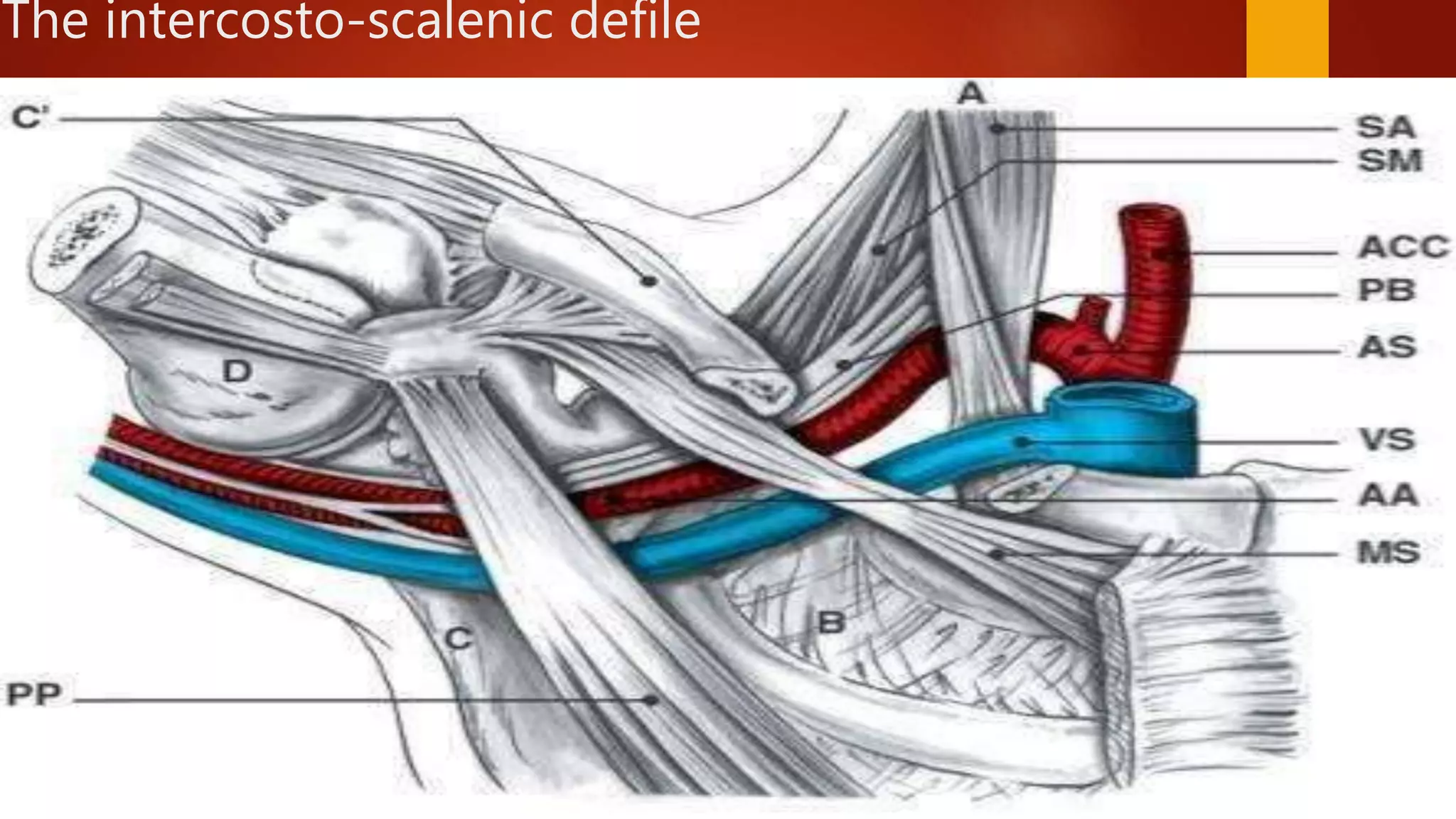
Thoracic outlet syndrome is caused by compression of the neurovascular structures in the thoracic outlet. It has three main types - neurogenic, venous, and arterial. Neurogenic TOS is the most common, caused by scalene muscle anomalies compressing the brachial plexus. Symptoms include pain, numbness, and weakness in the arm. Conservative treatments focus on postural changes, stretching, and strengthening to relieve compression. Precise diagnosis relies on clinical examination, and surgery may be considered if conservative measures fail.