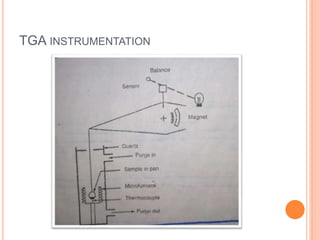
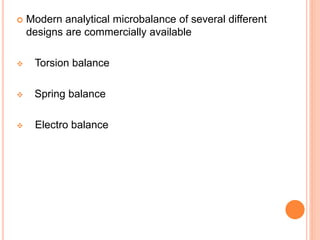
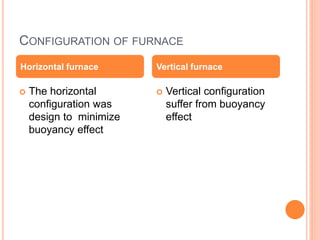
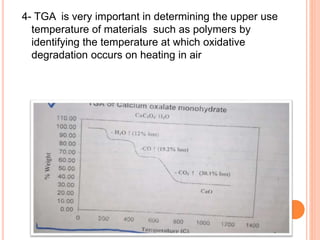
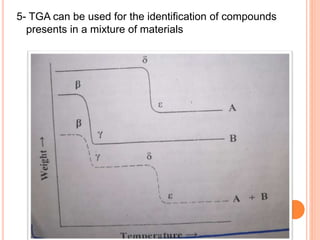
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) measures the mass of a sample as the temperature is increased. The output is a plot of mass vs. temperature called a thermal curve. Weight loss indicates decomposition or evaporation, while weight gain shows adsorption. TGA can identify the temperature at which materials are stable and the gases they release. It uses a sensitive microbalance, furnace surrounding the sample holder, and gas system. TGA is useful for determining drying temperatures, identifying released gases, and compositions of residues.