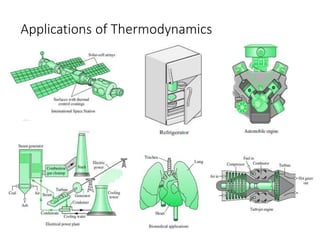
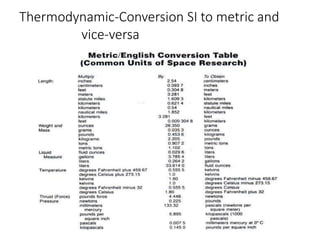
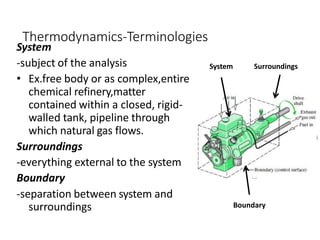
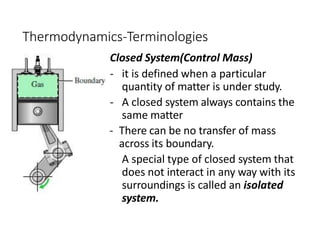
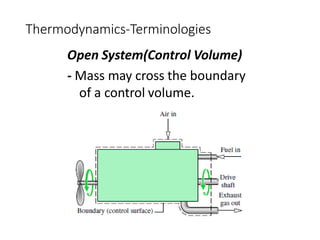
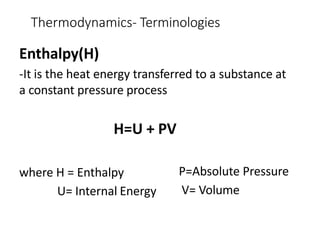
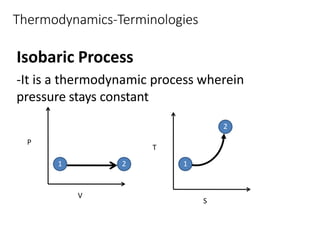
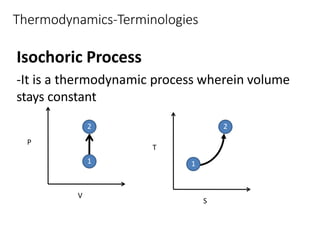
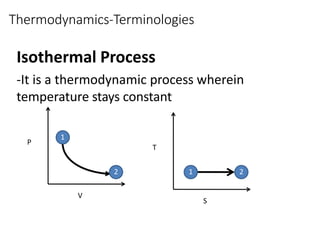
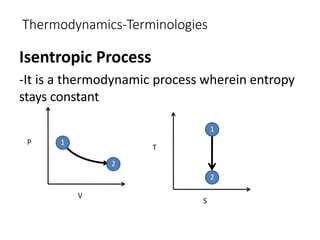
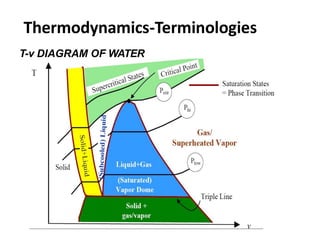
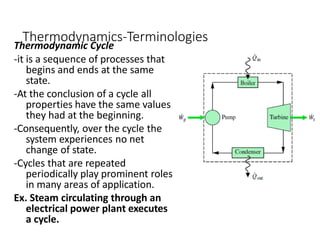
Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, radiation, and physical properties of matter. The document defines key concepts in thermodynamics including system, surroundings, boundary, state, process, extensive and intensive properties, and phases. It also provides examples of thermodynamic processes like isobaric, isochoric, and isothermal processes. The document concludes by defining thermodynamic cycles and providing computational problems to practice applying thermodynamic concepts.