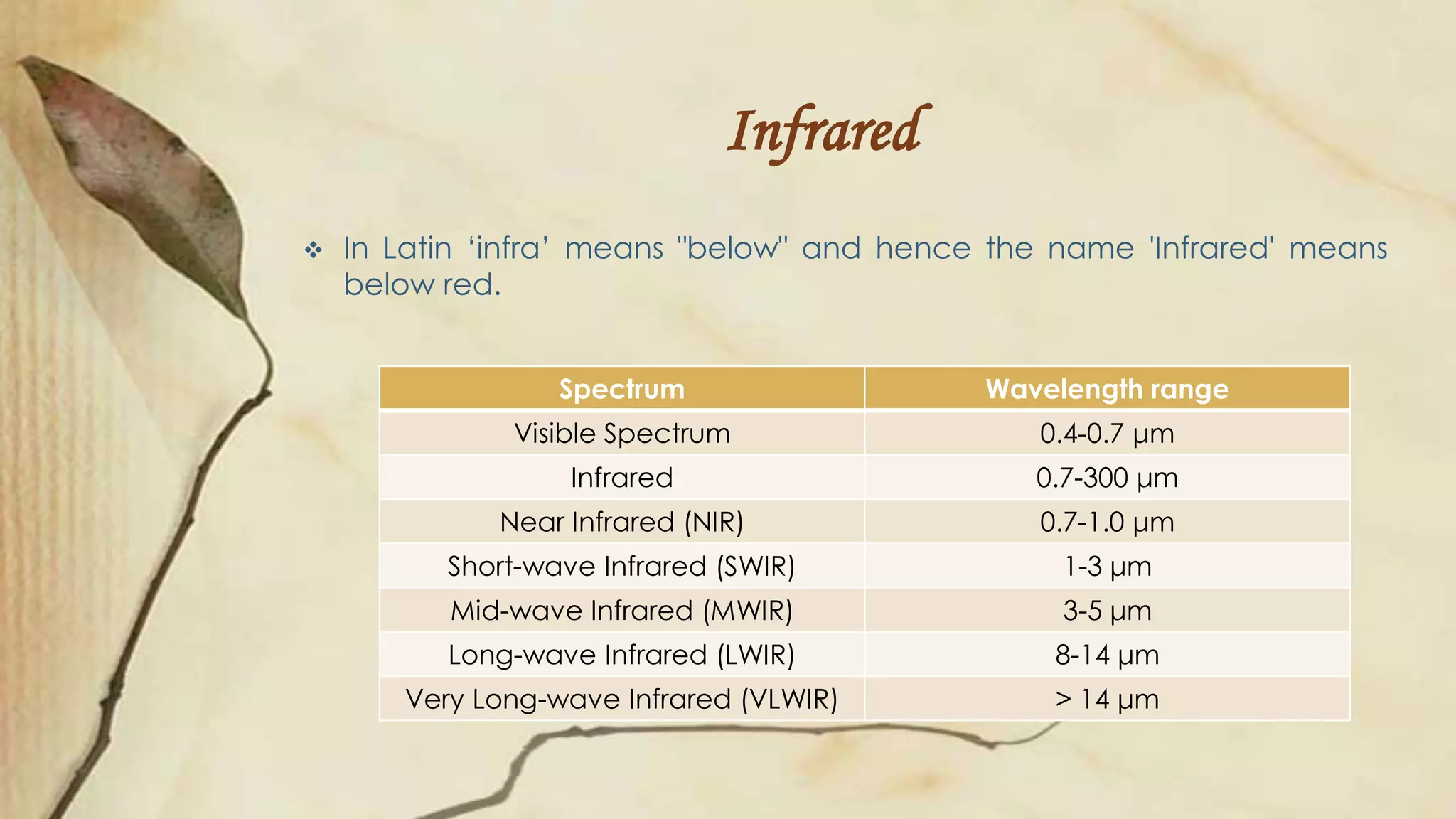
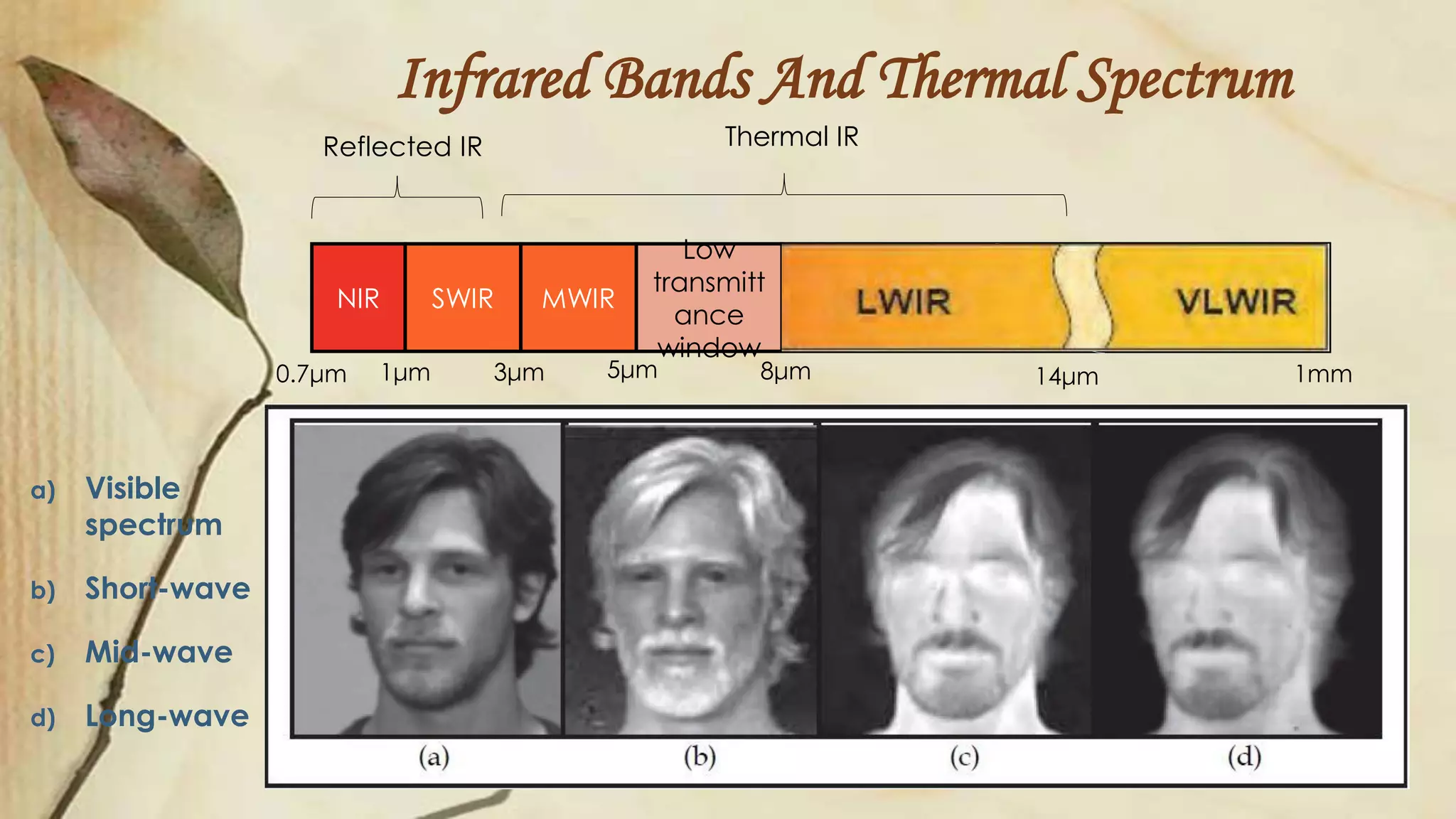
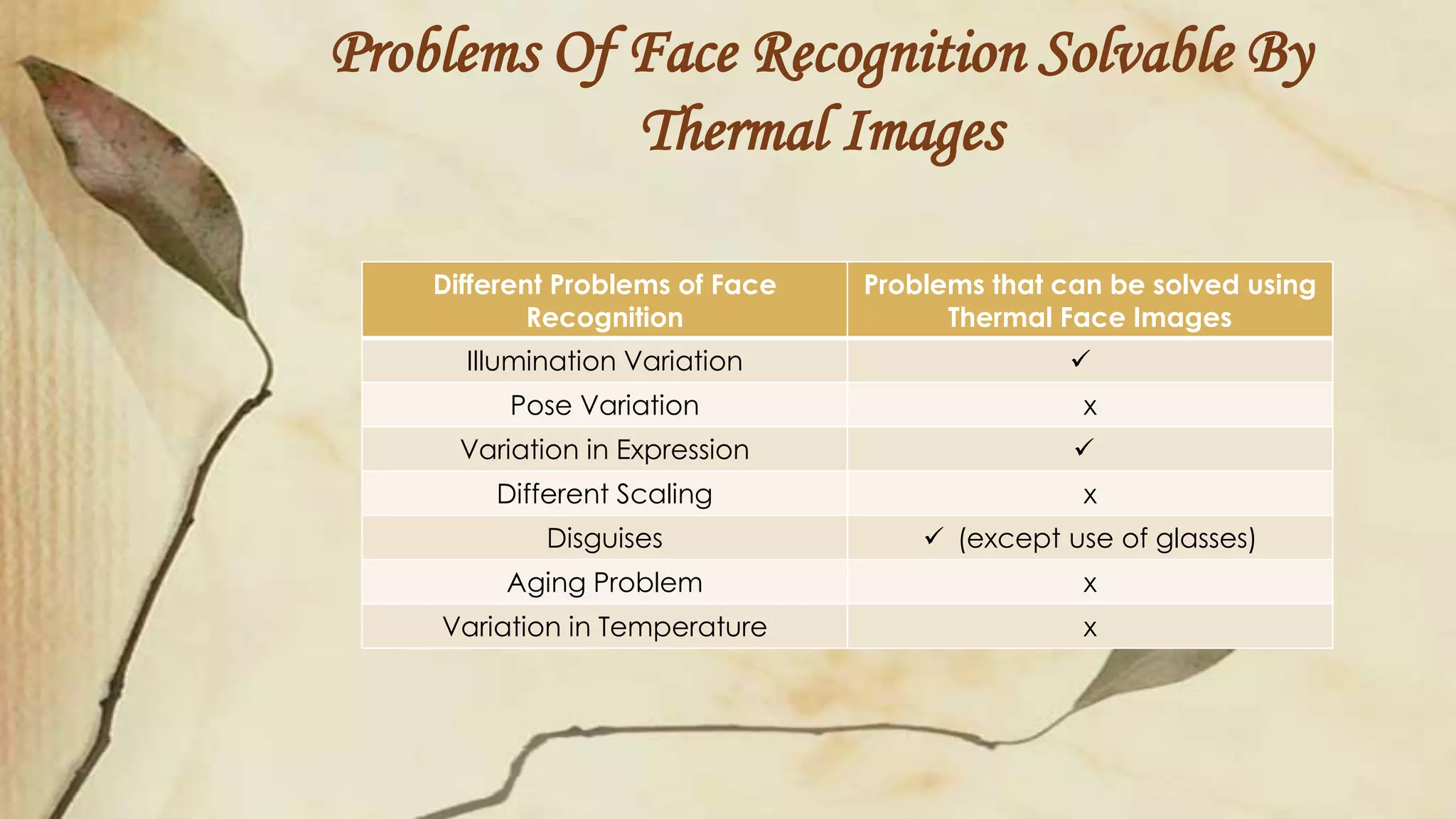
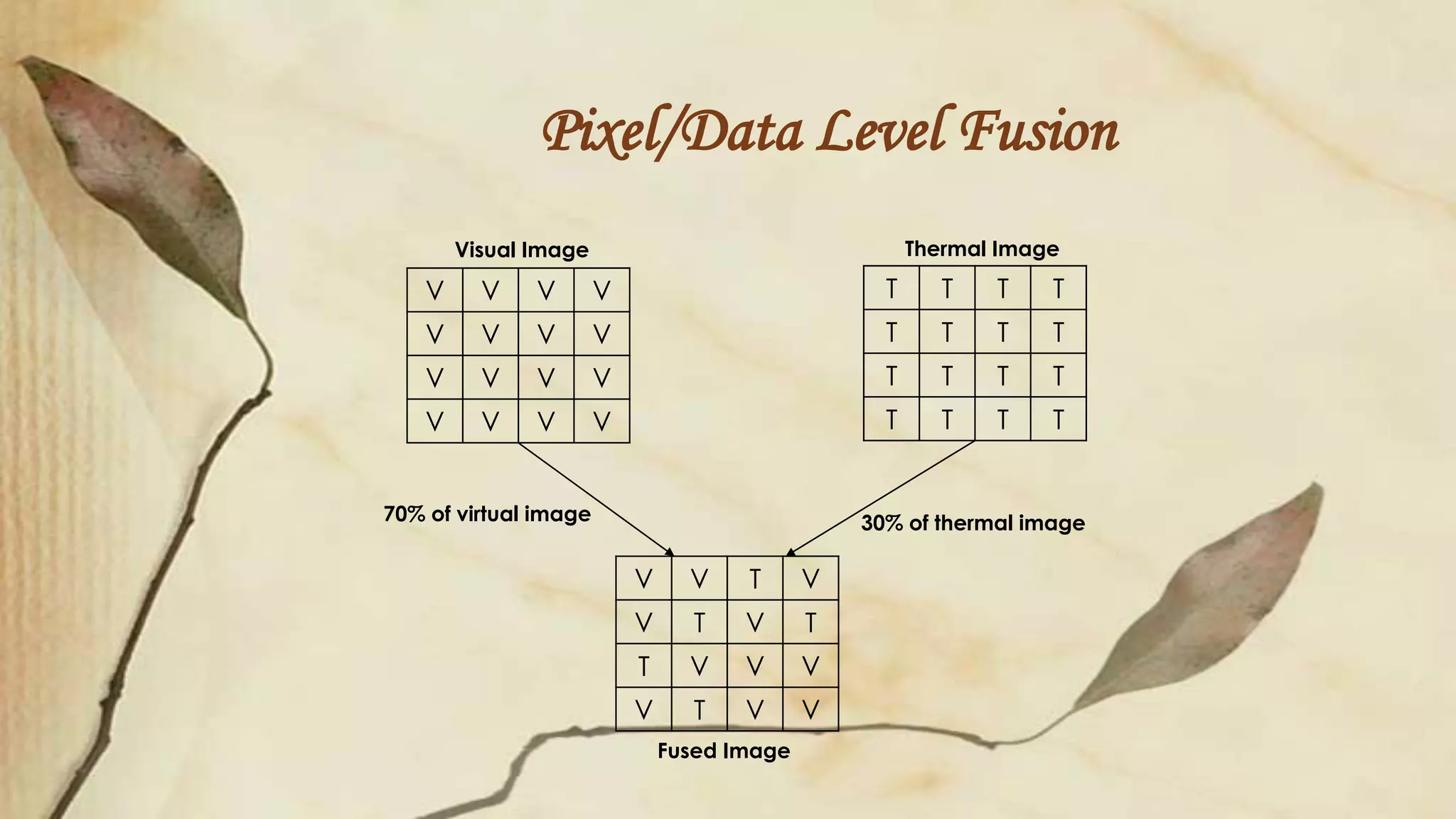
This document discusses thermal infrared face recognition. It begins by introducing thermal face recognition and noting the advantages of using thermal images over visual images, such as insensitivity to illumination changes. It then describes the different infrared spectrums and how thermal face images are generated from human body heat patterns. Some critical observations of thermal imaging are discussed, such as its inability to distinguish identical twins or effects of breathing. The document also covers limitations of thermal imaging and how fusing thermal and visual images can generate more informative data for face recognition.