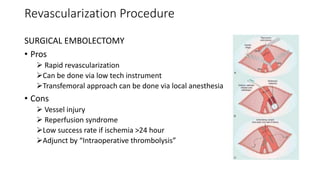
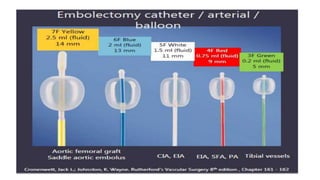
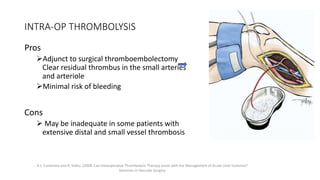
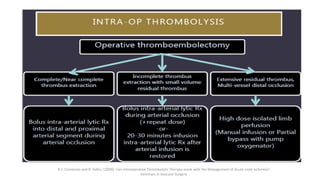
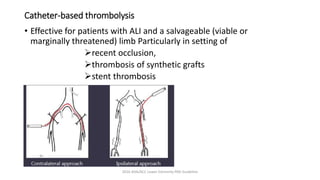
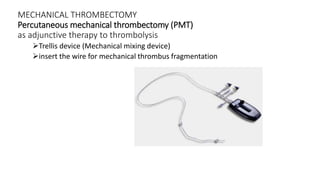
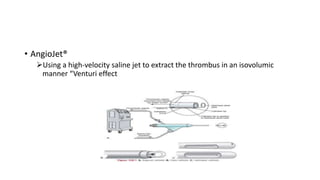
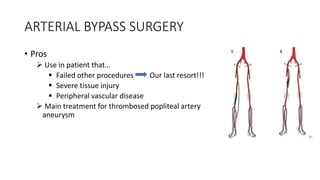
4) Treatment depends on viability of the limb and includes oxygen, fluids, anticoagulation, analgesia, and revascularization through catheter-directed thrombolysis, open surgery, or bypass if other options fail. Comp