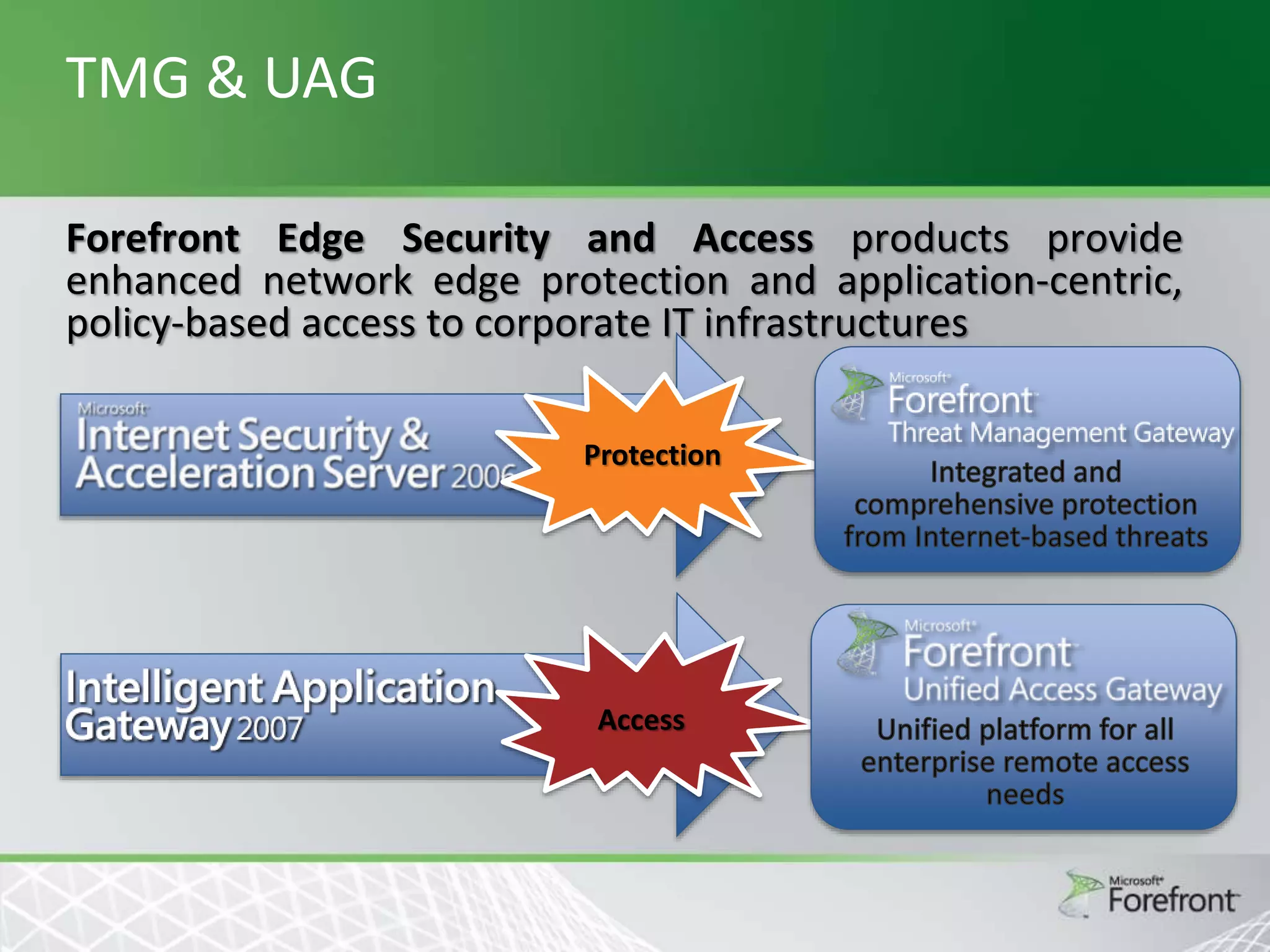
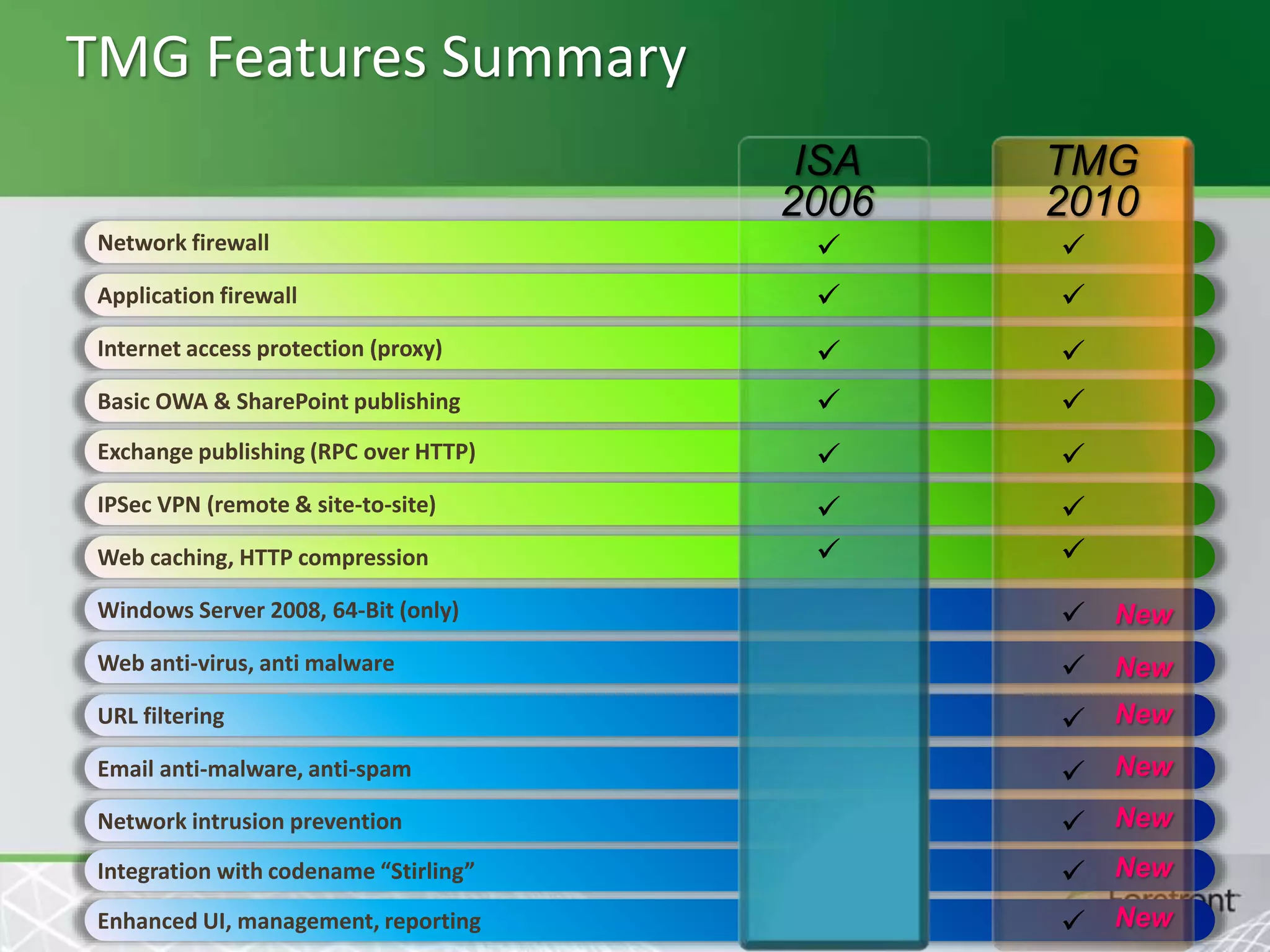
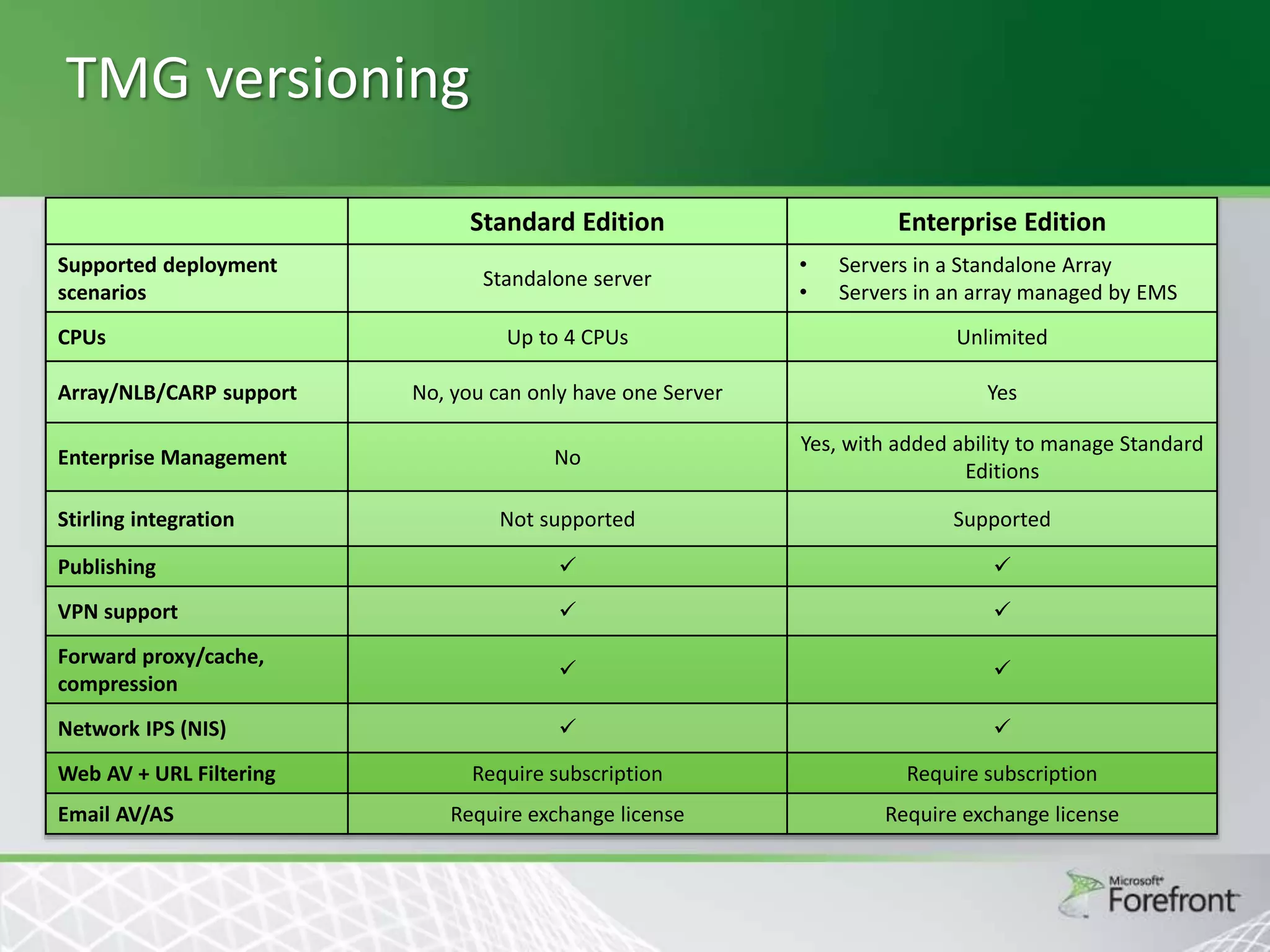
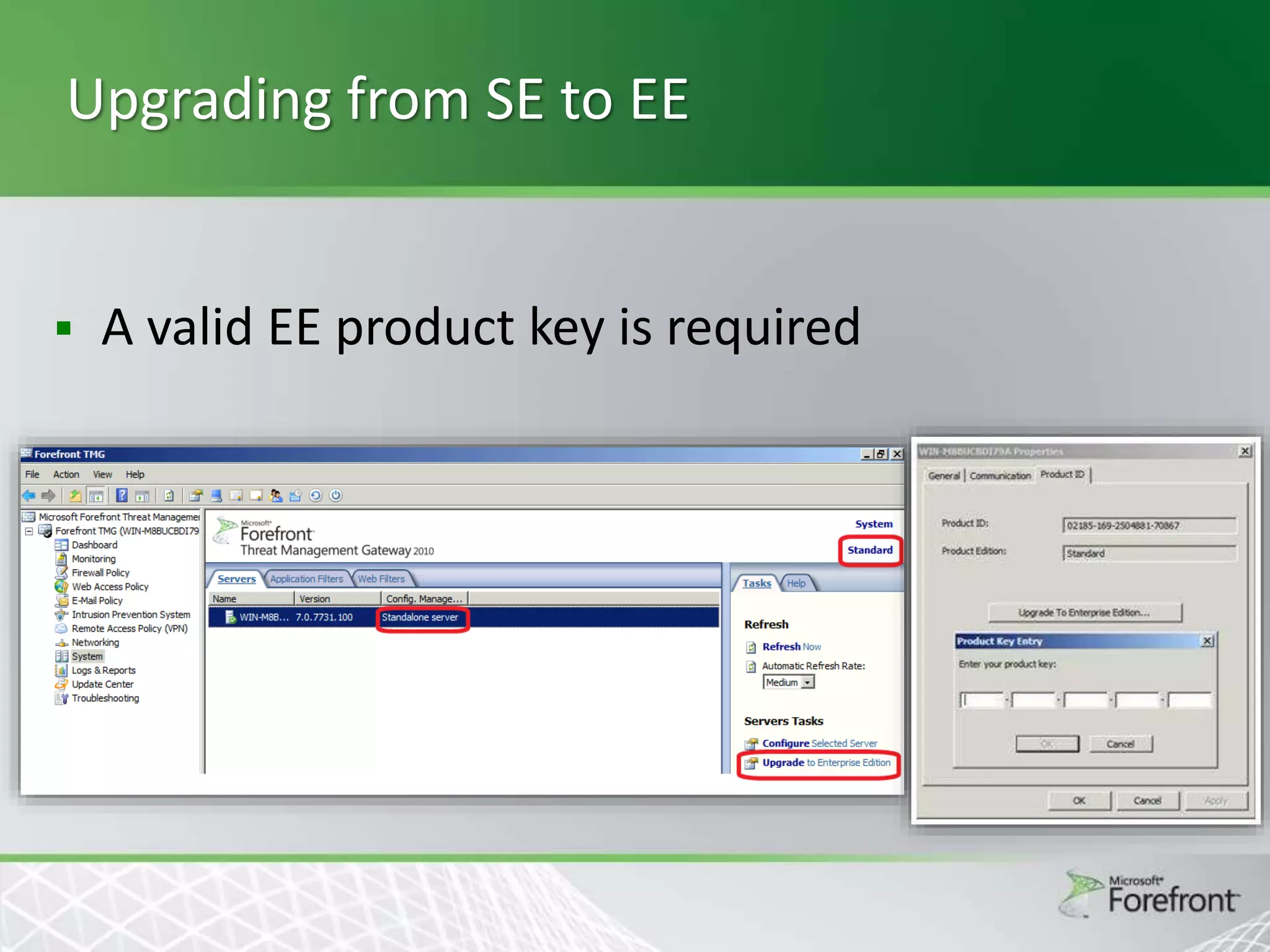
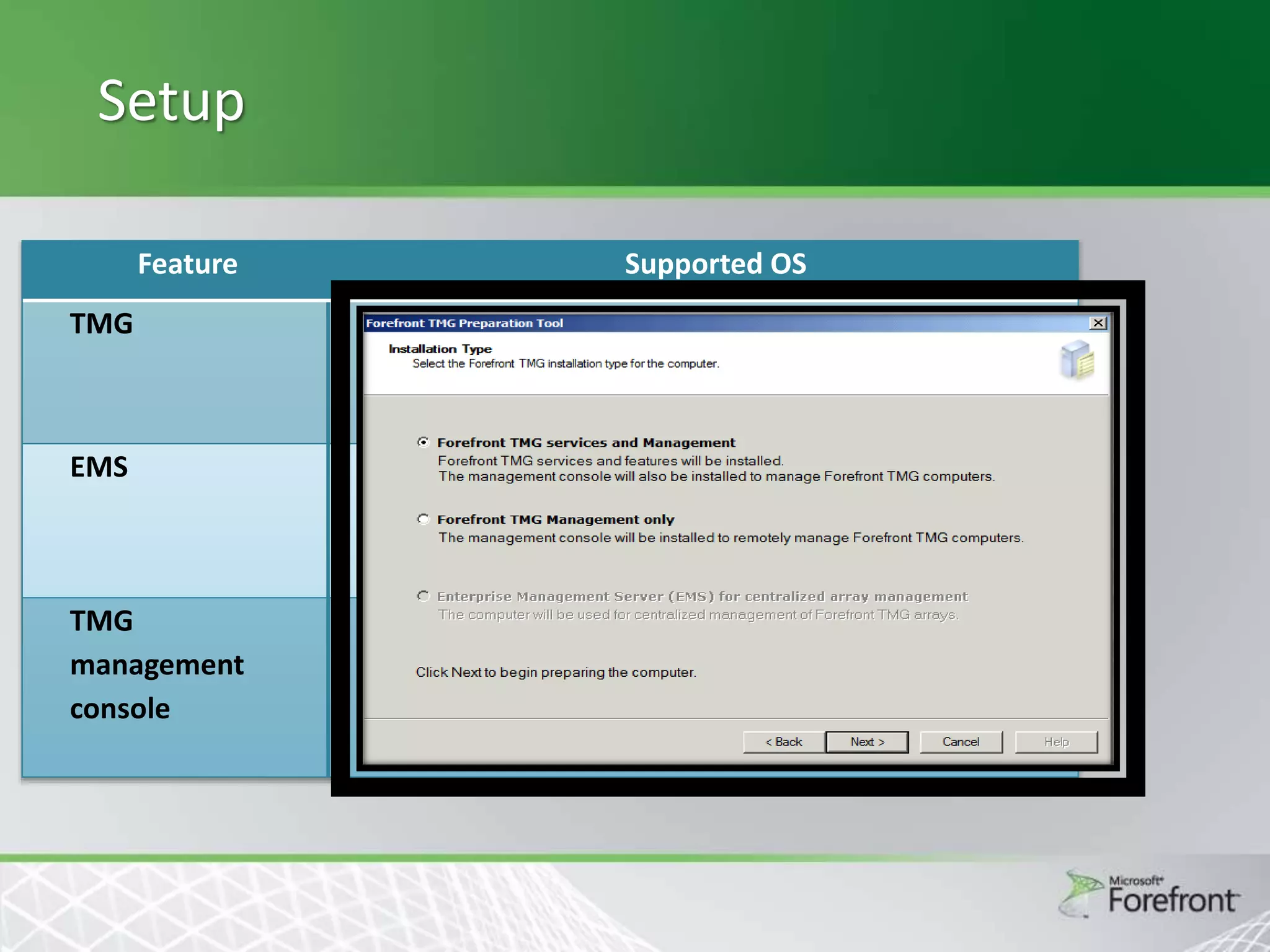
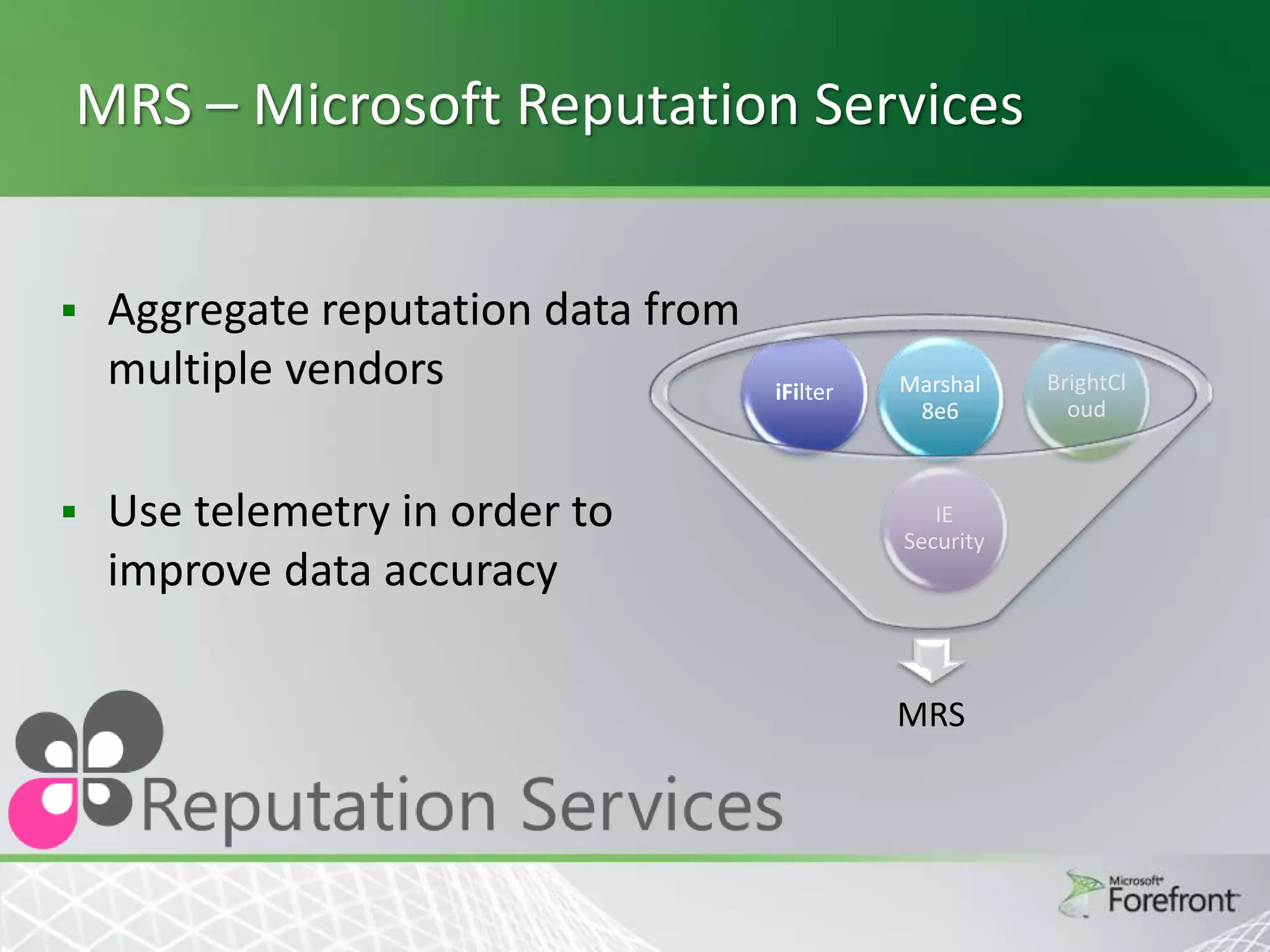
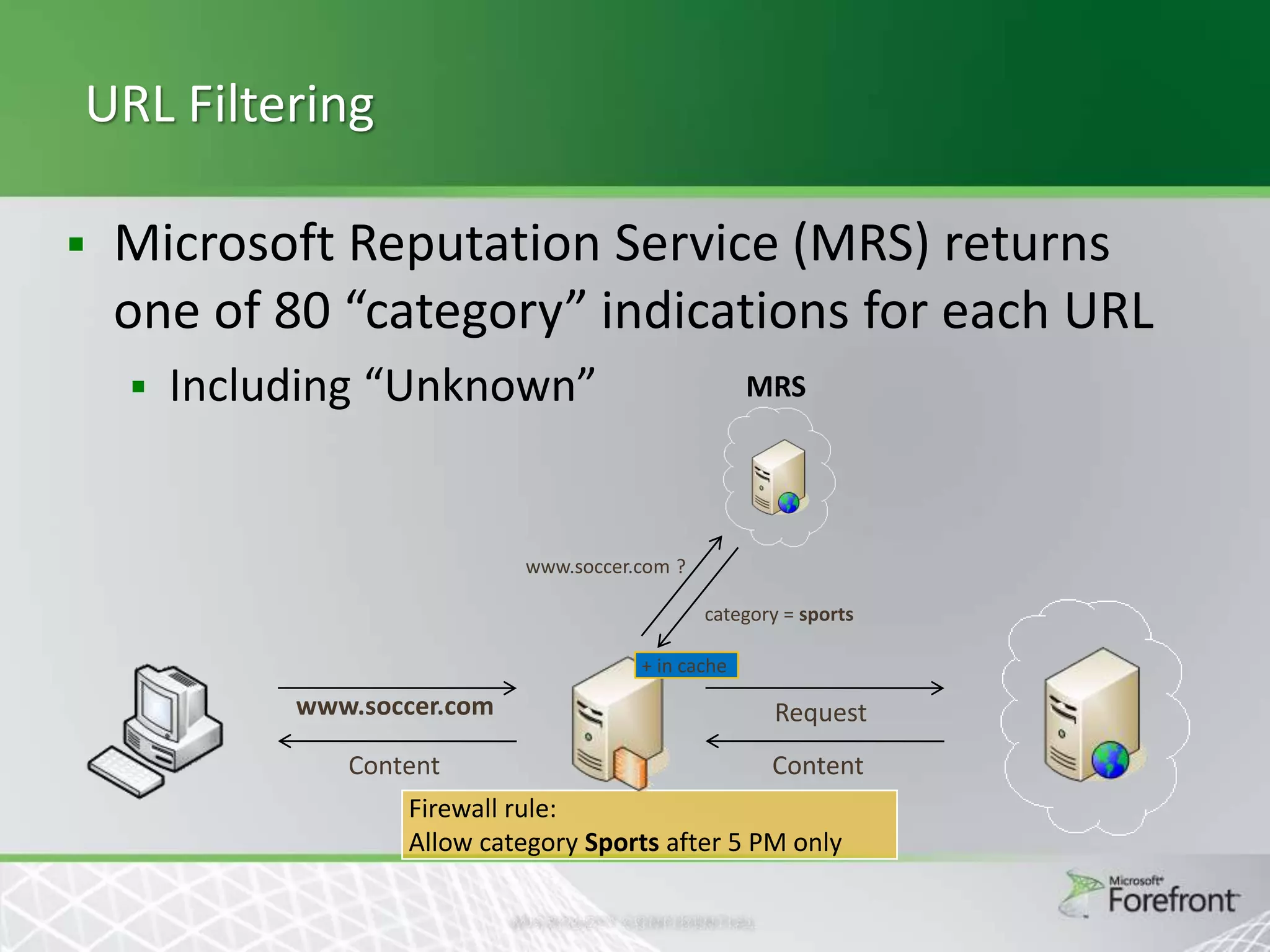
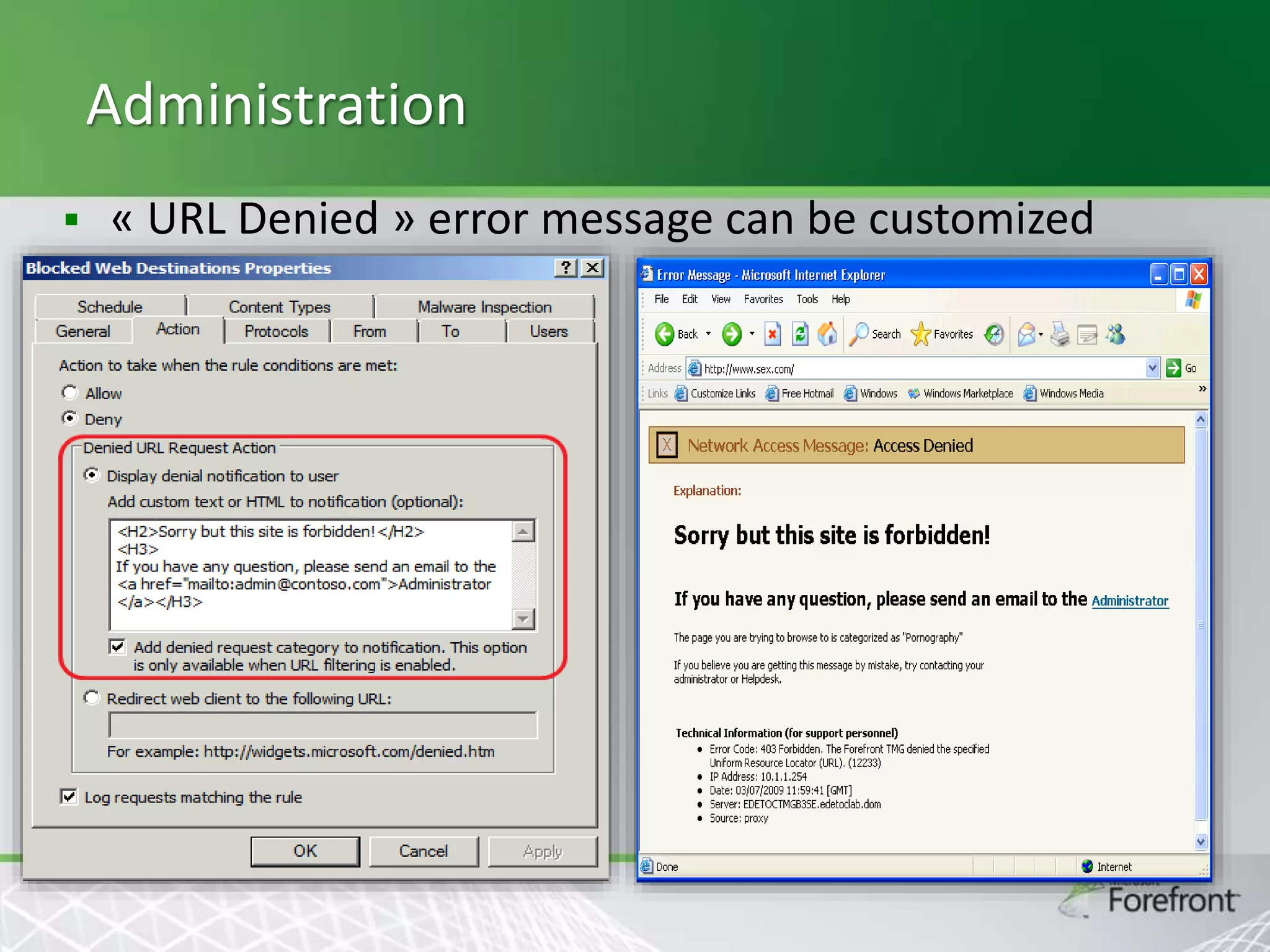
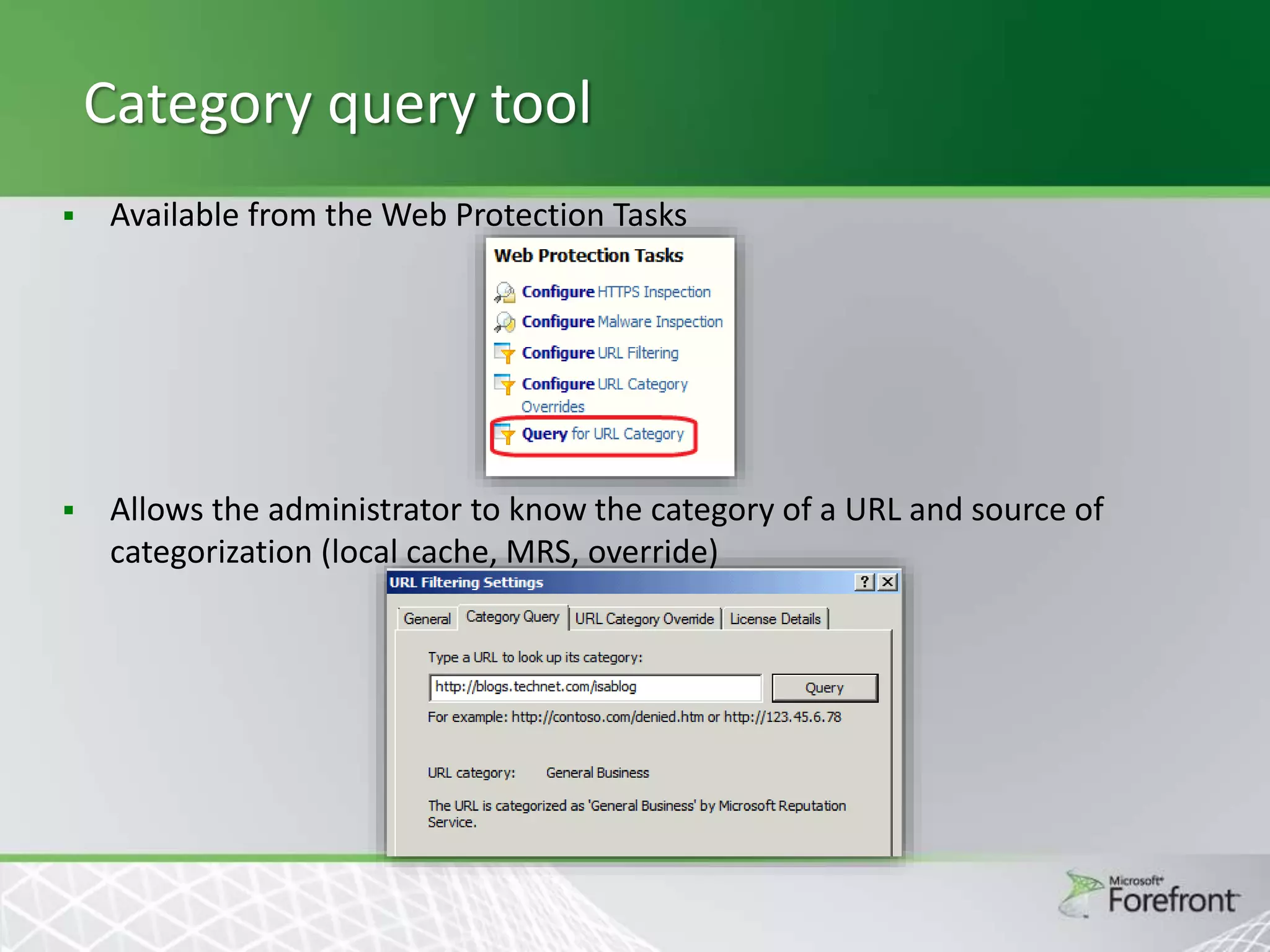
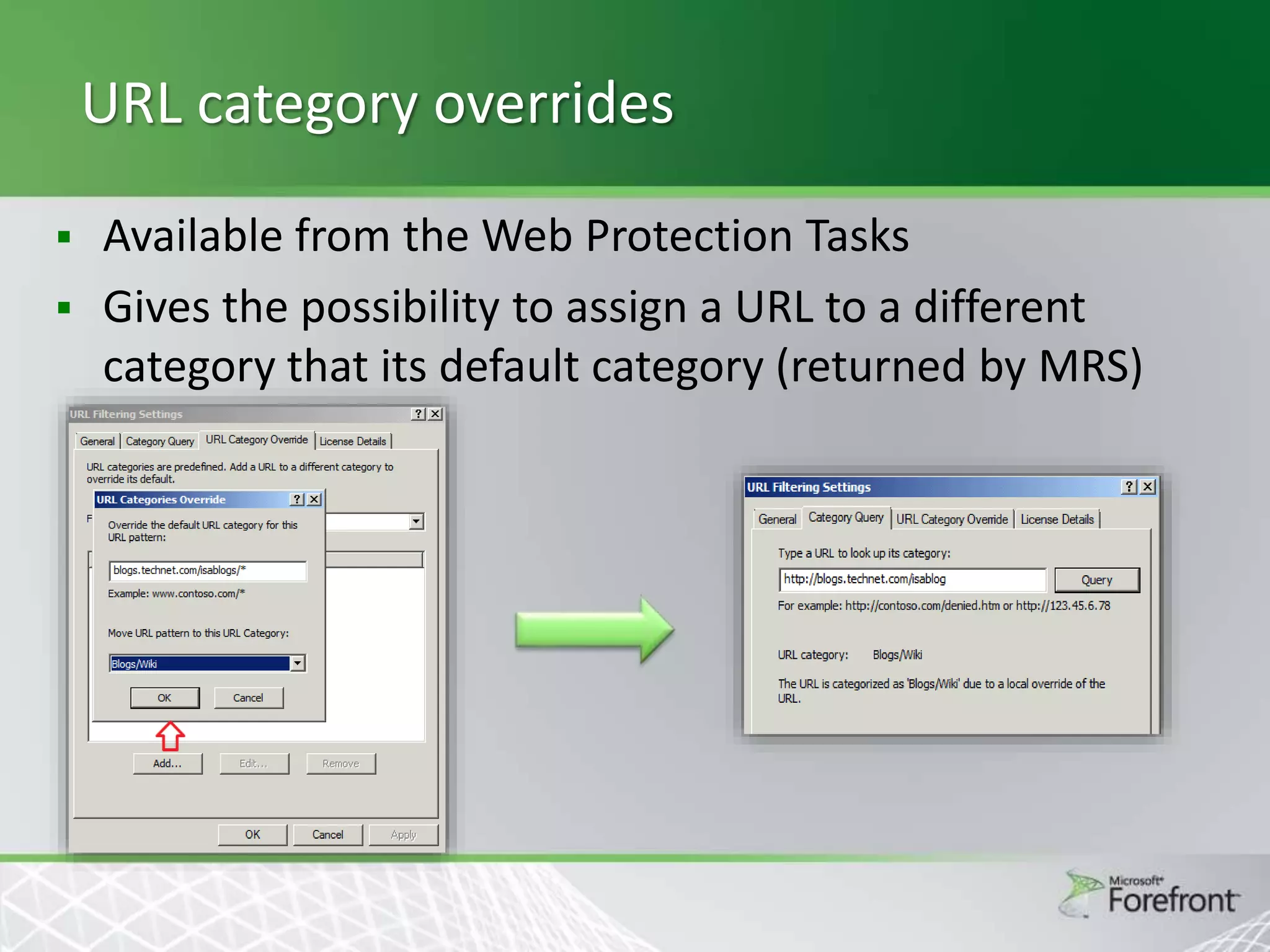
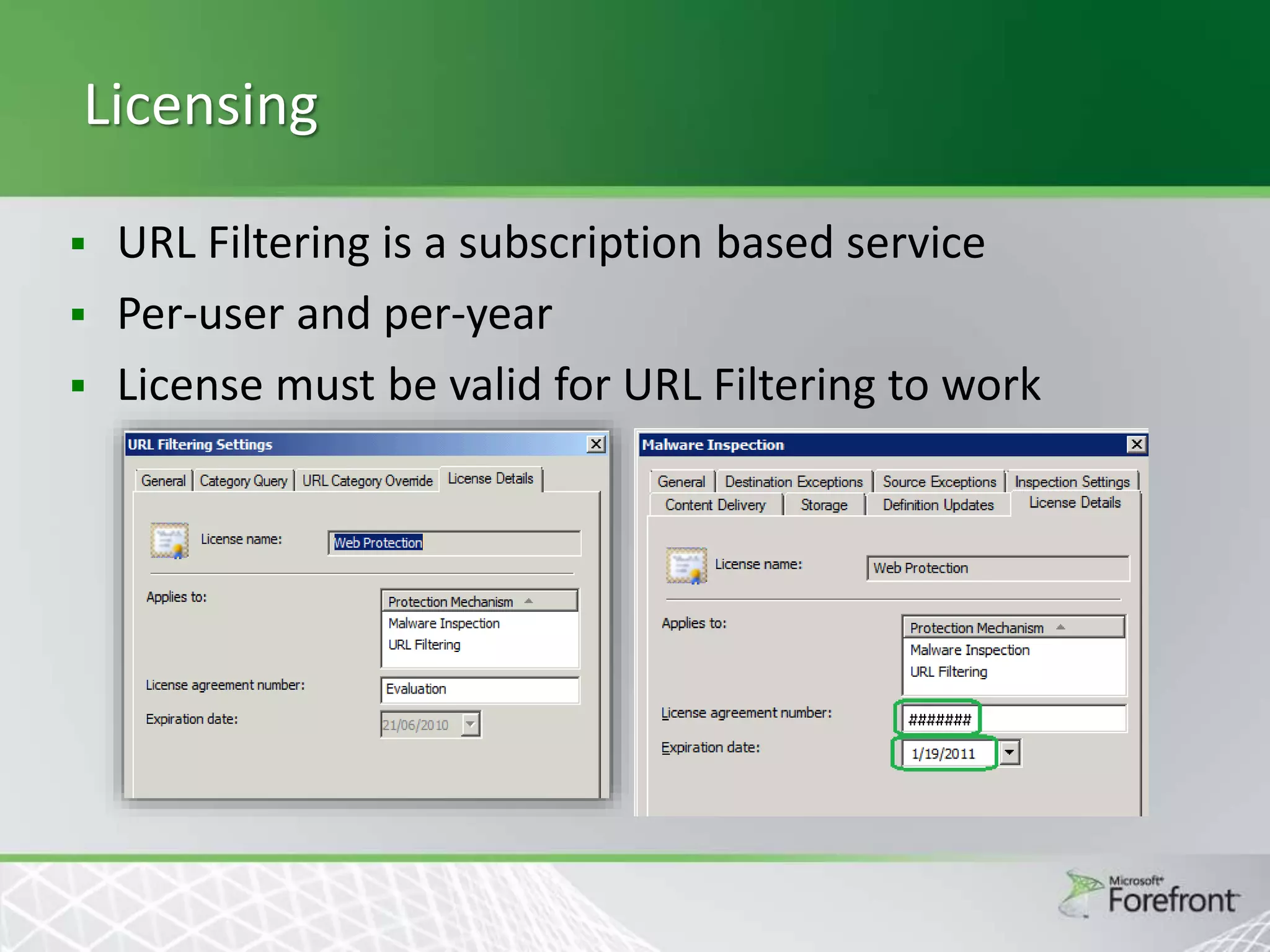
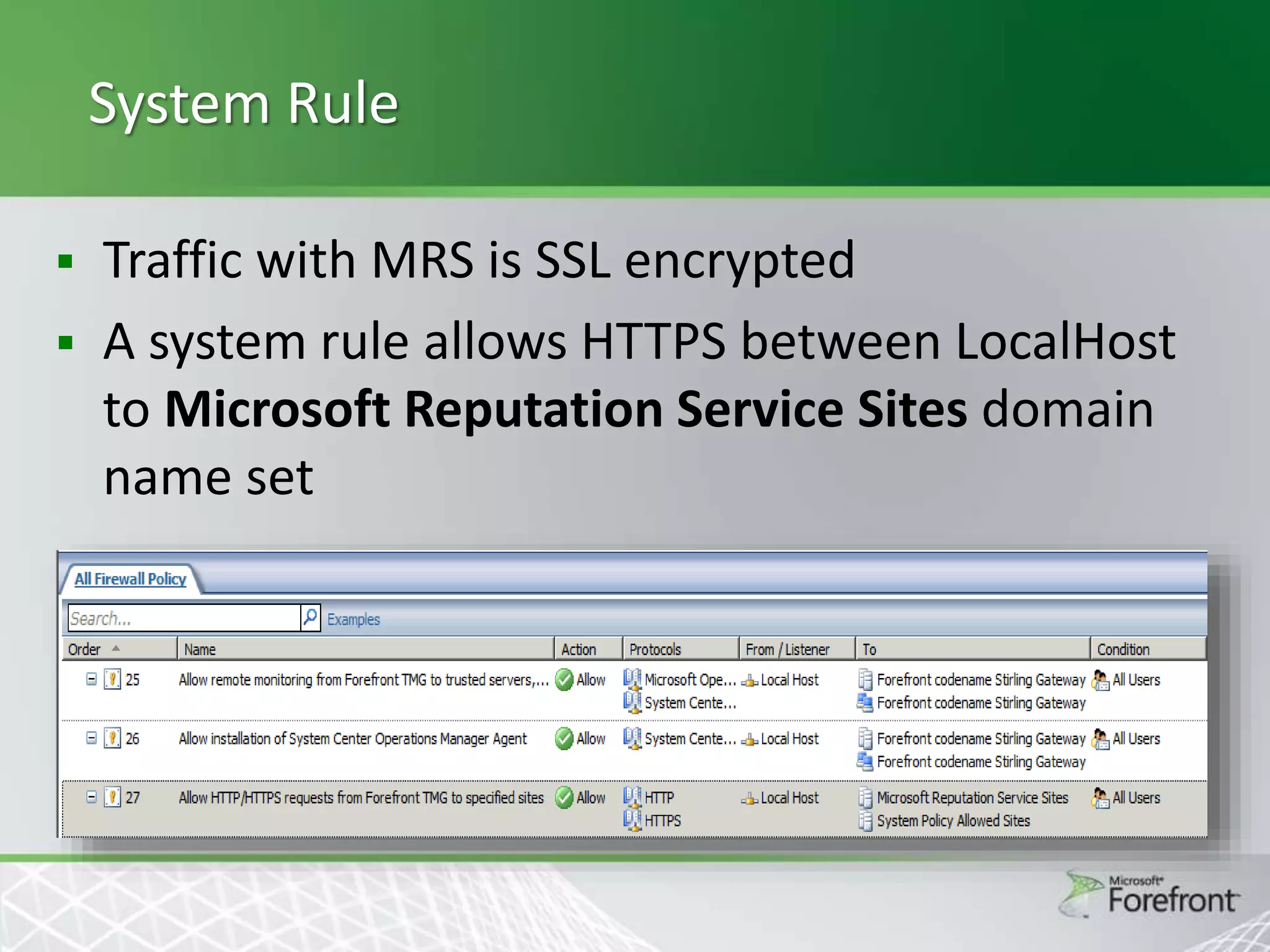
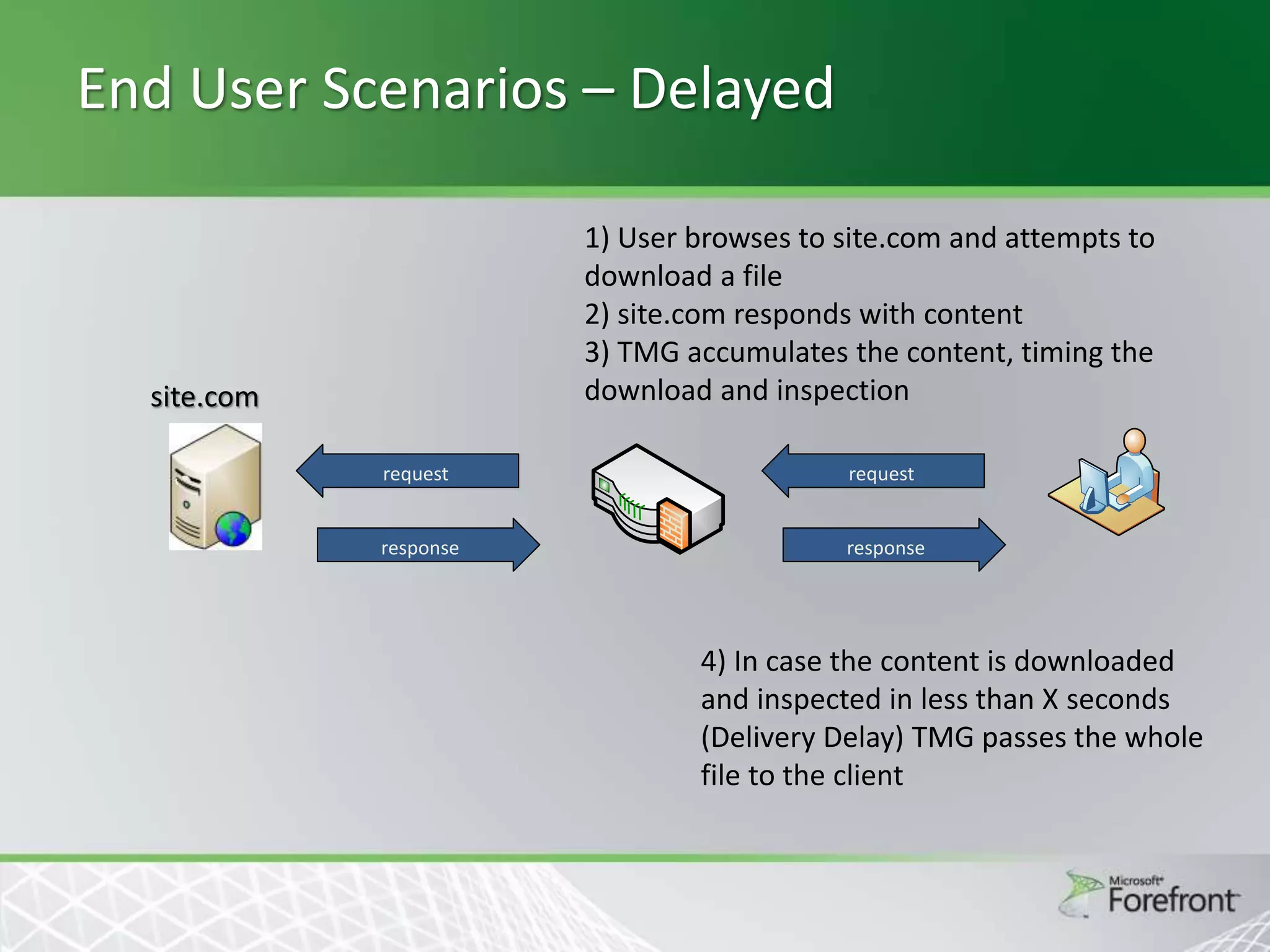
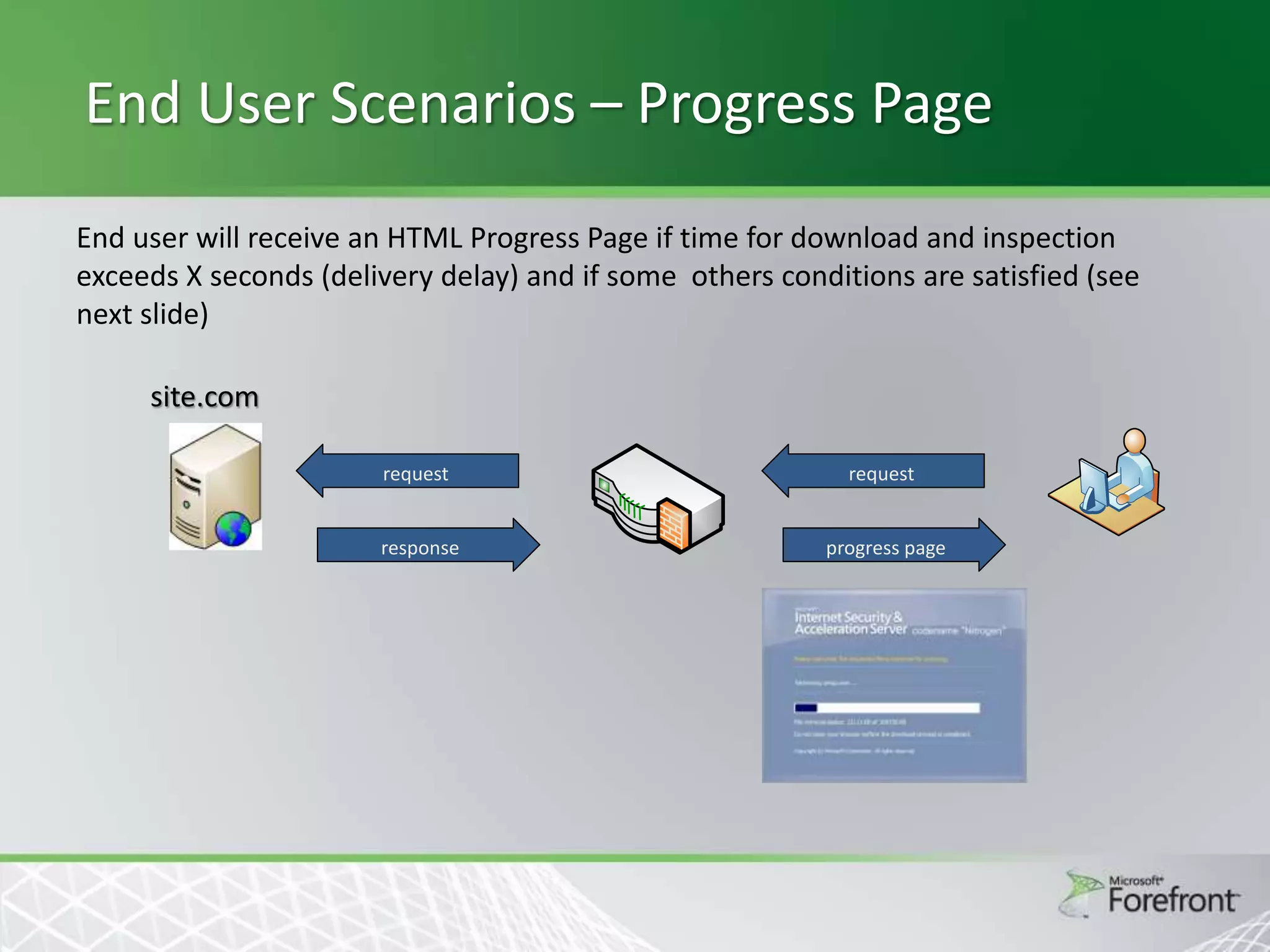
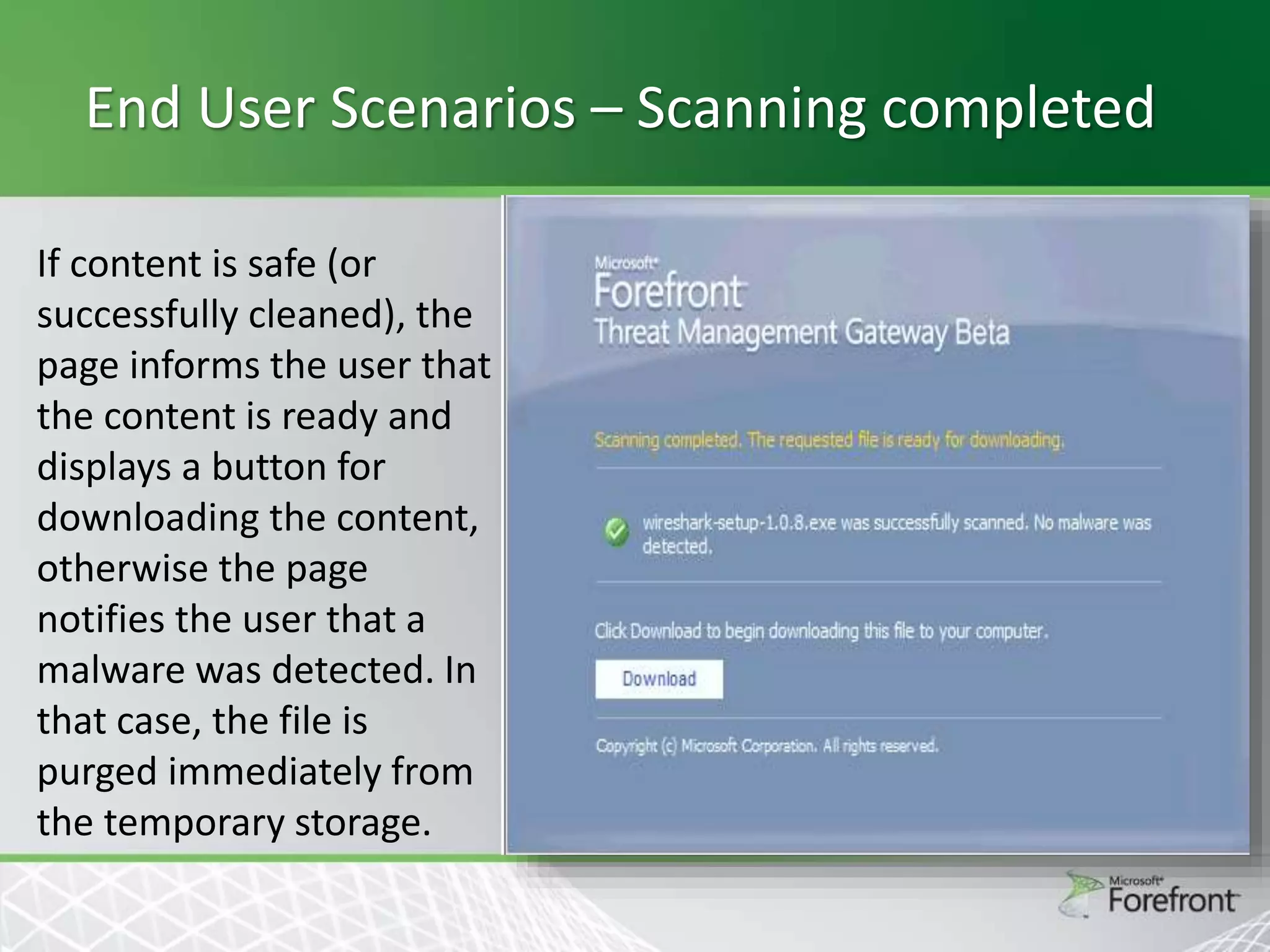
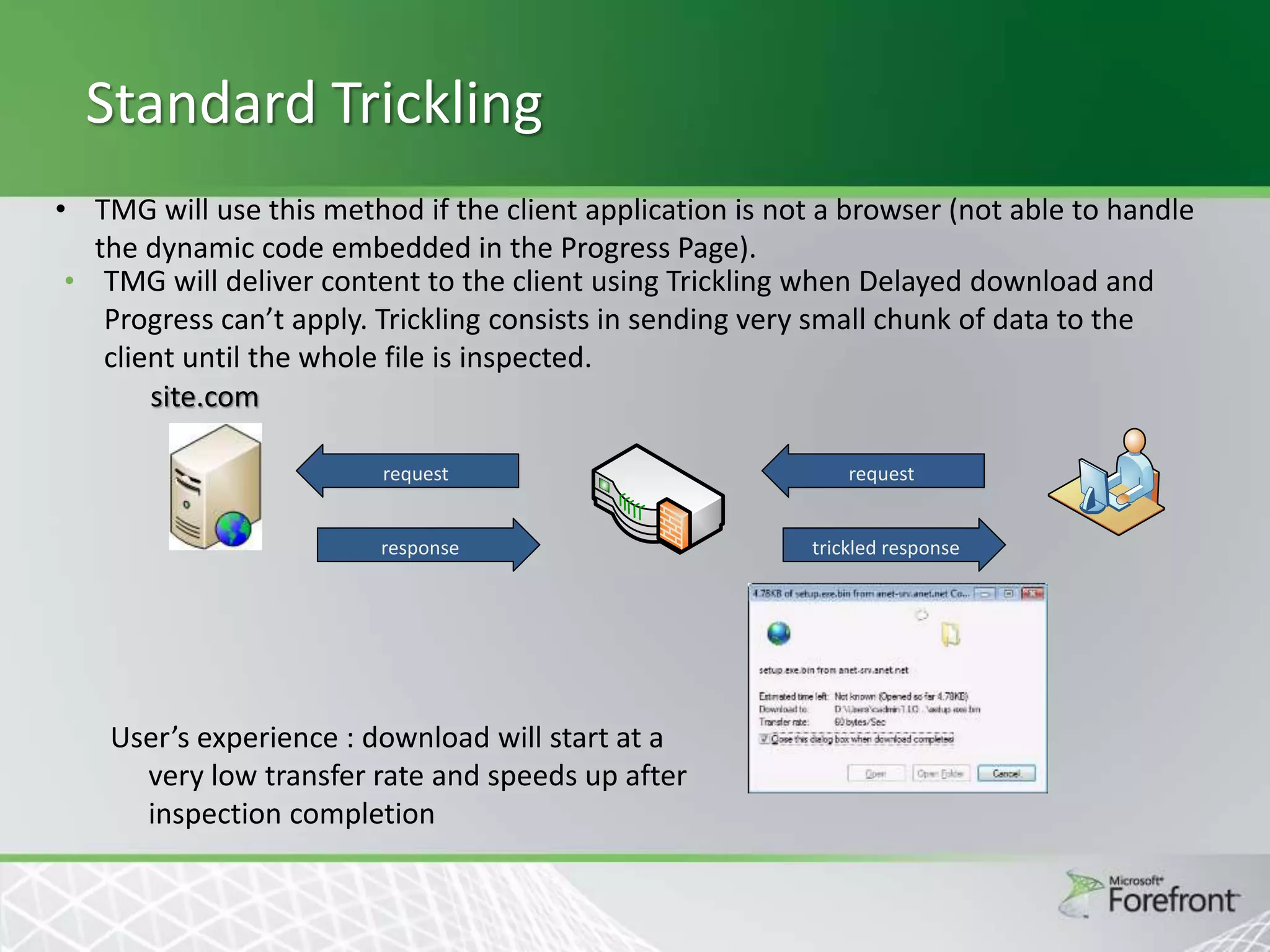
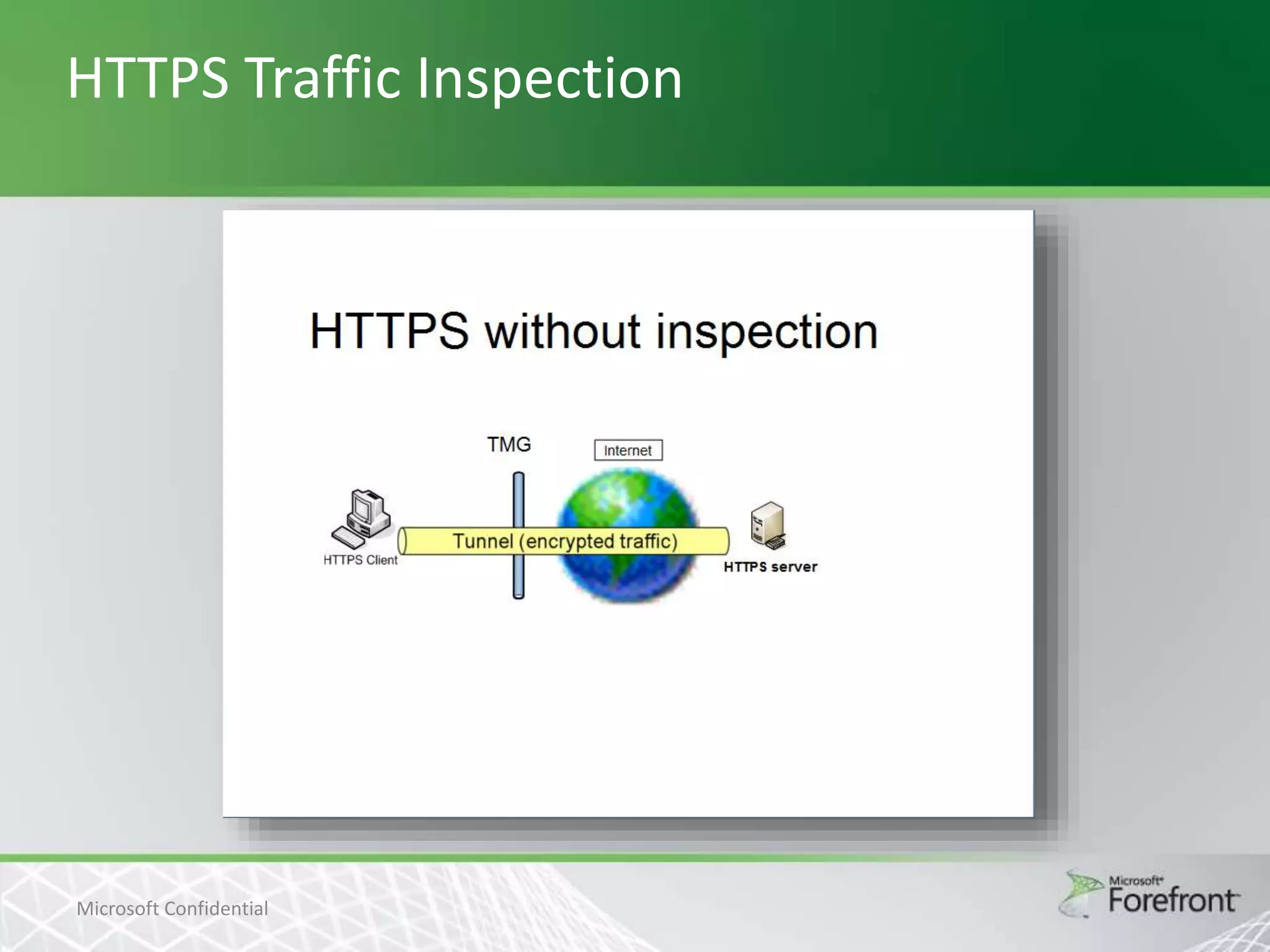
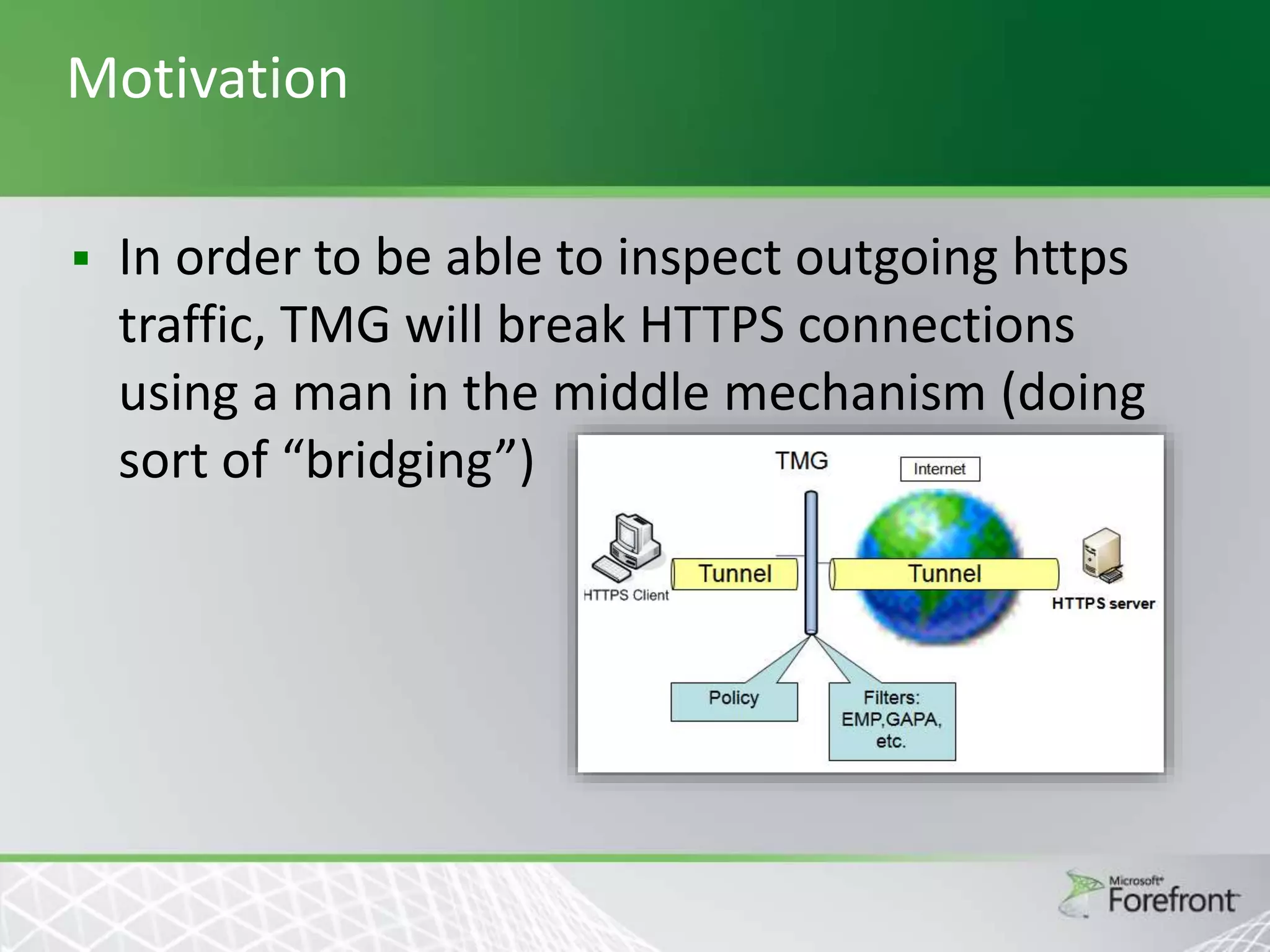
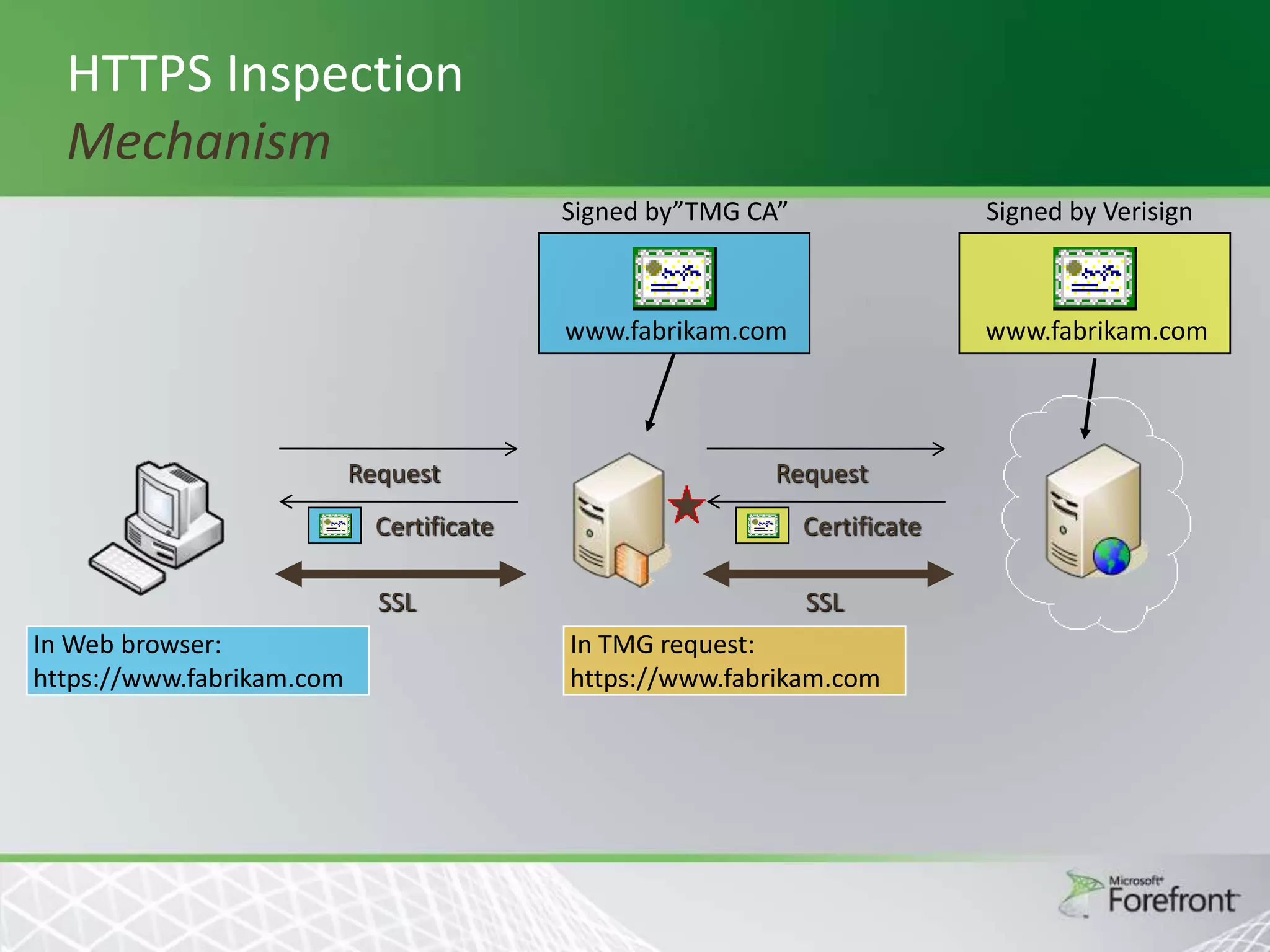
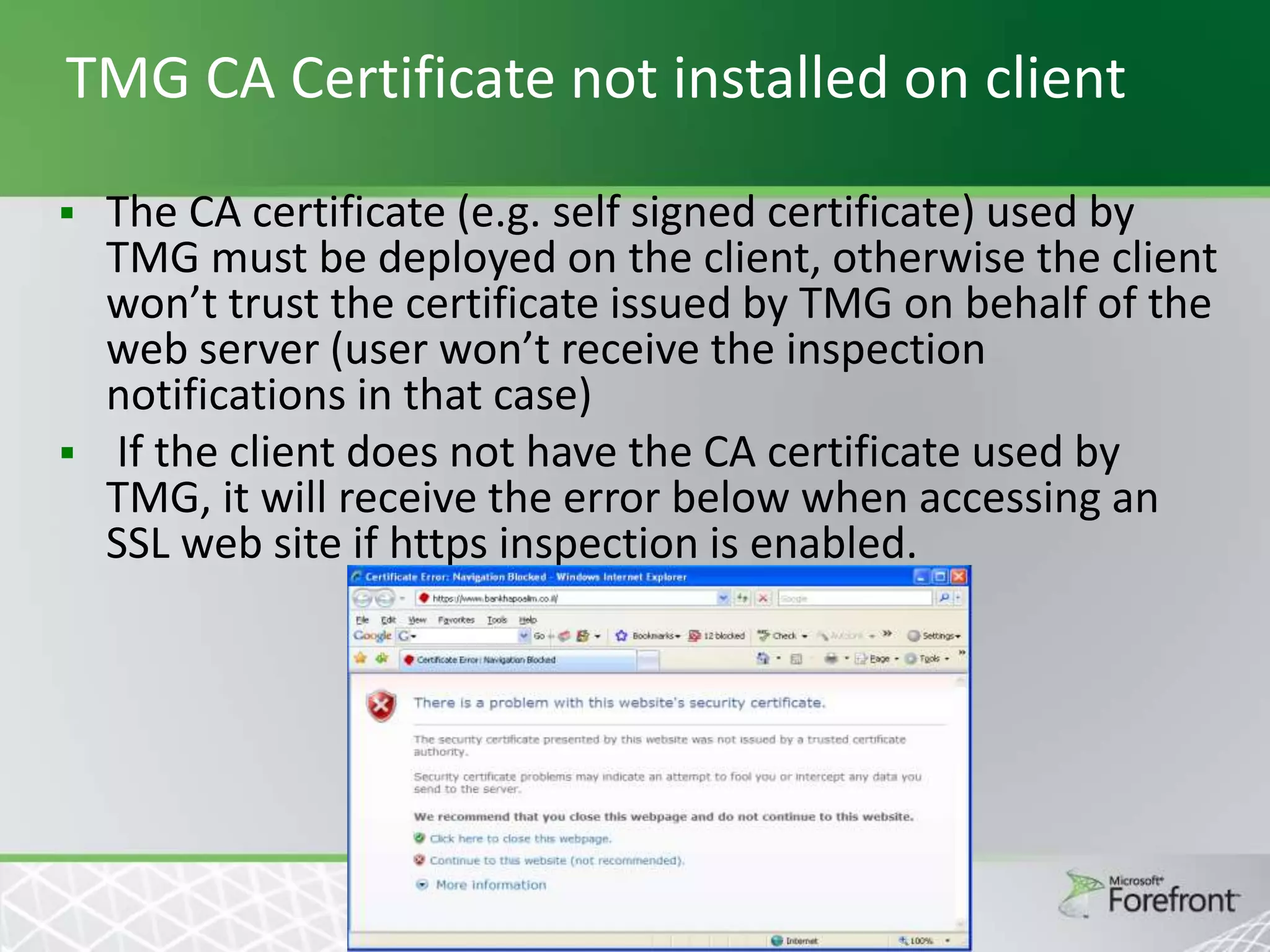
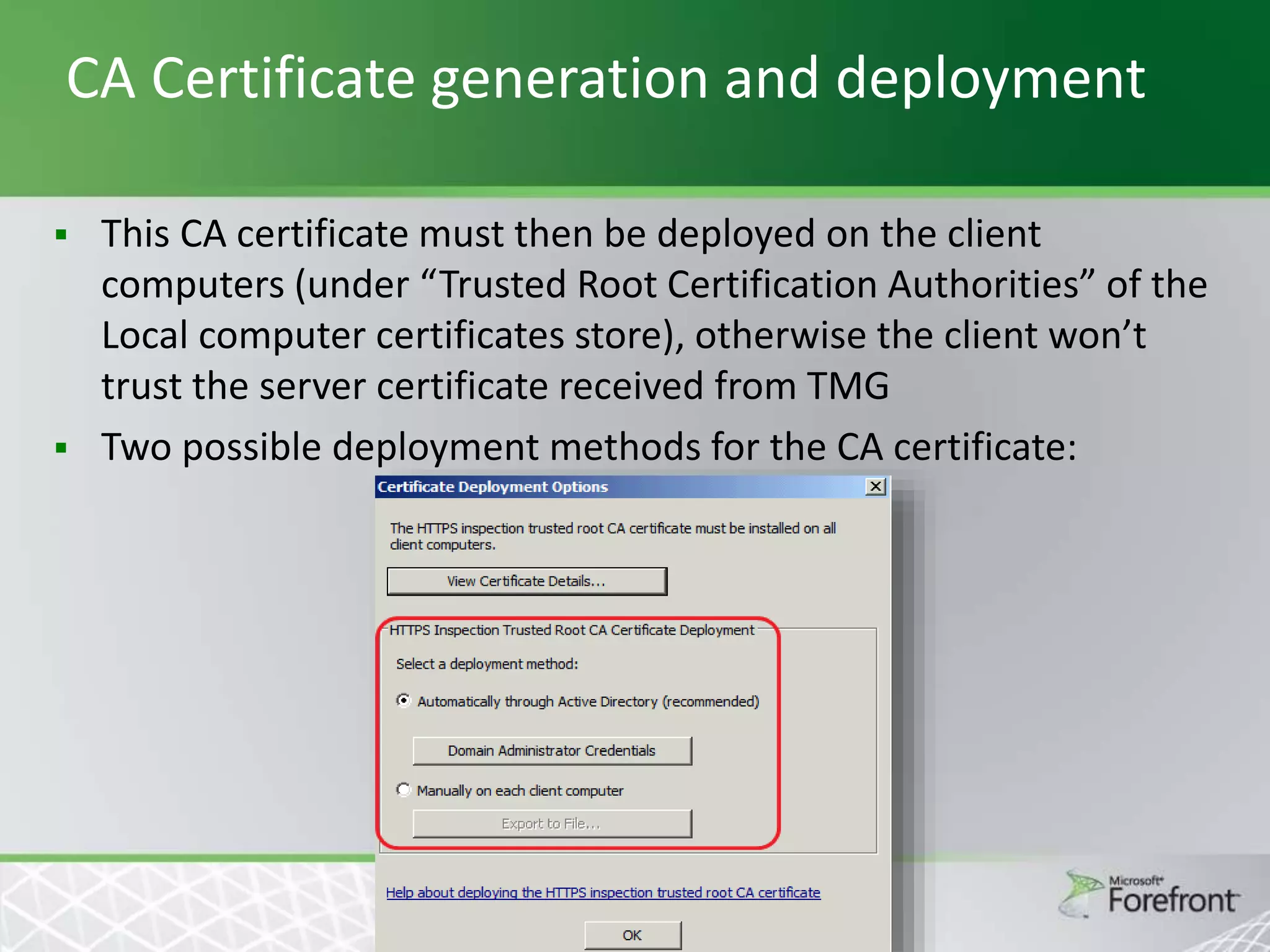
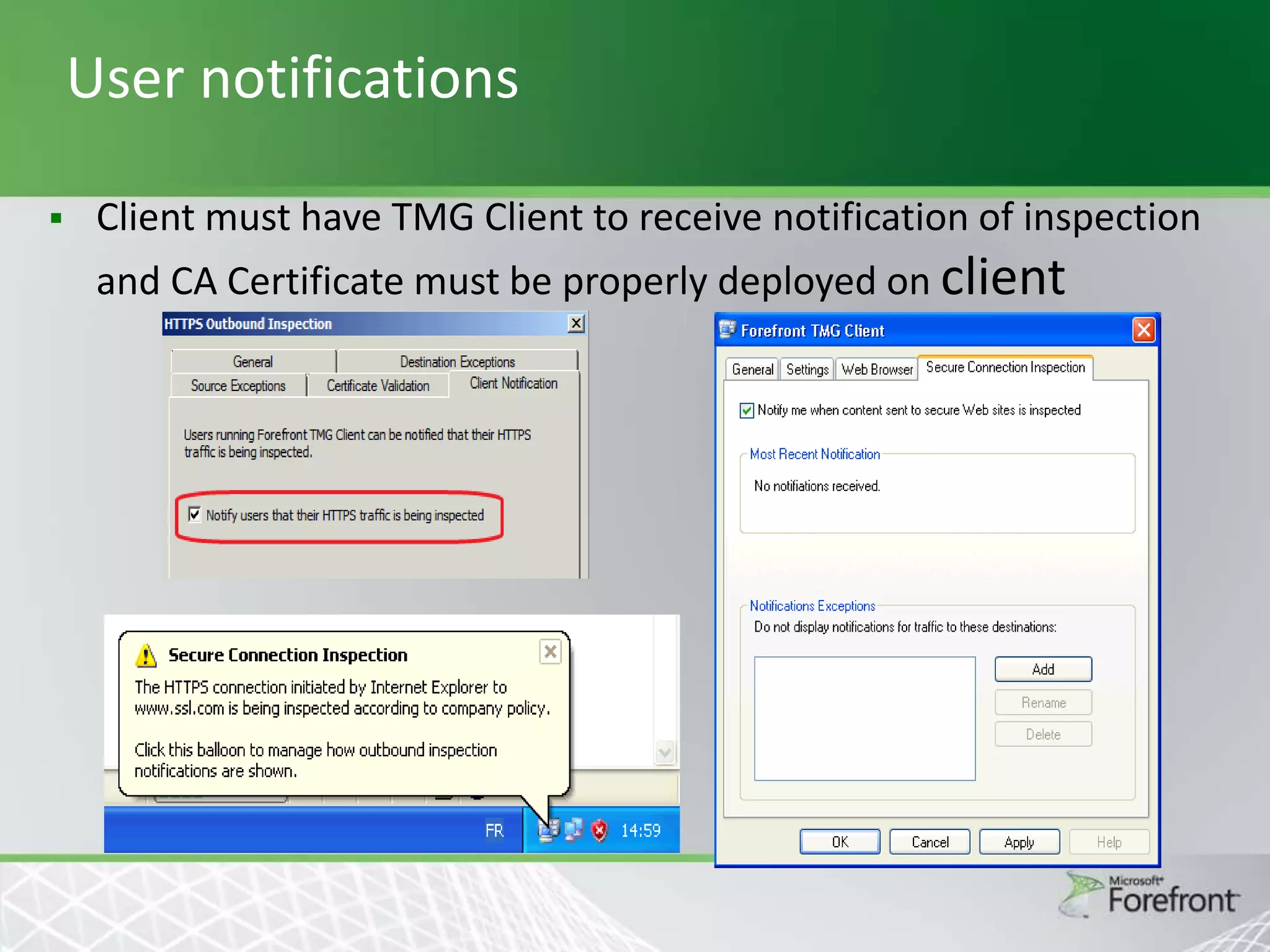
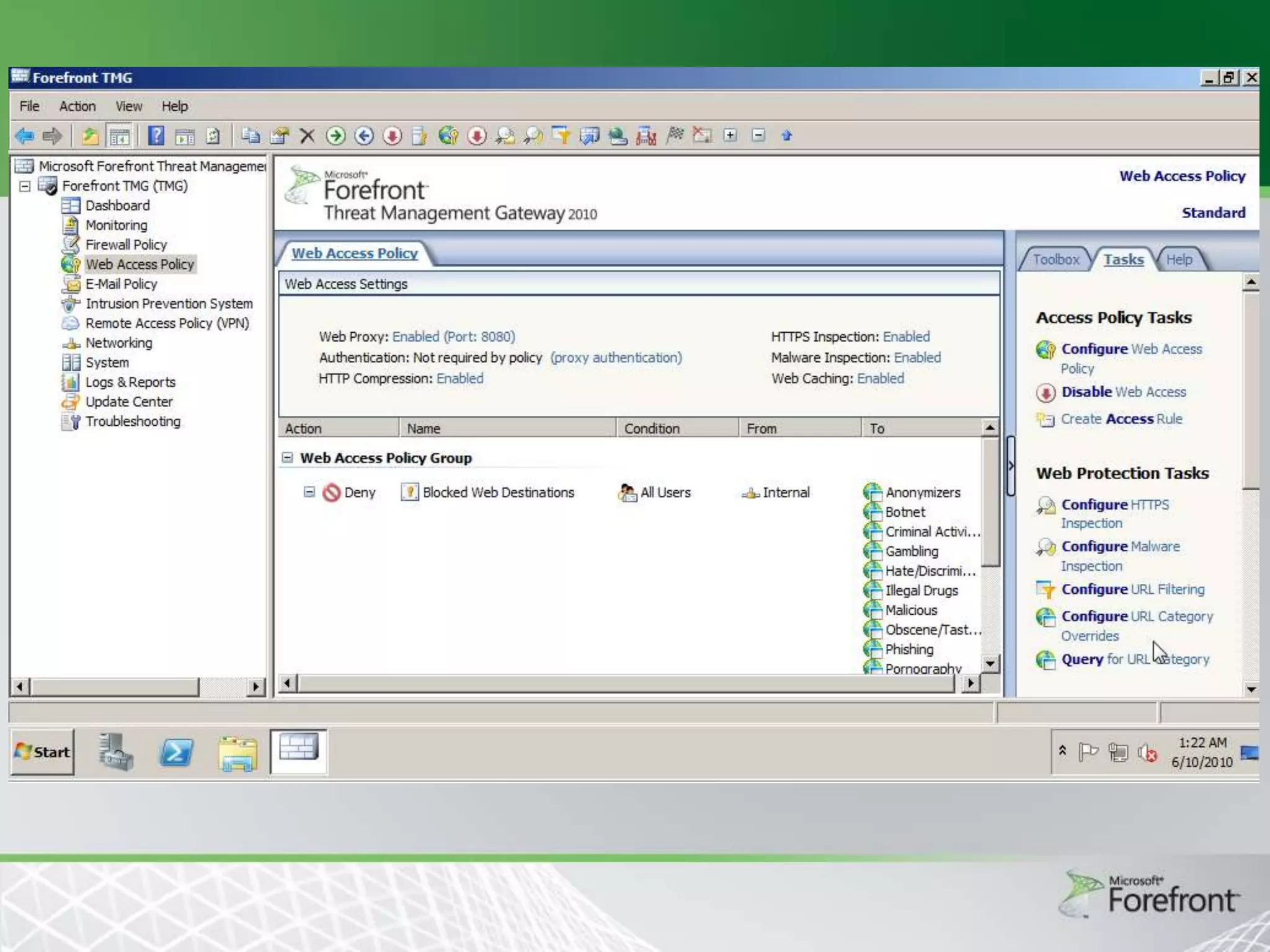
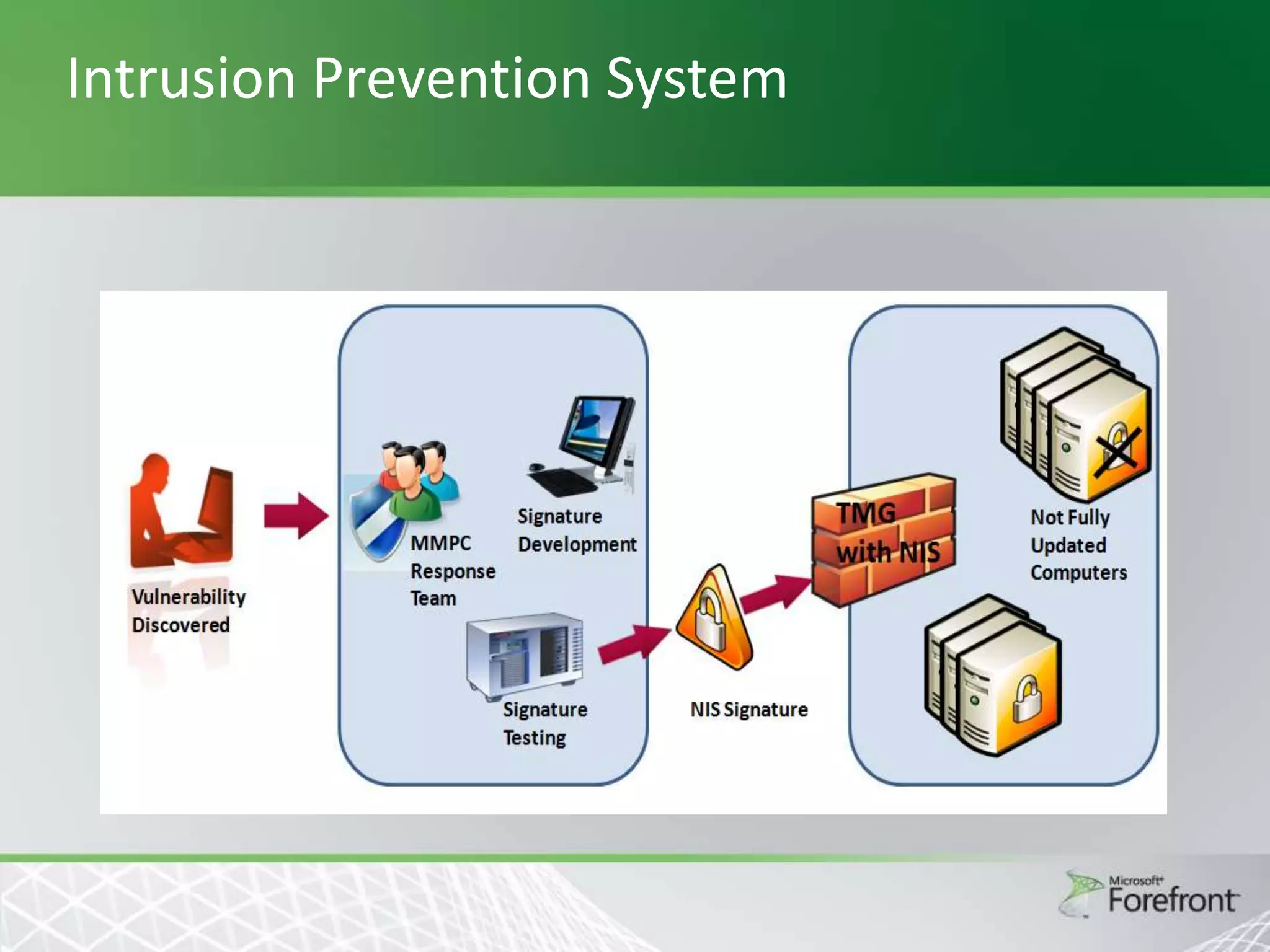
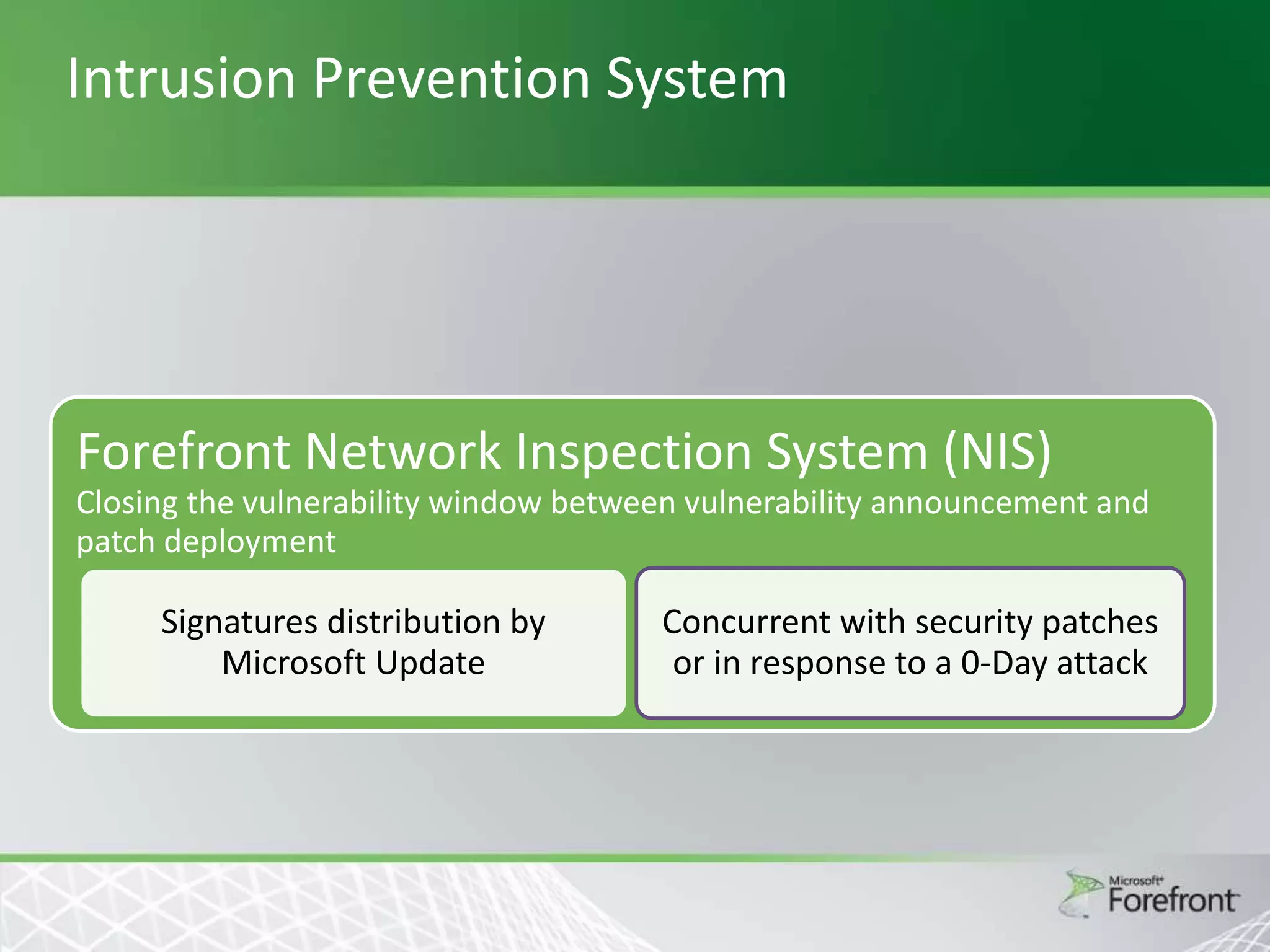
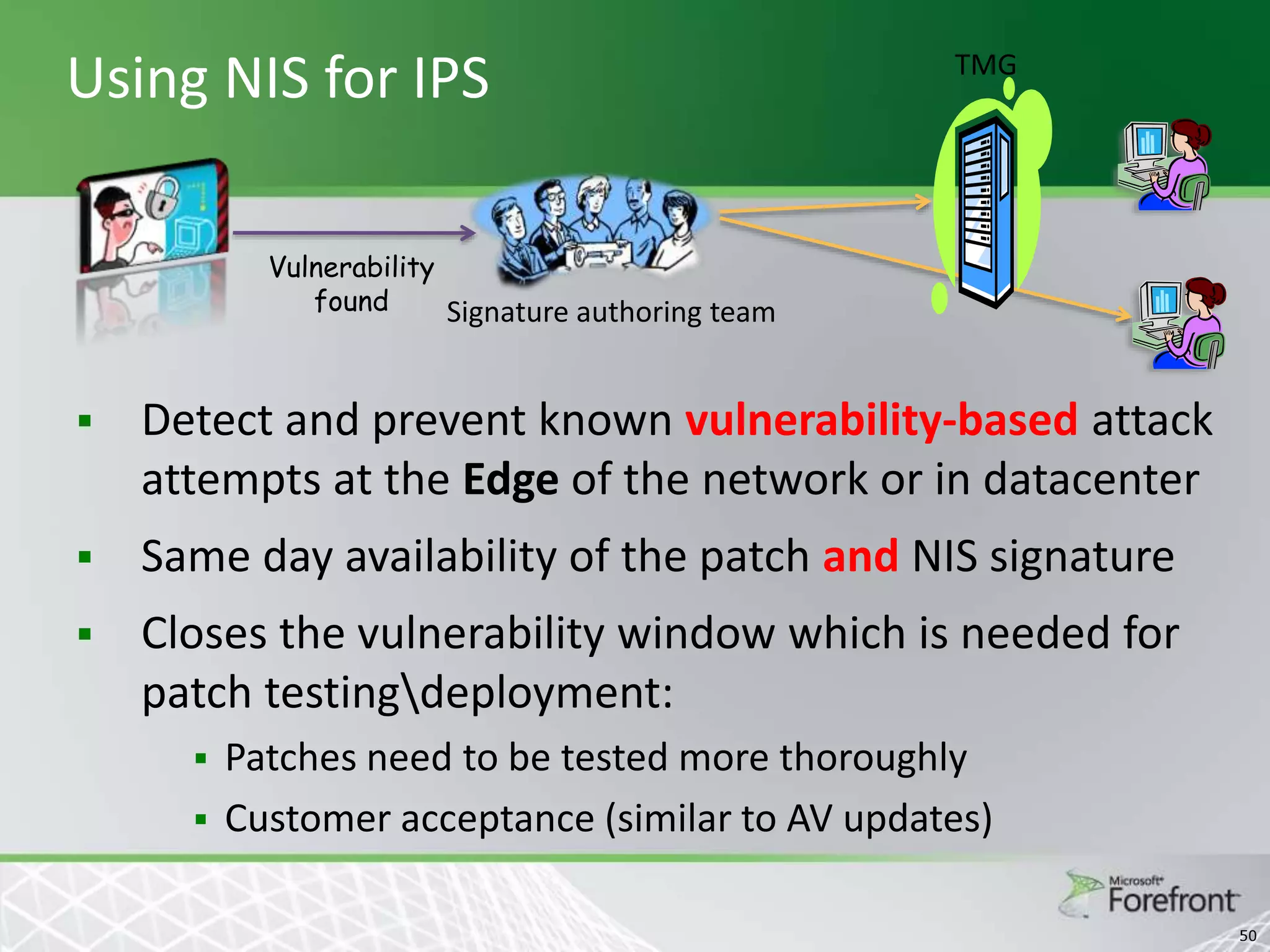
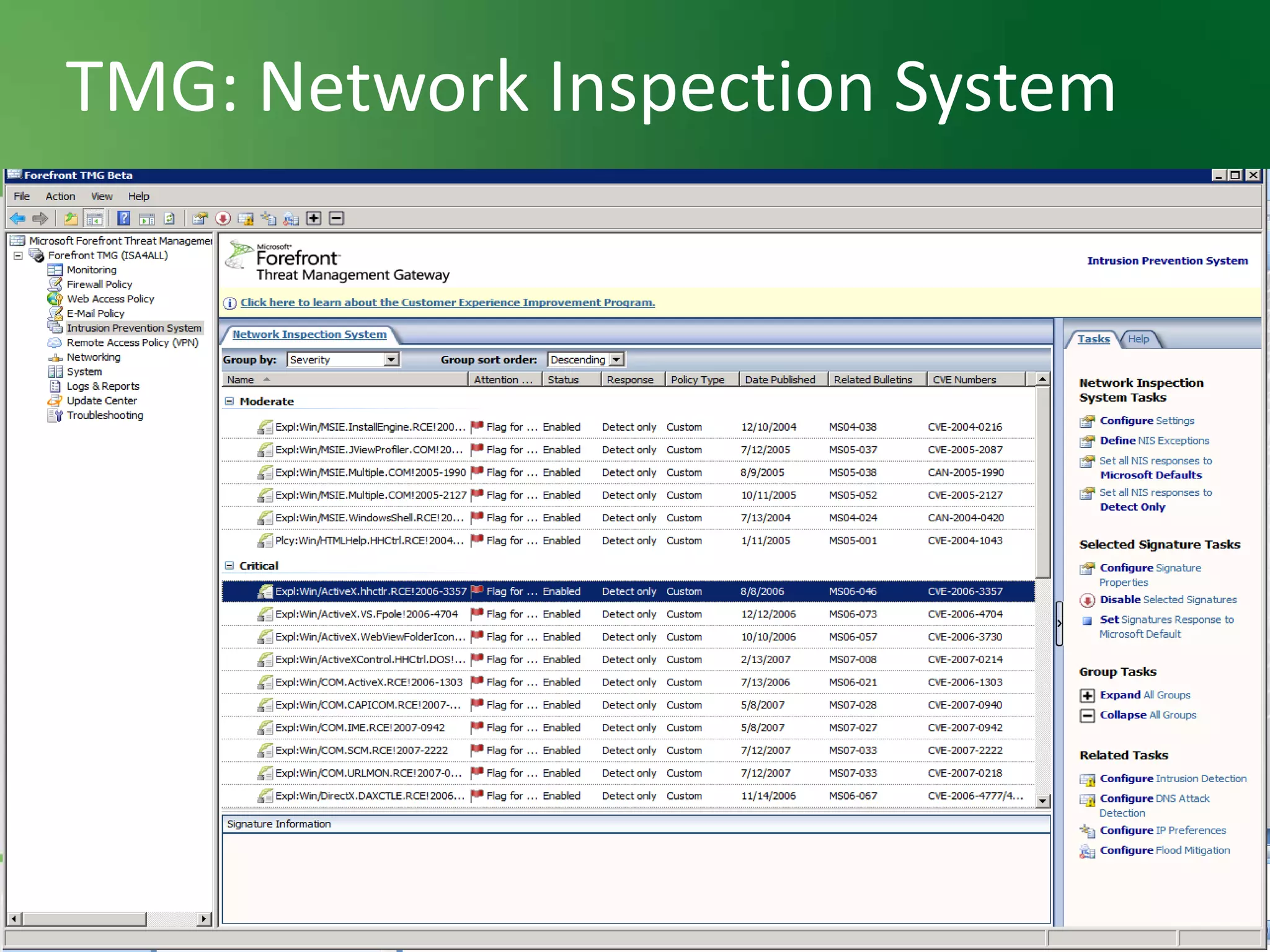
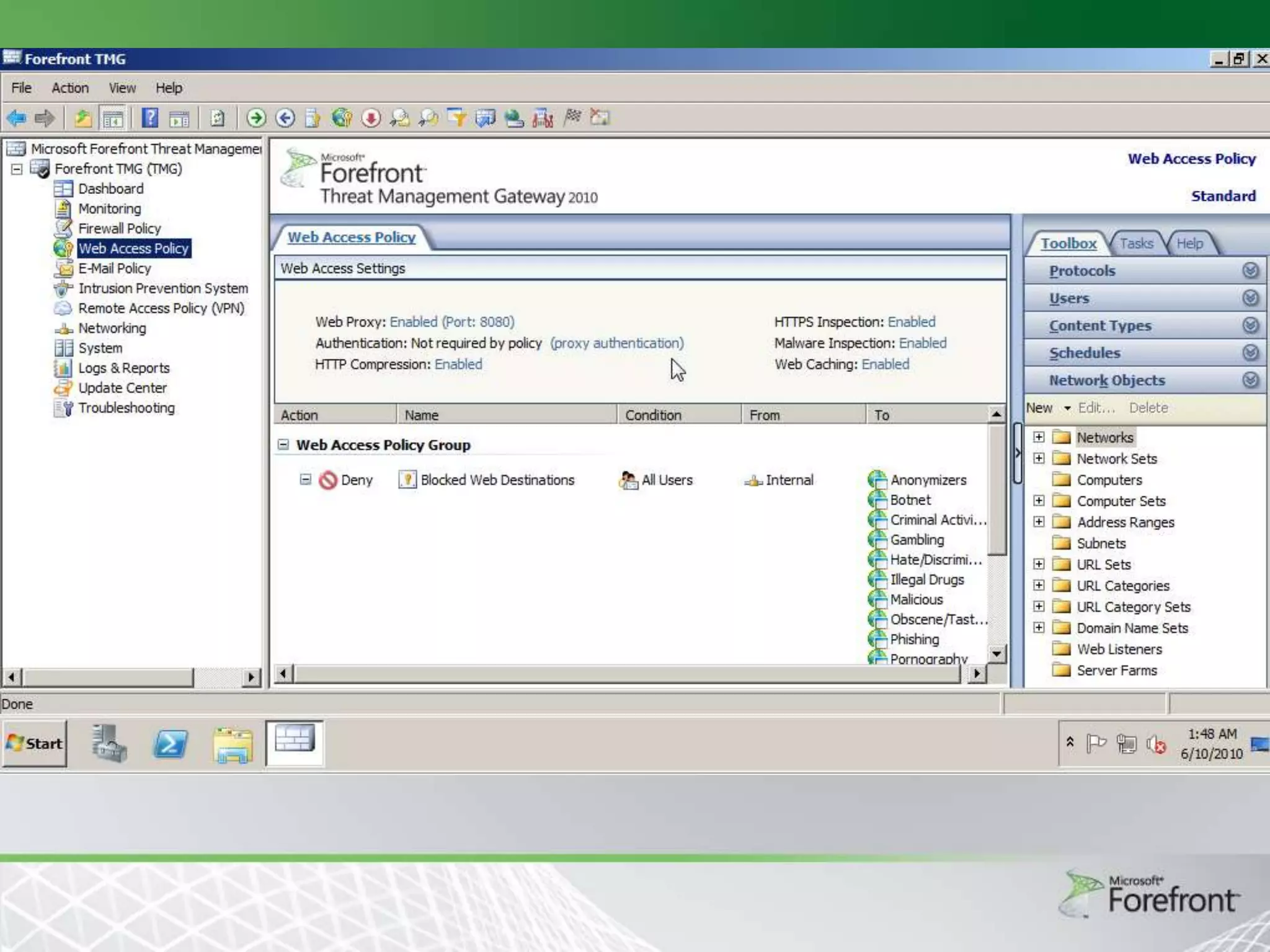
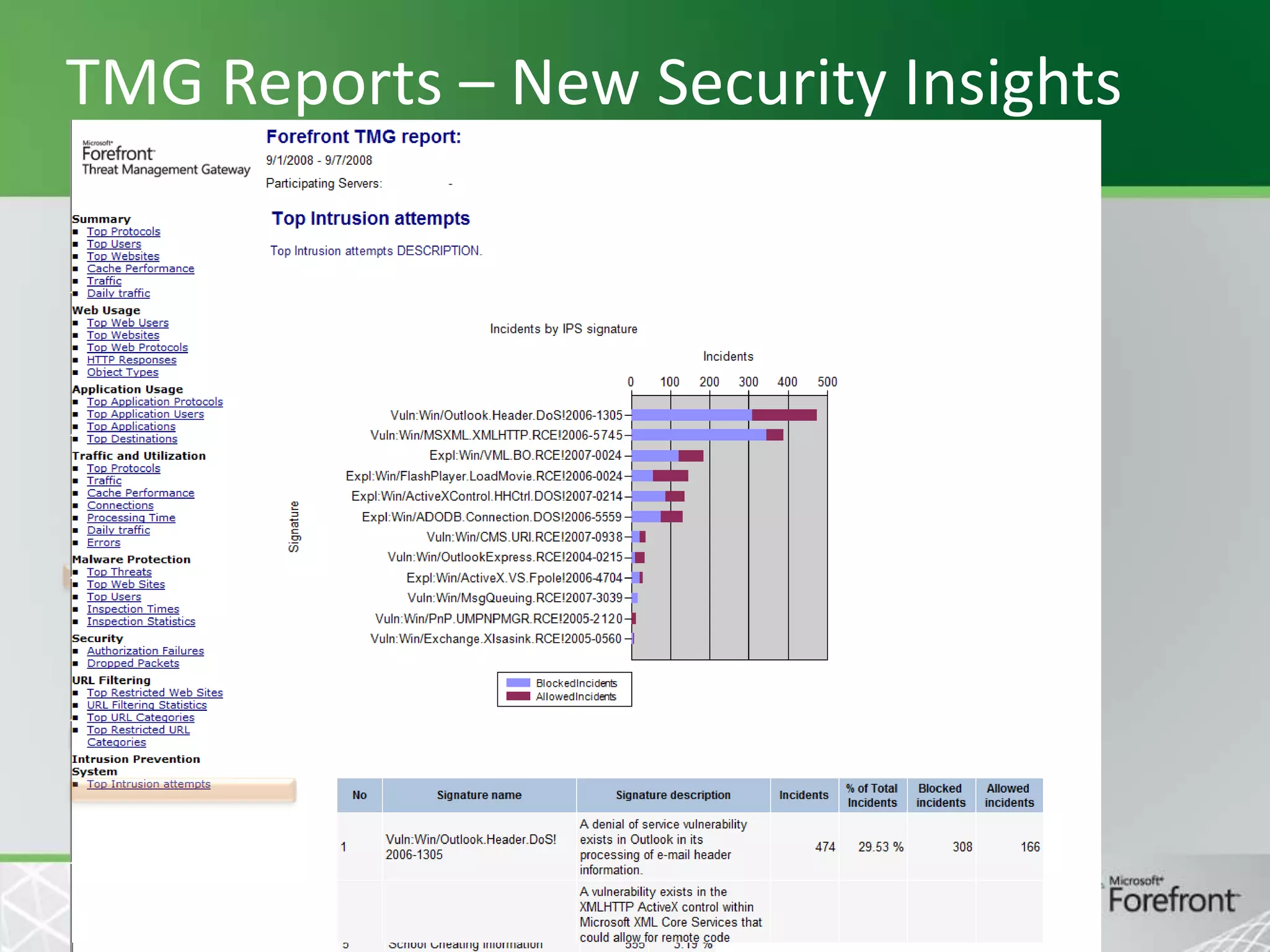
This document provides an overview and agenda for Threat Management Gateway 2010. It discusses several key features including URL filtering, Edge Malware Protection, HTTPS inspections, and the Network Inspection System. The document is intended to outline how these features can enhance network security and protection. It provides high-level information on configuration and usage of the different Threat Management Gateway 2010 components.