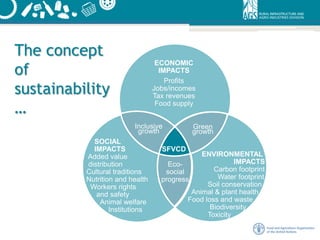
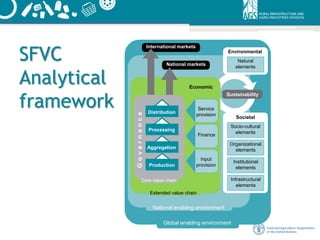
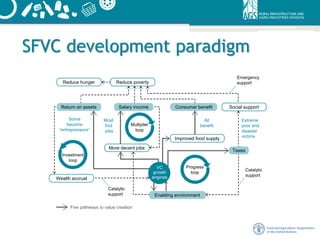
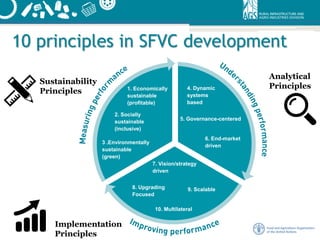
This document outlines a framework for sustainable food value chains. It defines a sustainable food value chain as one that is profitable, provides broad social benefits, and has a neutral or positive environmental impact. It presents an analytical framework that considers the economic, social, and environmental impacts of food value chains. It also describes 10 guiding principles for developing sustainable food value chains, including that they should be economically sustainable, socially inclusive, environmentally green, and driven by a clear vision and strategy.